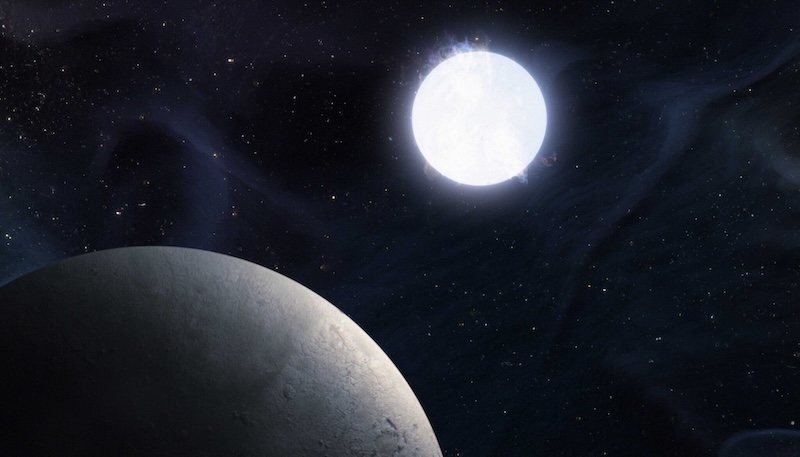

White dwarfs might host life-supporting planets
Does a star need to be alive – that’s, shining from inside, burning thermonuclear gasoline at its core – with a view to maintain life? Scientists assumed that white dwarfs – the dense remnants of lifeless stars – would possible be unable to assist life on close by planets. They assumed these constantly cooling stellar corpses can be unable to supply a constant supply of power. However on March 18, 2025, researchers on the Florida Institute of Expertise mentioned they’d investigated whether or not white dwarfs might energy three processes which have helped life to thrive on Earth. They usually discovered these lifeless stars might present the right situations for all times on an Earth-like planet for practically 7 billion years.
They revealed their peer-reviewed ends in The Astrophysical Journal Letters on December 12, 2024.
White dwarfs are fading star cores
White dwarfs are the ultimate evolutionary stage for many low-to-moderate-mass stars, together with our solar. In actual fact, some 97% of stars in our Milky Manner galaxy are destined to turn out to be white dwarfs. When certainly one of these stars ultimately begins to expire of hydrogen gasoline, it should develop right into a bloated purple big earlier than shedding its outer layers altogether. This can produce a phenomenal planetary nebula, with the star’s roughly Earth-sized core at its middle. This remnant is what we name a white dwarf.
The growth right into a purple big would in lots of instances destroy the planets surrounding it. That is possible (though not definitely) what is going to occur to Earth in some 5 billion years. However research have discovered that this destiny is way from inevitable. And, positive sufficient, scientists in recent times have made numerous detections of planets orbiting white dwarfs.
The larger impediment to life orbiting a white dwarf is that these lifeless stars lack the gasoline to carry out nuclear fusion. So, though white dwarfs begin their lives extremely scorching, over billions of years they leak out their trapped warmth. This regular cooling is why scientists have lengthy thought that white dwarfs are unlikely to host liveable planets. The lifeless stars appear unable to supply the constant power life would wish to determine itself.

Measuring liveable zones
However a white dwarf’s warmth dissipates over a timescale of billions of years. So the researchers got down to set up how lengthy life on a close-by planet might be sustained earlier than the white dwarf cooled an excessive amount of.
They constructed a mannequin to simulate how lengthy a planet might stay inside a white dwarf’s progressively shrinking “liveable zone”. The liveable zone is the area during which the temperature is good for a planet to maintain liquid water on its floor. They usually discovered that, if positioned completely, an Earth-like planet near a white dwarf might obtain sufficient starlight to keep up liquid water for 7 billion years. Contemplating Earth is round 4.5 billion years previous and commenced internet hosting life not less than 3.5 billion years in the past, 7 billion years would appear greater than sufficient time for all times to emerge.
It’s value noting that, in recent times, scientists have come to appreciate that the idea of liveable zones may be outdated. We now consider moons like Enceladus and Europa, far past our photo voltaic system’s Goldilocks zone, have world liquid oceans hidden beneath huge sheets of ice. And these oceans could be liveable, and even inhabited. However this examine centered on the one atmosphere we know to have produced life: a planet like Earth, with ample liquid water on its floor.
Can a white dwarf assist life’s key processes?
To get a greater understanding of this theoretical planet’s true habitability, the researchers additionally investigated whether or not the white dwarf’s power can be sufficient to maintain two chemical processes which have helped life thrive on Earth.
The primary is photosynthesis, which not solely powers a lot of Earth’s life, however has additionally made our planet’s biosphere extra liveable. And the second is UV-induced abiogenesis, or the era of life from non-living matter through ultraviolet radiation. The transformation of straightforward molecules into extra complicated ones via ultraviolet radiation is seen as a possible origin of life on Earth.
And the researchers discovered that an ideally positioned planet would obtain the power to assist photosynthesis and UV-induced abiogenesis for everything of its 7-billion-year liveable interval. And that, based on examine lead Caldon Whyte, is very uncommon. He defined:
That isn’t actually widespread round most stars. One thing like [our] solar, after all, can present sufficient power, however brown dwarfs and purple dwarfs smaller than the solar don’t actually present the power in [both] the UV and the photosynthesis vary.
Removed from being unsuited to sustaining alien life, it seems white dwarfs are uniquely suited to the duty.
So are white dwarfs the important thing to future alien searches?
This shocking availability of power makes planets orbiting near white dwarfs sturdy candidates within the seek for alien life. That is very true given the 7 billion years of potential habitability they provide. Such an prolonged timeframe, the paper factors out, raises the potential for technologically superior life. So a planet orbiting near a white dwarf star might be a primary location to seek for technosignatures.
The most important complication is that we haven’t but discovered a planet orbiting shut sufficient to a white dwarf for this stage of habitability. The paper acknowledges {that a} star’s purple big section would possible engulf a planet on this orbital area. Nonetheless, that doesn’t imply they don’t exist. Research have instructed that planets might kind once more on this zone after the purple big section, constituted of the recycled materials of destroyed planets.
Our present era of telescopes struggles to identify small exoplanets very near their stars, so it’s arduous to say how widespread this sort of planet is. But when Earth-like planets near white dwarfs are widespread, they might be among the almost certainly areas to search out alien life.
Backside line: In response to a shocking new examine, white dwarfs might present sufficient power to maintain life on a close-by Earth-like planet for some 7 billion years.
Supply: Potential for Life to Exist and be Detected on Earth-like Planets Orbiting White Dwarfs
By way of Florida Institute of Expertise
Learn extra: A liveable zone planet for a lifeless star?
Learn extra: Is that this white dwarf exoplanet a preview of Earth’s destiny?

