Perseverance Encounters a Doable Meteorite

Written by Candice Bedford, Analysis Scientist at Purdue College
Oct. 1, 2025
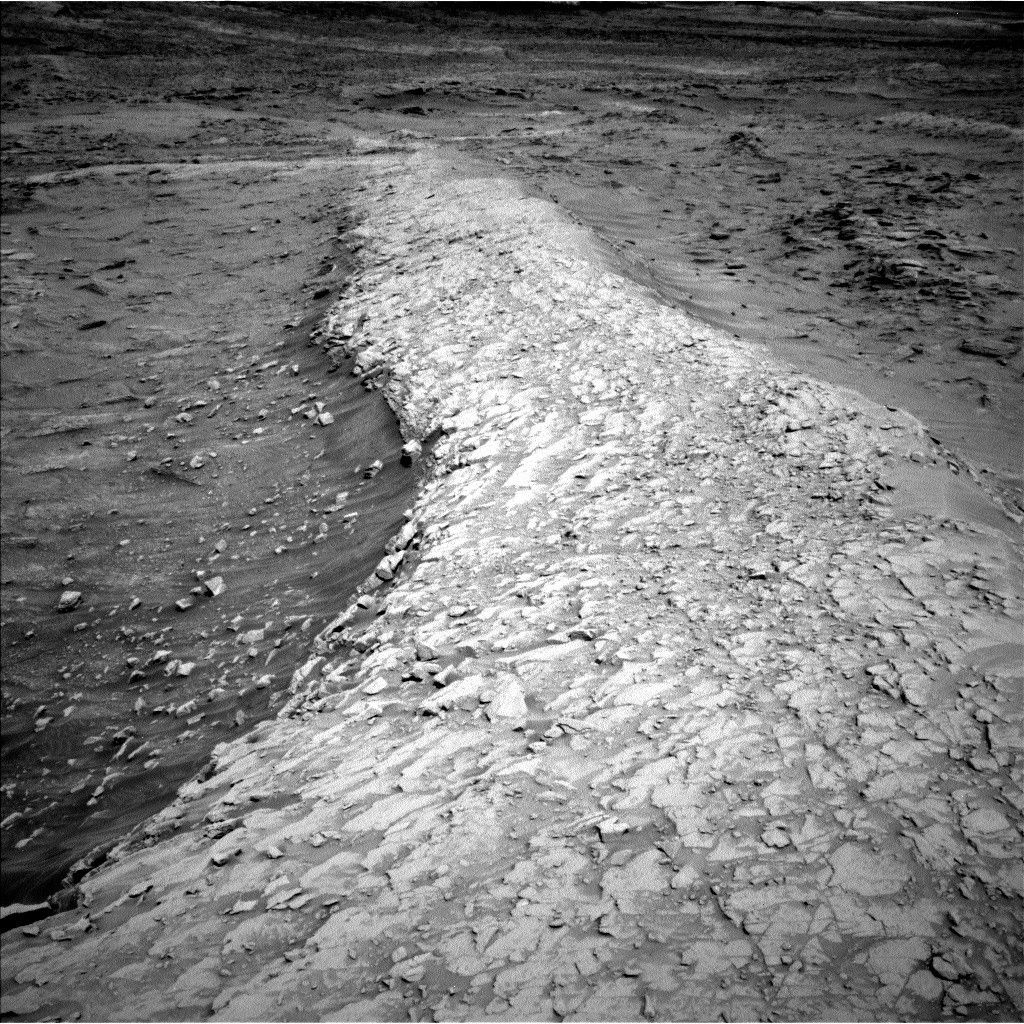
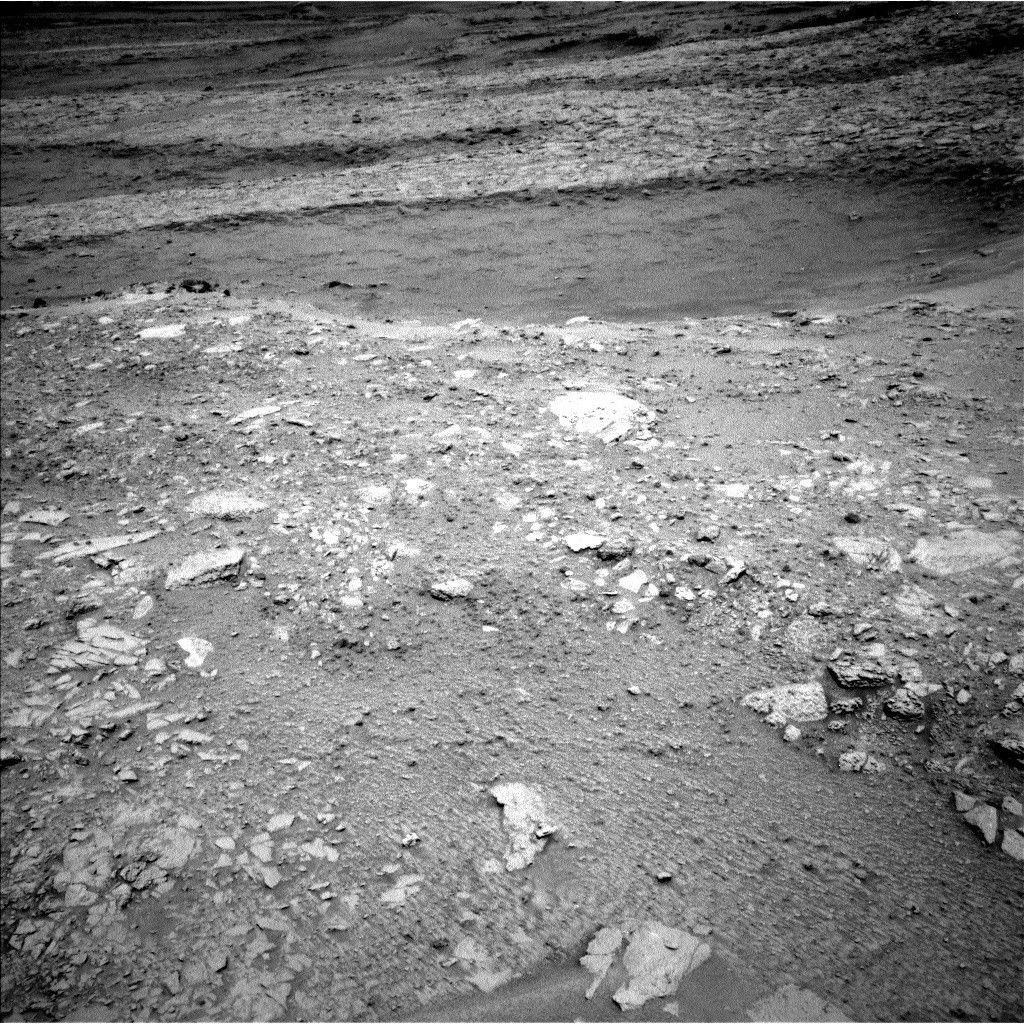
