Our current give attention to habitability addresses a major downside. To ensure that astrobiologists to house in on the perfect targets for present and future telescopes, we’d like to have the ability to prioritize them when it comes to the probability for all times. I’ve typically commented on how lazily the phrase ‘liveable’ is used within the fashionable press, however it’s likewise hanging that its utilization varies extensively within the scientific literature. Alex Tolley at present seems at a brand new paper providing a quantitative solution to assess these issues, however the points are thorny certainly. We lack, as an illustration, an accepted definition of life itself, and when discussing what can emerge on distant worlds, we typically select completely different units of variables. How carefully do our assumptions observe our personal terrestrial mannequin, and when could this not be relevant? Alex goes by means of the chances and affords a few of his personal because the hunt for an appropriate methodology continues.
by Alex Tolley
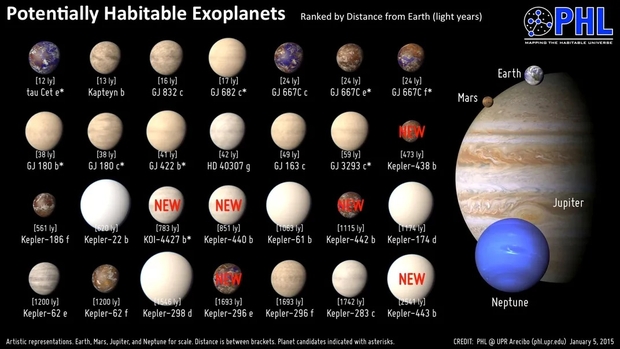
Artist illustrations of explanets within the liveable zone as of 2015. None look like illustrated as doable hanbitable worlds. This has modified within the final decade. Credit score: PHL @ UPR Arecibo (phl.upr.edu) January 5, 2015 Supply [1]
We now know that the galaxy is stuffed with exoplanets, and lots of methods have rocky planets of their liveable zones (HZ). So how ought to we prioritize our searches to maximise our sources to verify extraterrestrial life?
A brand new paper by Dániel Apai and colleagues of the Quantitative Habitability Science Working Group, a gaggle inside the Nexus for Exoplanet System Science (NExSS) initiative, seems on the issues hindering our quest to prioritize searches of the various doable life-bearing worlds found thus far and persevering with to be found with new telescope devices.
The authors state that the issue we face within the seek for life is:
“A important step is the identification and characterization of potential habitats, each to information the search and to interpret its outcomes. Nevertheless, a well-accepted, self-consistent, versatile, and quantitative terminology and technique of evaluation of habitability are missing.”
The authors expend appreciable house and energy itemizing the issues which have accrued: Astrobiologists and establishments have by no means outlined “liveable” and “habitability” rigorously, even confounding “liveable” with “Liveable Zone” (HZ), and utilizing “liveable” and “inhabited” nearly interchangeably. They argue that this creates issues for astrobiologists when making an attempt to plan how you can develop methods when figuring out which exoplanets are price investigating and the way. Due to this fact, defining terminology is essential to keep away from confusion. Because the authors level out, researchers typically assume that planets within the HZ ought to be liveable and people outdoors its boundaries uninhabitable, despite the fact that each assertions are unfaithful.
[I am not clear that the first assertion is claimed without caveats, for example, the planet must be rocky and not a gaseous world, such as a mini-Neptune.]
As our information of exoplanets is information poor, it is probably not doable to outline whether or not a planet is liveable primarily based on the out there info, which results in the imprecision of the time period “liveable”. As well as, not solely has “liveable” not been well-defined, however neither have the necessities for all times been outlined, which is extra restrictive than the unfastened requirement for floor liquid water.
Finally, the foundation of the issue that hampers the group’s efforts to converge on a definition for habitability is that habitability will depend on the necessities for all times, and we would not have a extensively agreed-upon definition for all times.
The authors settle for {that a} common definition of life is probably not doable, however that we will, nonetheless, decide the habitat necessities of explicit types of life.
The authors’ most well-liked resolution is to mannequin habitability with joint likelihood assessments of planetary circumstances with already acquired information, and prolonged with new information. This retains some flexibility in the usage of the time period “liveable” within the gentle of latest information.
Determine 1 beneath illustrates the varied qualitative approaches to defining habitability. Adhering to any single definition is just not doable for a common definition. The paper means that a greater strategy is to make use of quantitative strategies which can be each rigorous, but versatile within the gentle of latest information and data.
