One concept for deep area probes that resurfaces each few years is the inflatable sail. We’ve seen eager curiosity particularly since Breakthrough Starshot’s emergence in 2016 in meter-class sails, maybe as small as 4 meters to the aspect. But when we select to work with bigger designs, sails don’t scale effectively. Enhance sail space and issues of mass come up because of the required cables between sail and payload. An inflatable beryllium sail stuffed with a low-pressure gasoline like hydrogen avoids this downside, with payload mounted on the space-facing floor. Such sails have already been analyzed within the literature (see under).
Roman Kezerashvili (Metropolis College of New York), actually, not too long ago analyzed an inflatable torus-shaped sail with a twist, one which makes use of compounds included into the sail materials itself as a ‘propulsive shell’ that may benefit from desorption produced by a microwave beam or a detailed cross of the Solar. Laser beaming additionally produces this propulsive impact however microwaves are preferable as a result of they don’t harm the sail materials. Kezerashvili has analyzed carbon within the sail lattice in photo voltaic flyby situations. The sail is conceived as “a skinny reflective membrane hooked up to an inflatable torus-shaped rim.”
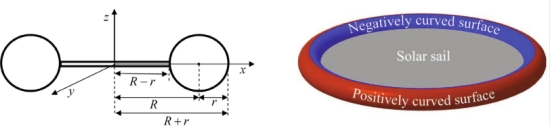
Picture: That is Determine 1 from the paper. Credit score: Kezerashvili et al.
Inflatable sails return to the late Nineteen Eighties. Joerg Strobl revealed a paper on the idea within the Journal of the British Interplanetary Society, and it acquired swift follow-up in a sequence of research within the Nineties analyzing an inflatable radio telescope known as Quasat. A sequence of conferences involving Alenia Spazio, an Italian aerospace firm based mostly in Turin, took the concept additional. In 2018, Claudio Maccone, Greg Matloff, and NASA’s Les Johnson joined Kezerashvili in analyzing inflatable applied sciences for missions as difficult as a probe to the Oort Cloud.
Certainly, working with Joseph Meany in 2023, Matloff would additionally describe an inflatable sail utilizing aerograpahite and graphene, enabling increased payload mass and envisioning a ‘sundiver’ trajectory to speed up an Alpha Centauri mission. The conception right here is for a real interstellar ark carrying a crew of a number of hundred, utilizing a sail with radius of 764 kilometers on a 1300 yr journey. So the examination of inflatable sails in various supplies is clearly not slowing down.
The Inflatable Starshade
However there are makes use of for inflatable area constructions that transcend outer system missions. I see that they’re now the topic of a NIAC Section I examine by John Mather (NASA GSFC) that places a brand new wrinkle into the idea. Mather’s curiosity is just not propulsion however an inflatable starshade that, in varied configurations, might work both with the deliberate Liveable Worlds Observatory or an Extraordinarily Giant Telescope just like the 39 m diameter European Extraordinarily Giant Telescope now being inbuilt Chile. Starshades are a substitute for coronagraph applied sciences that suppress mild from a star to disclose its planetary companions.
Inflatables might be candidates for any type of massive area construction. Present planning on the Liveable Worlds Observatory, scheduled for launch no sooner than the late 2030s, features a coronagraph, however Mather thinks the 2 applied sciences provide helpful synergies. Right here’s a quote from the examine abstract:
A starshade mission might nonetheless develop into obligatory if: A. The HWO and its coronagraph can’t be constructed and examined as required; B. The HWO should observe exoplanets at UV wavelengths, or a 6 m HWO is just not massive sufficient to watch the specified targets; C. HWO doesn’t obtain sufficient efficiency after launch, and deliberate servicing and instrument substitute can’t be applied; D. HWO observations present us that fascinating exoplanets are uncommon, distant, or are hidden by thick mud clouds across the host star, or can’t be totally characterised by an upgraded HWO; or E. HWO observations present that the subsequent step requires UV knowledge, or a a lot bigger telescope, past the aptitude of conceivable HWO coronagraph upgrades.
So Mather’s concept can be meant to be a type of insurance coverage coverage. It’s price declaring that coronagraphs are effectively studied and compact, whereas starshade applied sciences are theoretically sound however untested in area. However because the abstract mentions, work at ultraviolet wavelengths is out of the coronagraph’s vary. To get into that a part of the spectrum, pairing Liveable Worlds Observatory with a 35-meter starshade appears the one possibility. This conceivably would enable a rest of some HWO optical specs, and thus decrease the general value. The NIAC examine will discover these choices for a 35-meter in addition to a 60-meter starshade.
I discussed the opportunity of combining a starshade with observations by way of an Extraordinarily Giant Telescope, an eye-widening notion that Mather proposed in a 2022 NIAC Section I examine. The concept right here is to put the starshade in an orbit that will match place and velocity with the telescope, occulting the star to render the planets extra seen. This may demand an energetic propulsion system to keep up alignment in the course of the remark, whereas additionally making use of the adaptive optics already constructed into the telescope to suppress atmospheric distortion. The mission known as Hybrid Observatory for Earth-like Exoplanets.
Picture: Artist idea highlighting the novel method proposed by the 2025 NIAC awarded choice of Inflatable Starshade for Earthlike Exoplanets idea. Credit score: NASA/John Mather.
As mentioned earlier, mass concerns play into inflatable designs. Within the HOEE examine, Mather referred to his plan “to chop the starshade mass by greater than an element of 10. There isn’t a cause to require 1000’s of kg to assist 400 kg of skinny membranes.” His design purpose is to create a starshade that may be assembled in area, thus avoiding launch and deployment points. All this to create what he calls “essentially the most highly effective exoplanet observatory but proposed.”
You may see how the inflatable starshade concept grows out of the hybrid observatory examine. By experimenting with designs producing the wanted energy, stiffness, stability and thermal necessities and the problems raised by bonding massive sheets of supplies of the requisite energy, the mass targets could also be realized. So the inflatable sail possibility as soon as once more morphs right into a associated design, one optimized as an adjunct to an exoplanet observatory, offered this early work can result in an answer that would profit each astronomy and sails.
The paper on inflatable beryllium sails is Matloff, G. L., Kezerashvili, R. Ya., Maccone, C. and Johnson, L., “The Beryllium Hole-Physique Photo voltaic Sail: Exploration of the Solar’s Gravitational Focus and the Inside Oort Cloud”, arXiv:0809.3535v1 [physics.space-ph] 20 Sep 2008. The later Kezerashvili paper is Kezerashvili et al., “A torus-shaped photo voltaic sail accelerated by way of thermal desorption of coating,” Advances in House Analysis Vol. 67, Subject 9 (2021), pp. 2577-2588 (summary). The Matloff and Meany paper on an Alpha Centauri interstellar ark is ”Aerographite: A Candidate Materials for Interstellar Photon Crusing,” JBIS Vol. 77 (2024) pp. 142-146. Summary. Due to Thomas Mazanec and Antonio Tavani for the pointer to Mather’s most up-to-date NIAC examine.