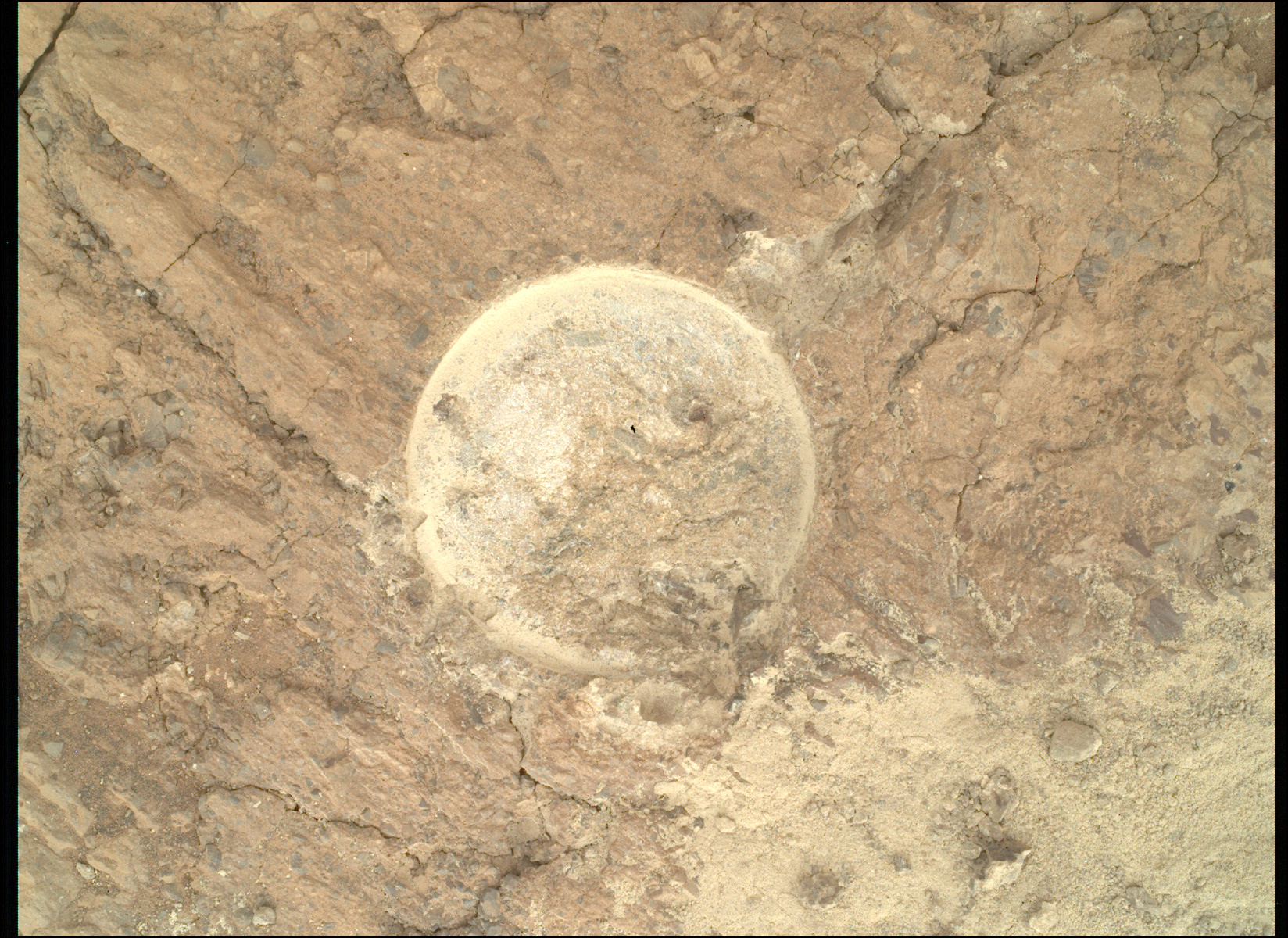
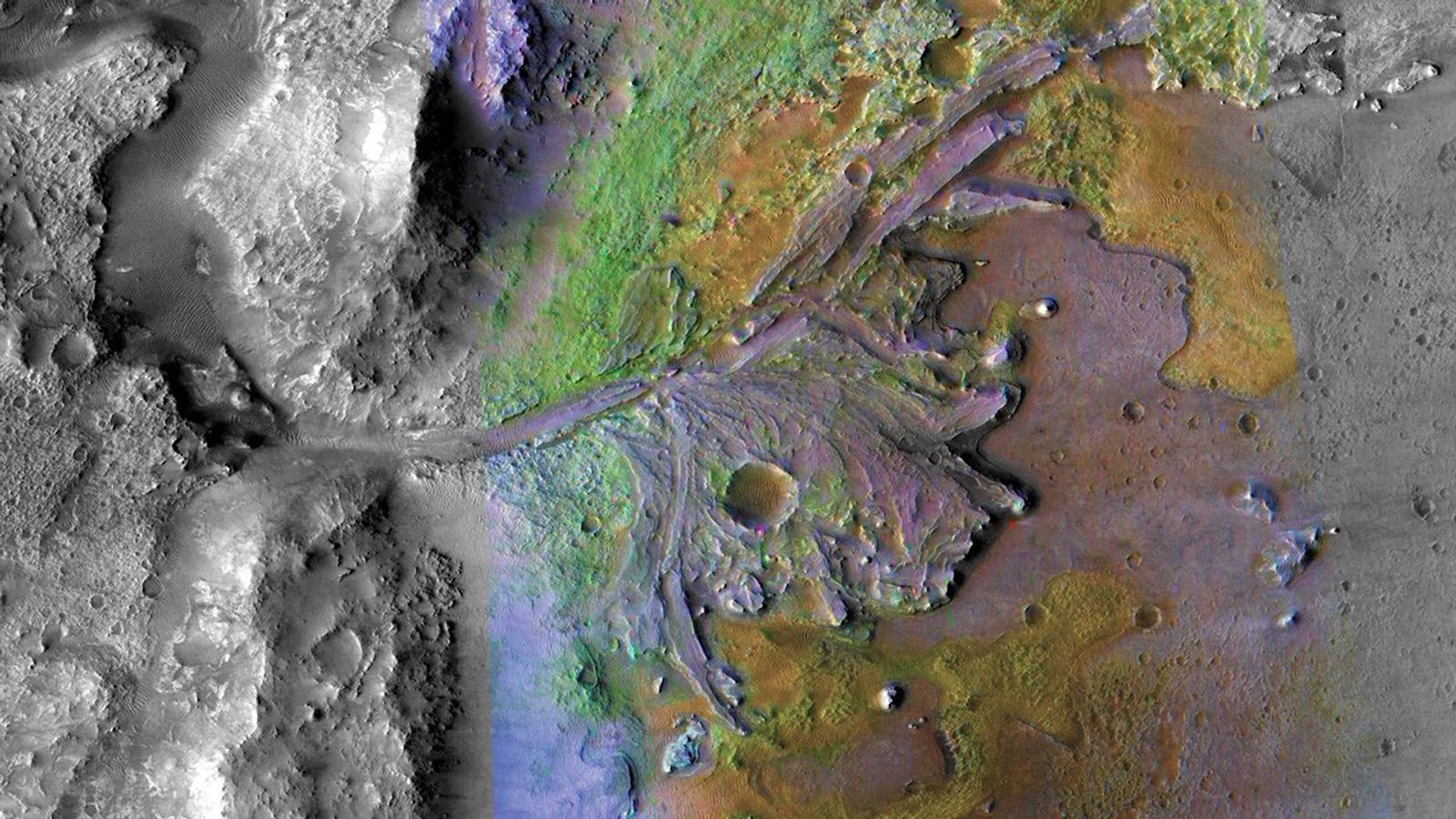
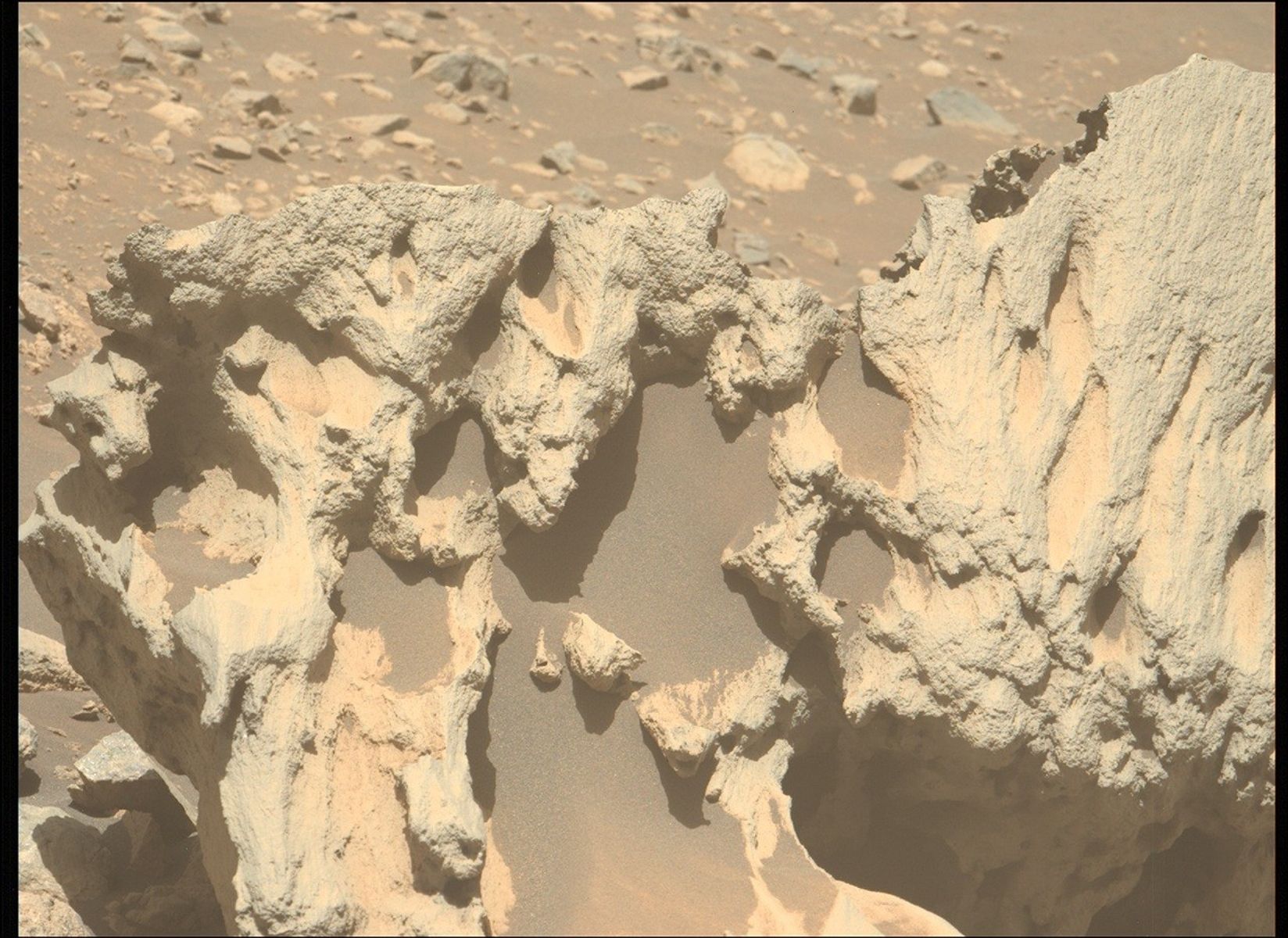
Throughout the rover’s current investigation of the bedrock at “Vernodden,” Perseverance encountered an unusually formed rock about 80 centimeters throughout (about 31 inches) known as “Phippsaksla.” This rock was recognized as a goal of curiosity primarily based on its sculpted, high-standing look that differed from that of the low-lying, flat and fragmented surrounding rocks. Final week, Perseverance focused Phippsaksla with the SuperCam instrument revealing that it’s excessive in iron and nickel. This factor mixture is often related to iron-nickel meteorites shaped within the core of enormous asteroids, suggesting that this rock shaped elsewhere within the photo voltaic system.
