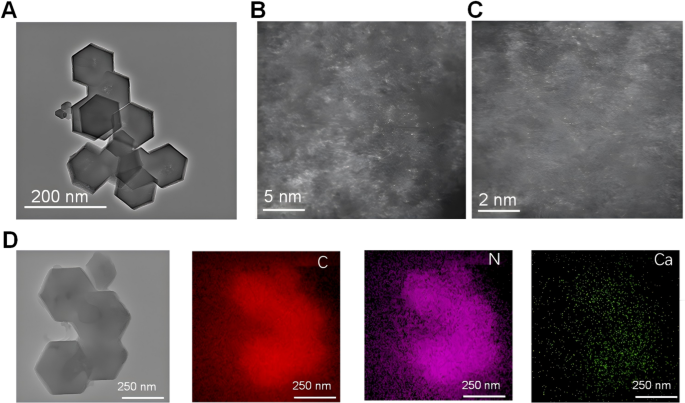
Synthesis technique and microstructure evaluation
We beforehand demonstrated that piezoelectric polymer membranes primarily based on single metallic atoms are efficient by anchoring remoted calcium (Ca) atoms onto nitrogen-doped carbon and polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) composites [12]. Drawing on this prior analysis, we designed and improved the method to synthesize CaCN.
ZIF-8 coated Ca (Ca/ZIF-8) was ready through a hydrothermal technique, adopted by calcination to fabricate CaCN (Supplementary Fig. 1). Zinc nitrate hexahydrate, calcium chloride, and dimethylimidazole had been used as uncooked supplies, and synthesis was carried out utilizing a hydrothermal technique in methanol, adopted by carbonization. Then, acid etching was carried out to not solely take away residual zinc and calcium to keep away from secondary air pollution but additionally to generate extra mesopores on the unique construction of MOF, selling pollutant adsorption and producing extra floor catalytic response lively websites. Morphology research displayed that the introduction of Ca didn’t have an effect on the construction of ZIF. SEM photographs of ZIF-8 and Ca/ZIF-8 supplies depicted comparable common dodecahedron morphology (Supplementary Fig. 2 A). The powder XRD spectrum (Supplementary Fig. 2B) confirmed that ZIF-8 and Ca/ZIF-8 had comparable crystal phases.
The morphological traits of CaCN had been evaluated utilizing transmission electron microscopy (TEM). As illustrated in Fig. 2A, the HR-TEM picture of CaCN after high-temperature pyrolysis nonetheless confirmed a normal dodecahedron construction, indicating that high-temperature remedy didn’t have an effect on the construction of the fabric and validating the high-temperature stability of CaCN supplies. With a purpose to make clear the existence type of Ca, aberration-corrected HAADF-STEM characterization of atomic decision was performed. As displayed in Figs. 2B and C, a lot of Ca atoms had been dispersed within the carbon skeleton, additional supporting the anchoring of a single Ca atom within the carbon framework by N and C atoms. In the meantime, the energy-dispersive X-ray component mapping spectrum (EDS) picture offered that the weather C, N, and Ca had been evenly distributed in CaCN, as delineated in Fig. 2D. As well as, the existence of Ca and N was confirmed by electron power loss spectroscopy (EELS). Two peaks at roughly 350 eV and 400 eV had been distributed on the attribute Ca L edge and N Ok edge, respectively, which offered robust proof that Ca exists as single atoms in CaCN (Supplementary Fig. 2 C).