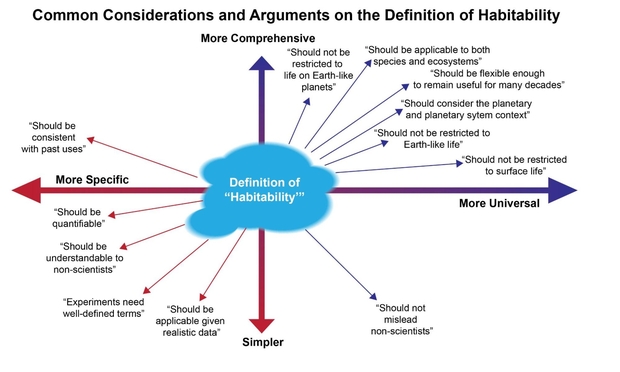
Determine 1. Numerous approaches to defining “liveable”. Any single definition for “habitability” fails to fulfill nearly all of the necessities.
The equation beneath illustrates the thought of quantifying the likelihood of a planet’s habitability as a joint likelihood of the identified standards:
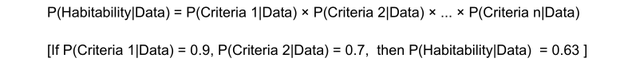
The authors use the joint likelihood of the planet being liveable. For instance, it’s within the HZ, is rocky, and has water vapor within the environment. Clearly, underneath this strategy, if water vapour can’t be detected, the likelihood of habitability declines to zero.
Maybe of even better significance, the group additionally seems at habitability primarily based on whether or not a planet helps the necessities for identified examples of terrestrial life, whose necessities range significantly. For instance, is there ample vitality to help life? If there isn’t a helpful gentle from the father or mother star within the habitat, vitality have to be equipped by geological processes, resulting in the probability that solely anaerobic chemotrophs may dwell underneath these circumstances, for instance, as hypothesized in darkish, glacial-covered subsurface oceans..
The authors embody extra fastidiously outlined phrases, together with: Earth-like life. Rocky Planet, Earth-Sized Planet, Earth-Like Planet, Liveable Zone, Metabolisms, Viability Mannequin, Appropriate Habitat for X, and lastly Habitat Suitability which they outlined as:
The measure of the overlap between the required environmental circumstances for a metabolism and environmental circumstances within the habitat.
Due to the likelihood that life (a minimum of some species of terrestrial life) will inhabit a planet, the authors recommend a framework the place the Venn diagram of the likelihood of a planet being liveable intersects with the likelihood that the necessities are met for particular species of terrestrial life.
The Quantitative Habitability Framework (QHF) is proven in Determine 2 beneath.
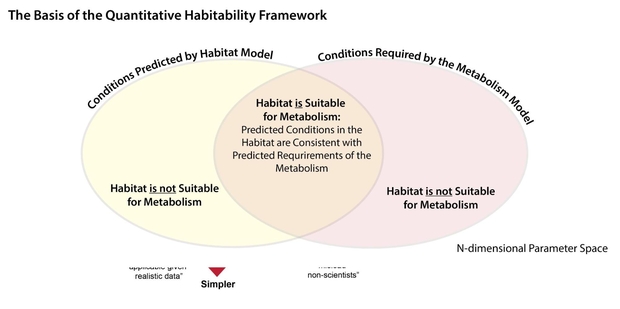
Determine 2. Illustration of the premise of the Framework for Habitability: The comparability of the environmental circumstances predicted by the habitat mannequin and the environmental circumstances required by the metabolism mannequin.
The likelihood of the viability of an organism for every variable is a binary worth of 0 for non-viability and 1 for viability. For archaea and temperature, that is:
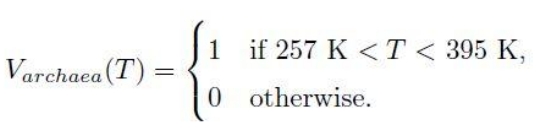
The equation signifies that the likelihood of viability of the archaea at temperature T in levels Kelvin is 1 if the temperature is between 257 Ok ( -16 °C) and 395 Ok (122 °C). In any other case 0 if the temperature is outdoors the viable vary. (Paradoxically, that is imprecise, as it’s for a species of archaean methanogen extremophile, not all archaeans.)
This strategy is utilized to different variables. If any variable likelihood is zero, the joint likelihood of viability turns into 0.
The determine beneath reveals varied terrestrial organism sorts, principally unicellular, with their identified temperature ranges for survival. The mannequin subsequently permits for some terrestrial organisms to be extant on an exoplanet, while others wouldn’t survive.