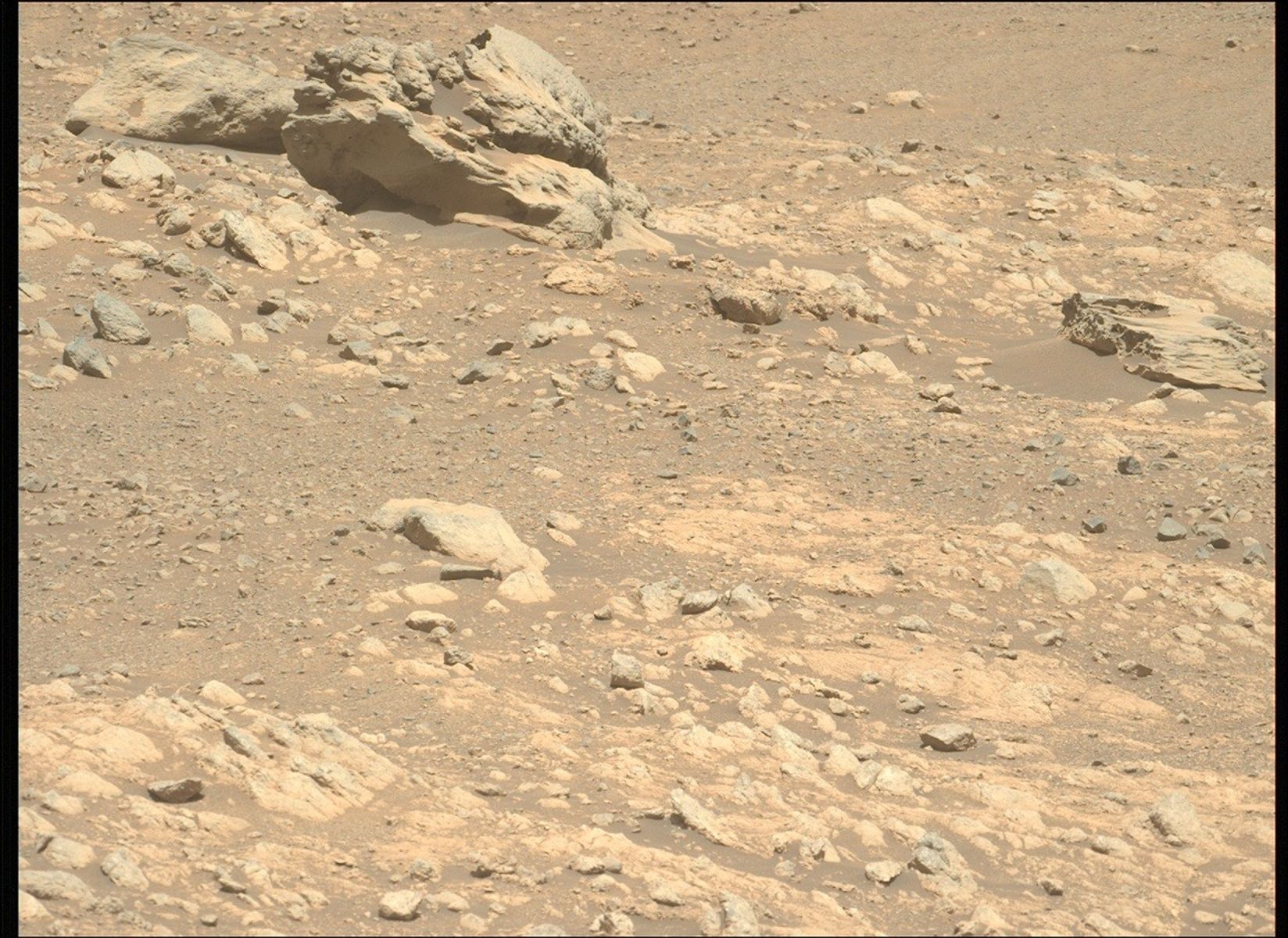

This isn’t the primary time a rover has encountered an unique rock on Mars. The Curiosity rover has recognized many iron-nickel meteorites throughout its traverse in Gale crater together with the 1-meter large (about 39 inches) “Lebanon” meteorite again in 2014 and the “Cacao” meteorite noticed in 2023. Each Mars Exploration Rovers, Alternative and Spirit, additionally discovered iron-nickel meteorites throughout their missions. As such, it has been considerably sudden that Perseverance had not seen iron-nickel meteorites inside Jezero crater, significantly given its comparable age to Gale crater and variety of smaller influence craters suggesting that meteorites did fall on the crater ground, delta, and crater rim all through time. Now, on the surface of the crater, atop bedrock identified to have shaped from influence processes up to now, Perseverance has doubtlessly discovered one. As a result of unique composition of this rock, extra investigation by the workforce must be completed to verify its standing as a meteorite. But when this rock is deemed to be a meteorite Perseverance can in the end add itself to the record of Mars rovers who’ve investigated the fragments of rocky guests to Mars.

The submit A Stranger in Our Midst? appeared first on NASA Science.