For generations, scientists and science fiction writers have contemplated how people might sometime dwell on Mars. Whereas the thought as soon as appeared like a far-off chance, the various robotic missions which have travelled to Mars and efficiently landed on its floor have given new life to the thought. This presents many challenges, which embody the time it takes to succeed in Mars (6 to 9 months utilizing typical propulsion) and the risks of long-term publicity to cosmic radiation and microgravity. However constructing long-term habitats and services on the Martian floor can also be difficult.
Merely put, sending rockets carrying all the development supplies, provides, and equipment wanted to construct a human outpost on Mars is neither cost-effective nor sensible.
For many years, mission planners have researched strategies for utilizing Martian sources to fulfill these wants – a course of often known as In-Situ Useful resource Utilization (ISRU). In a latest examine, Texas A&M College Professor Congrui Grace Jin and her colleagues from the College of Nebraska-Lincoln current a novel concept that would result in bio-engineered constructions on Mars. The method they suggest was detailed in a paper just lately revealed within the Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering.
For years, Jin and her colleagues have labored with bio-manufacturing and residing supplies, which led to the event of an artificial lichen system that may produce constructing supplies with out human intervention. Of their newest examine, funded by the NASA Progressive Superior Ideas program, they show how this analysis could be mixed with 3D printing to construct constructions utilizing Martian regolith, sand, and rocks. As Jin stated in a Texas A&M press launch:
We are able to construct an artificial neighborhood by mimicking pure lichens. We have developed a option to construct artificial lichens to create biomaterials that glue Martian regolith particles into constructions. Then, via 3D printing, a variety of constructions could be fabricated, corresponding to buildings, homes, and furnishings.
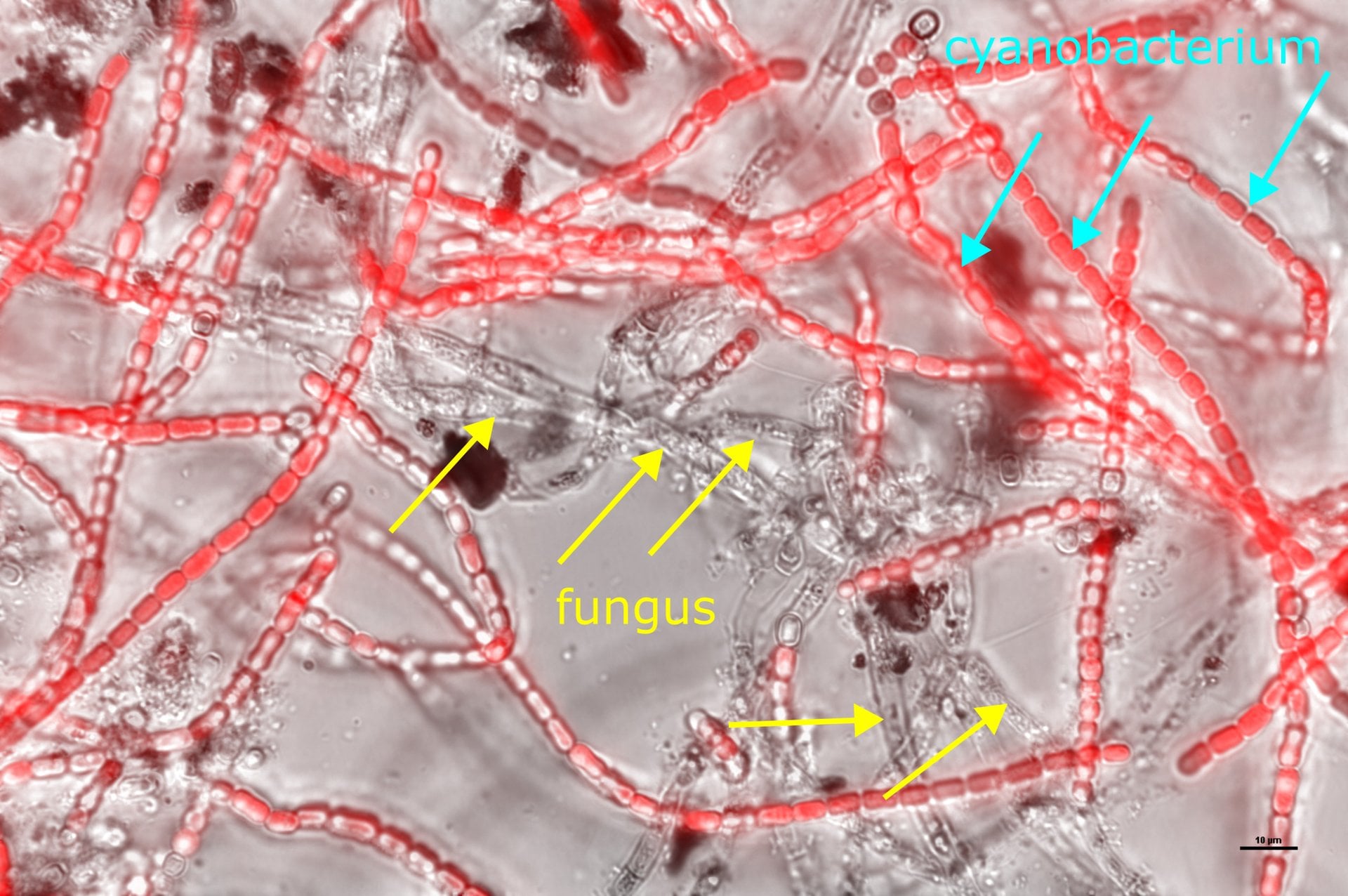 Microscopic view of the artificial lichen system, wherein red-colored fluorescent cells are cyanobacterial cells and the non-fluorescent cells are fungal cells. | Picture: Courtesy of Dr. Congrui Grace Jin.
Microscopic view of the artificial lichen system, wherein red-colored fluorescent cells are cyanobacterial cells and the non-fluorescent cells are fungal cells. | Picture: Courtesy of Dr. Congrui Grace Jin.
A number of strategies have been proposed for Martian regolith particles into constructing supplies, together with bombarding them with microwaves to create a molten plasma (aka sintering) or utilizing magnesium-based, sulfur-based, or geopolymer bonding brokers. These strategies are both energy-intensive or require human oversight (or each), making them much less sensible for long-duration missions to Mars, the place sources and the potential for laborers are restricted.