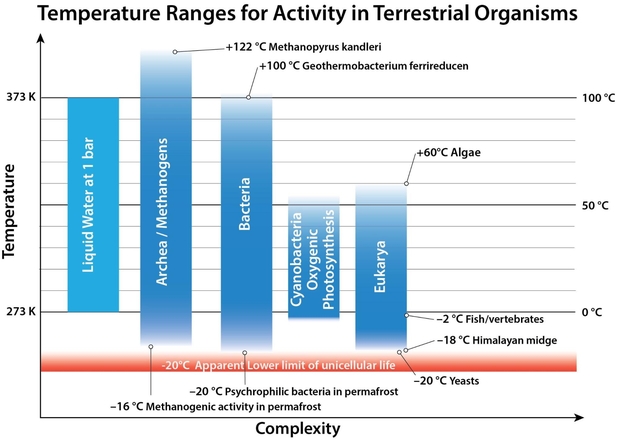
Determine 3. Examples of temperature ranges for various kinds of organisms, taken for species on the excessive ranges of survival within the laboratory.
To display their framework, they work by means of fashions for archaean life on Trappist 1e and Trappist 1f, cyanobacteria on the identical 2 planets, methanogens (that would come with archaea) within the subsurface of Mars, and the subsurface ocean of Enceladus.
Determine 4 beneath reveals the simplified mannequin for archaea on Trappist 1e. The values and customary deviations used for the priors aren’t all defined within the textual content. For instance, the imply floor strain is about at 5 Bar for illustrative functions, as no environment has been detected for Trappist-1e. The community mannequin for the varied modules that decide the viability of an archaean is mapped in a). Solely 2 variables, floor temperature and strain, decide viability of the archaean prokaryotes within the modeled floor temperature. In additional subtle fashions, this may be a multidimensional plot maybe utilizing principal part evaluation (PCA) to indicate a 3D plot. The varied assumed (prior) and calculated (end result) values and their assumed distributions are proven as charts in b). The plot of viability (1) and non-viability (0) for floor temperature and strain is proven within the 3D plot c. The distributions point out the likelihood of suitability of the habitat.
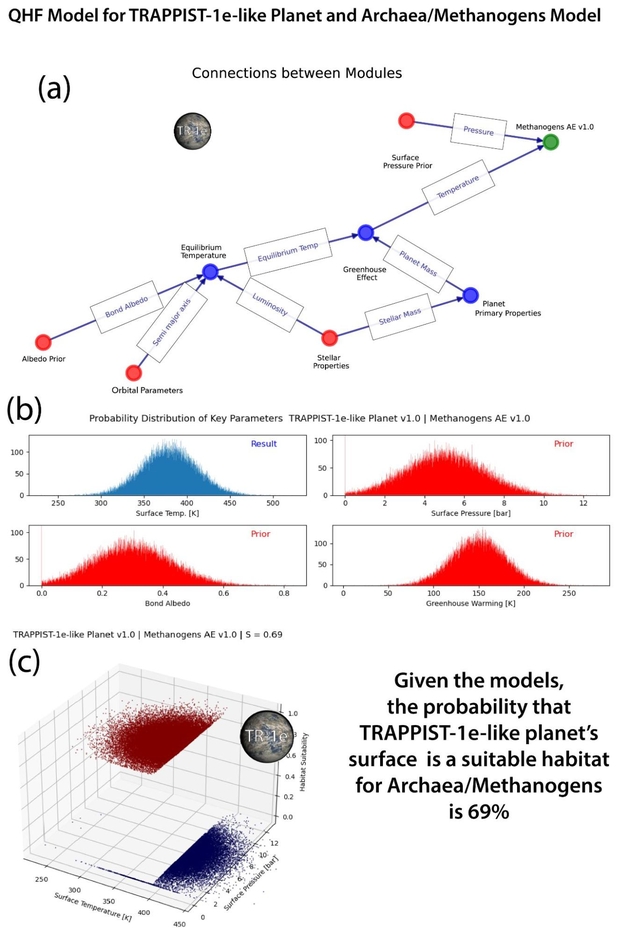
Determine 4. QHF evaluation of the viability of archaea/methanogens in a modeled TRAPPIST-1e-like planet’s floor habitat. a: Connections between the mannequin modules. Purple are priors, blue are calculated values, inexperienced is the viability mannequin. b: Relative likelihood distributions of key parameters. c: The distribution of calculated viability as a perform of floor temperature and strain. The sharp temperature cutoff at 395K separates the habitat as viable or not.
The examples are then tabulated to indicate the chances of various unicellular life inhabiting the varied instance worlds.
