In case you’re headed for an additional planet, celestial markers can preserve your spacecraft correctly oriented. Mariner 4 used Canopus, a brilliant star within the constellation Carina, as an perspective reference, its star tracker digital camera locking onto the star after its Solar sensor had locked onto the Solar. This was the primary time a star had been used to supply second axis stabilization, its brightness (second brightest star within the sky) and its place properly off the ecliptic making it an excellent referent.
The celebs are, in fact, a navigation software par excellence. Mariners of the sea-faring type have used celestial navigation for millennia, and I vividly keep in mind an evening coaching flight in upstate New York when my teacher switched off our instrument panel by pulling a fuse and advised me to search out my means residence. I used to be forcefully reminded how far we’ve come from the times when the night time sky really was a celestial map for vacationers. Thankfully, just a few brilliant cities alongside the way in which made lifeless reckoning a straightforward strategy to get residence that night time. However I advised myself I might study to do higher at stellar navigation. I can nonetheless hear my exasperated teacher as he identified one celestial marker: “For God’s sake, see that brilliant star? Park it over your left wingtip!”
Celestial navigation of varied varieties could be completed aboard a spacecraft, and using pulsars will assist future deep area probes navigate autonomously. Till then, our strategies rely closely on ground-based installations. Delta-Differential One-Method Ranging (Delta-DOR or ∆DOR) can measure the angular location of a goal spacecraft relative to a reference path, the latter being decided by radio waves from a supply like a quasar, whose angular place is well-known. Solely the downlink sign from the spacecraft is utilized in a precision method that has been employed efficiently on such missions as China’s Chang’e, ESA’s Rosetta and NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
The Deep House Community and Delta-DOR can carry out marvels by way of the directional location of a spacecraft. However we’ve additionally simply had a primary by way of autonomous navigation by means of the work of the New Horizons crew. With out utilizing radio monitoring from Earth, the spacecraft has decided its distance and path by inspecting photos of star fields and the noticed parallax results. Splendidly, the 2 stars that the crew selected for this calculation have been Wolf 359 and Proxima Centauri, two close by purple dwarfs of appreciable curiosity.
The pictures in query have been captured by New Horizons’ Lengthy Vary Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) and studied in relation to background stars. These twp stars are virtually 90 levels aside within the sky, permitting crew scientists to flag New Horizons’ location. The LORRI instrument presents restricted angular decision and is right here getting used properly outdoors the parameters for which it was designed, besides, this primary demonstration of autonomous navigation didn’t do badly, discovering a distance near the precise distance of the spacecraft when the pictures have been taken, and a path on the sky correct to a patch concerning the measurement of the complete Moon as seen from Earth. That is the biggest parallax baseline ever taken, extending for over 4 billion miles. Increased decision imagers, as reported on this JHU/APL report, ought to be capable of do significantly better.
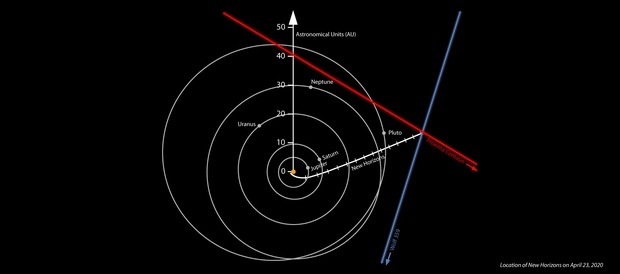
Picture: Location of NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft on April 23, 2020, derived from the spacecraft’s personal photos of the Proxima Centauri and Wolf 359 star fields. The positions of Proxima Centauri and Wolf 359 are strongly displaced in comparison with distant stars from the place they’re seen on Earth. The place of Proxima Centauri seen from New Horizons means the spacecraft have to be someplace on the purple line, whereas the noticed place of Wolf 359 signifies that the spacecraft have to be someplace on the blue line – placing New Horizons roughly the place the 2 traces seem to “intersect” (in the actual three dimensions concerned, the traces don’t truly intersect, however do cross shut to one another). The white line marks the correct Deep House Community-tracked trajectory of New Horizons since its launch in 2006. The traces on the New Horizons trajectory denote years since launch. The orbits of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune and Pluto are proven. Distances are from the middle of the photo voltaic system in astronomical items, the place 1 AU is the typical distance between the Solar and Earth. Credit score: NASA/Johns Hopkins APL/SwRI/Matthew Wallace.
Brian Could, recognized for his guitar abilities with the band Queen in addition to his data of astrophysics, helped to provide the pictures under that present the comparability between these stars as seen from Earth and from New Horizons. A co-author of the paper on this work, Could provides:
“It might be argued that in astro-stereoscopy — 3D photos of astronomical objects – NASA’s New Horizons crew already leads the sector, having delivered astounding stereoscopic photos of each Pluto and the distant Kuiper Belt object Arrokoth. However the newest New Horizons stereoscopic experiment breaks all information. These pictures of Proxima Centauri and Wolf 359 – stars which are well-known to beginner astronomers and science fiction aficionados alike — make use of the biggest distance between viewpoints ever achieved in 180 years of stereoscopy!”
Listed below are two animations exhibiting the parallax involving every star, with Proxima Centauri being the primary picture. Observe how the star ‘jumps’ in opposition to background stars because the view from Earth is changed by the view from New Horizons.


Picture: In 2020, the New Horizons science crew obtained photos of the star fields across the close by stars Proxima Centauri (high) and Wolf 359 (backside) concurrently from New Horizons and Earth. More moderen and complicated analyses of the precise positions of the 2 stars in these photos allowed the crew to infer New Horizons’ three-dimensional place relative to close by stars – undertaking the primary use of stars imaged straight from a spacecraft to supply its navigational repair, and the primary demonstration of interstellar navigation by any spacecraft on an interstellar trajectory. Credit score: JHU/APL.
This end result from New Horizons marks the primary time that optical stellar astrometry has been utilized to the navigation of a spacecraft, however it’s clear that our hitherto Earth-based strategies of navigation in area must give strategy to on-board strategies as we enterprise nonetheless farther out of the Photo voltaic System. Up to now using X-ray pulsars has been demonstrated solely in Earth orbit, however it should absolutely be among the many strategies employed. These rudimentary observations are likewise proof-of-concept whose accuracy will want dramatic enchancment.
The paper notes the subsequent steps in utilizing parallactic measurements for autonomous navigation:
Significantly higher efficiency ought to be attainable utilizing the cameras presently deployed on different interplanetary spacecraft, or contemplated for future missions. Telescopes with apertures plausibly bigger than LORRI’s, with diffraction-limited optics, delivering photos to Nyquist-sampled detectors [a highly accurate digital signal processing method], mounted on platforms with matching finepointing management, ought to be capable of present astrometry with few milli-arcsecond accuracy. Extrapolating from LORRI, place vectors with accuracy of 0.01 au ought to be attainable within the close to future.
The paper on this work is Lauer et al., “A Demonstration of Interstellar Navigation Utilizing New Horizons,” accepted at The Astronomical Journal and obtainable as a preprint.