A number of different strategies that depend on self-growing know-how utilizing microbes have additionally been developed, like utilizing micro organism to bind sand particles, ureolytic micro organism to advertise the manufacturing of calcium carbonate to make bricks, and NASA’s exploration of using fungal mycelium as a bonding agent. Nonetheless, these strategies will not be autonomous as a result of the one strains or species of micro organism concerned require a steady provide of vitamins. Which means personnel should be on-site to make sure micro organism get the sustenance they should do their job.
In distinction, Jin and her group have created a course of that depends on two species (diazotrophic cyanobacteria and filamentous fungi) that require solely regolith, air, gentle, and an inorganic liquid medium to develop. First, the diazotrophic cyanobacteria repair carbon dioxide and dinitrogen from the ambiance and convert them into oxygen and natural vitamins. These assist the filamentous fungi develop and improve the focus of carbonate ions via photosynthesis.
In the meantime, the fungi bind metallic ions onto fungal cell partitions, permitting for biomineral manufacturing whereas offering water, minerals, and carbon dioxide for the cyanobacteria. The micro organism and lichens secrete biopolymers that improve their adhesion and the precipitation of particles that create the required constructions. This symbiotic relationship ensures that the system can function repeatedly and with out human oversight, and produces biomineral constructions able to serving the cruel Martian circumstances higher than different strains of micro organism.
 Workforce AI SpaceFactory’s idea, the winner of NASA’s 3D-Printed Habitat Problem. Credit score: AI SpaceFactory/Plomp/NASA
Workforce AI SpaceFactory’s idea, the winner of NASA’s 3D-Printed Habitat Problem. Credit score: AI SpaceFactory/Plomp/NASA
The know-how is nothing wanting revolutionary by enabling the creation of constructions within the harshest environments the place sources are restricted. The subsequent step, already underway, is to create regolith “ink” to facilitate building utilizing the Direct Ink Writing (DIW) methodology. Also referred to as robocasting, this 3D printing approach consists of fabric (or “ink”) being printed layer by layer via a nozzle. As with different 3D printing strategies, this know-how might even have purposes right here on Earth, significantly in harsh environments the place constructing supplies are scarce.
“The potential of this self-growing know-how in enabling long-term extraterrestrial exploration and colonization is important,” states Jin.
Their idea, “Biomineralization-Enabled Self-Rising Constructing Blocks for Habitat Outfitting on Mars,” was chosen by NASA for a Section I growth as a part of the NIAC 2023 Choices course of.
Additional Studying: Texas A&M College, JSME