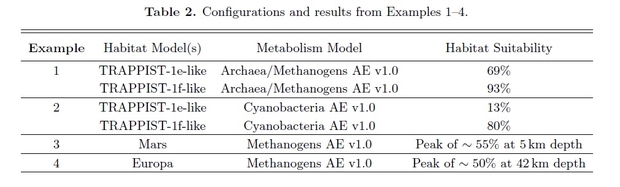
As you possibly can see, the archaea/methanogens on Trappist 1f have the best likelihood of being current inhabiting that world if we assume terrestrial life represents good examples. Due to this fact, Trappist 1f could be prioritized given the data presently out there. If spectral information advised that there was no water in Trappist 1f’s environment, this would scale back, and probably remove, this world’s habitability likelihood, and with it the likelihood of it assembly the requirement of archaean life and therefore decreasing the overlap within the habitability and life requirement phrases to nil.
My Critique of the Methodology
The worth of this paper is that it goes past the standard “Is the exoplanet liveable?” with the standard caveats about habitability that apply underneath sure circumstances, normally atmospheric strain and composition. The liveable zone (HZ) round a star is calculated for the vary of distances from the star the place, with a super environment composition and density, on a rocky floor, liquid water may very well be discovered. Thus, early Mars, with a denser environment, may very well be liveable [2], and certainly, the proof is that water was as soon as current on the floor. Venus may also as soon as have been liveable, positioned on the inside fringe of our solar’s HZ, earlier than a runaway greenhouse made the planet uninhabitable.
The idea of NASA’s “Observe the water” mantra is a primary step, however this paper then factors out that is solely a part of the equation when deciding the precedence of expending sources on observing a potential exoplanet for all times. The Earth as soon as had an anoxic environment, making Lovelock’s early concept that gases in disequilibrium would point out life, which rapidly turned interpreted as free oxygen (O2) and methane (CH4), largely irrelevant throughout this era earlier than oxygenic photosynthesis modified the composition of the environment.
But Earth was dwelling inside just a few hundred million years after its beginning, with organisms that predated the archaea and micro organism kingdoms [4]. Archaea are sometimes methanogens, releasing CH4 into the early environment at a charge exceeding that of geological serpentinization. Their habitat within the oceans should have been sufficiently temperate, albeit some are thermophilic, dwelling in water as much as 122 centigrade however underneath strain to forestall boiling. If the habitability calculations embody the essential variables, then their methodology affords a rigorous solution to decide the likelihood of explicit terrestrial life on a potential exoplanet.
The issue is whether or not the essential variables are included. As we see with Venus, if the environment was nonetheless Earthlike, then it’d properly be a potential goal. Due to this fact, an exoplanet on the inside fringe of its star’s HZ would possibly have to have its environment modeled for stability, given the age of its star, to find out whether or not the environment may nonetheless be earthlike and subsequently help liquid water on the floor.
Nevertheless, there could also be different variables that now we have repeatedly mentioned on this web site. Is the star secure or does it flare often? Does the star emit onerous UV and X-rays that might destroy life on the floor by destroying natural molecules? Is the star’s spectrum suited to supporting photosynthesis, and if not, does it enable or stop chemotrophs to outlive? For complicated life, is a big moon wanted to maintain the rotational axis comparatively secure to forestall local weather zones and circulation patterns from altering too drastically? Is the planet tidally locked, and if that’s the case, can life exist on the terminator, as now we have no terrestrial examples to judge? The Ramirez paper [3] contains his modeling of Trappist 1e, utilizing the anticipated synchronization of its rotation and orbital interval, leading to completely cold and hot hemispheres.
Whereas the authors recommend that the evaluation can lengthen past species to ecosystems, and maybe a biosphere, we actually don’t know what the related variables are usually. Unicellular organisms are typically simply cultured in a laboratory, however most aren’t. We simply don’t know what circumstances they want, and whether or not these circumstances exist on the exoplanet. It could be that the equation variables could also be fairly giant, making the analyses too unwieldy to be price doing to judge the likelihood of some terrestrial life kind inhabiting the exoplanet.
An additional critique is that organisms not often can exist as pure cultures besides in a laboratory setting with splendid tradition media. Organisms within the wild exist in ecosystems, the place completely different organisms contribute to the survival of others. For instance, bacterial biofilms typically comprise completely different species in layers permitting for various habitats to be supported, from anaerobes to aerobes.
The evaluation gamely seems at life beneath the floor, akin to lithophilic life 5 km beneath the floor of Mars, or ocean life within the subsurface Enceladan ocean. However even when the likelihood in both case was 100% that life was current, each environments are inaccessible in comparison with different determinants of life that we will observe with our telescopes. This could apply to icy moons of big exoplanets, even when future landers established that life existed in each Europan and Enceladan subsurface oceans.
What about exoplanets that aren’t in close to round orbits, however extra eccentric, like Brian Aldiss’ fictional “Heliconia”? Find out how to consider their habitability? Or circumbinary planets the place the two stars are creating differing instellation patterns because the planet orbits its shut binary?. Lastly, can tidally locked exoplanets help life solely on the terminator that helps the vary of their identified necessities, akin to Ramirez’ modeling of Trappist 1e?
A median floor temperature doesn’t cowl both the extremes, for instance the tropics and the poles, nor that water is at its densest at 277K (4 °C), guaranteeing that there’s liquid water even when the floor is totally glaciated above an ocean. Inside warmth may guarantee liquid water beneath an icy floor, and tidal heating can contribute to heating even on moons which have exhausted their radioactive components. If the Gaia speculation is right, then life can alter a planet to help life even underneath antagonistic circumstances, stabilizing the biosphere surroundings. The vary of floor temperatures is roofed by the Gaussian distribution of temperatures as proven in Determine 4 b.
Lastly, whereas the joint likelihood mannequin with Monte Carlo simulation to estimate the likelihood of an organism or ecosystem inhabiting the exoplanet is a comparatively computationally light-weight mannequin, it is probably not the correct strategy with extra variables added to the combo. The chances could also be disjoint with a union of various subsets of variables with joint possibilities. In different phrases, reasonably than “and” intersections of planet and organism requirement possibilities, there could also be an “or” union of possibilities. The modeled strategy could show brittle and fail, a identified downside of such fashions, which could be alleviated to some extent by utilizing solely subsets of the variables. One other downside I foresee is {that a} planet with richer observational information could rating extra poorly than a planet with few data-supported variables, merely because of the joint likelihood mannequin.
All of which makes me marvel if the strategy actually solves the terminology situation to prioritize exoplanet life searches, particularly if a planet is each liveable and doubtlessly inhabited. It’s extremely terrestrial-centric, as we’d anticipate, as now we have no different life to judge. If we discover one other life on Earth, as posited by Paul Davies’ “Shadow Biosphere,” [4] this technique may very well be prolonged. However we can not even decide the necessities of extinct animals and crops that haven’t any dwelling kin, however flourished in earlier intervals on Earth. Which species survived when Earth was a hothouse within the Carboniferous, or beneath the ice through the international glaciations? The place have been these circumstances outdoors the vary of extant species? For instance, post-glacial people couldn’t survive through the Eocene thermal most.
For me, this all boils down as to if this technique can usefully assist decide whether or not an exoplanet is price observing for all times. If an preliminary remark dominated out an environment like several of these Earth has skilled within the final 4.5 billion years, ought to the seek for life be instantly redirected to the subsequent finest goal, or ought to additional information be collected, maybe to search for gases in disequilibrium? Whereas I wouldn’t guess that Seager’s ‘MorningStar’ mission to search for life on Venus will discover something, if it did flip up microbes within the acidic environment’s temperate zone, that might add an entire new set of doable organism necessities to judge, making Venus-like exoplanets viable targets for all times searches. If we ultimately discover life on exoplanets with extensively various circumstances, with ranges outdoors of terrestrial life, would the habitat analyses then have to check all identified life from a catalog of planetary circumstances?
However suppose this technique fails, and we can not detect life, for varied causes, together with instrumentation limits? Then we must always fall again on the tactic I final posted on, which reduces the likelihood of extant life on an exoplanet, however leaves open the likelihood that life will ultimately be detected.
The paper is Apai et al (2025)., “A Terminology and Quantitative Framework for Assessing the Habitability of Photo voltaic System and Extraterrestrial Worlds,” in press at Planetary Science Journal. Summary.
References
1. Schulze-Makuch, D. (2015) Astronomers Simply Doubled the Variety of Probably Liveable Planets. Smithsonian Journal, 14 January 2015.
https://www.smithsonianmag.com/air-space-magazine/astronomers-just-doubled-number-potentially-habitable-planets-180953898/
2. Seager, S. (2013) “Exoplanet Habitability,” Science 340, 577.
doi: 10.1126/science.1232226
3. Ramirez R., (2024). “A New 2D Vitality Steadiness Mannequin for Simulating the Climates of Quickly and Slowly Rotating Terrestrial Planets,” The Planetary Science Journal 5:2 (17pp), January 2024
https://doi.org/10.3847/PSJ/ad0729
4. Tolley, A. (2024) “Our Earliest Ancestor Appeared Quickly After Earth Shaped” https://www.centauri-dreams.org/2024/08/28/our-earliest-ancestor-appeared-soon-after-earth-formed
5. Davies P. C. W. (2011) “Looking for a shadow biosphere on Earth as a check of the ‘cosmic crucial,” Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A.369624–632 http://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2010.0235