Synthesis technique and microstructure evaluation. (A) HR-TEM of CaCN. (B, C) Aberration-corrected HAADF-STEM picture of CaCN with scale bars of two nm and 5 nm, displaying that Ca within the carbon framework present as single atom. (D) The HAADF-STEM picture of the CaCN and the photographs of elemental mapping of C, N, and Ca within the CaCN
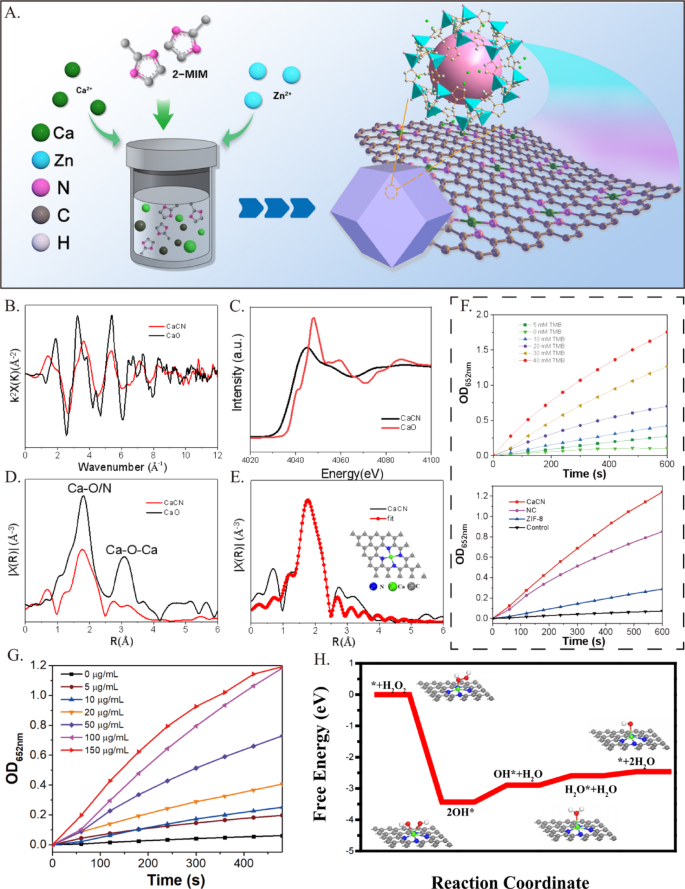
Chemical state and lively website evaluation
The digital construction and native coordination surroundings of monatomic calcium had been additional decided by X-ray absorption close to edge construction (XANES) and prolonged X-ray absorption superb construction (EXAFS) to disclose the construction of lively websites. On condition that Ca is very lively in air, the Ca Ok-edge XANES spectrum of CaO was used as a calibration reference materials. Determine 3B exhibits the Ok-space diagram of Ca Ok-edge EXAFS. It’s emphasizing noting that the EXAFS curve of CaCN markedly differed from that of CaO. The CaCN uncorrected Ca Ok-edge Fourier rework (FT) – EXAFS curve confirmed {that a} essential peak is at 1.9 Å, attributed to the Ca-N scattering path (Fig. 3C). As offered in Fig. 3D, the near-edge absorption spectrum of the CaCN catalyst carefully matched the calcium-containing reference (CaO), suggesting that the Ca metallic atom in CaCN was in a cationic state. Ca-O (1.8 Å) and Ca-O-Ca (3.1 Å) peaks weren’t detected in Ca/CN, corroborating the presence of solely a single calcium atom in Ca/CN. In the meantime, the quantitative native coordination parameters of the Ca atom had been additional examined through least sq. EXAFS becoming (Fig. 3E), uncovering a coordination variety of 4 for the primary shell and a Ca-N bond size of two.27 Å. Moreover, we beforehand demonstrated that the becoming outcomes of EXAFS revealed that the R-factor worth of the Ca-N4 construction was 0.0044, which is in good settlement with the characterization outcomes of the pattern, indicating that Ca-N4 is the lively middle of CaCN [12]. These outcomes signified that the Ca atom coordinated with N atoms to type an lively website. Taken collectively, the aforementioned outcomes offered sturdy proof for the profitable synthesis of CaCN on the Ca – N4 website by combining atomic dispersed Ca with 4 N atoms.
To additional examine the catalytic efficiency of CaCN, the response kinetics and environmental responsiveness had been evaluated below varied circumstances. The catalytic exercise, monitored by the oxidation of TMB (3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine) to provide a chromogenic product, demonstrated a transparent dependence on catalyst focus and substrate focus (Fig. 3G), with CaCN exhibiting considerably increased exercise in comparison with management supplies (NC, ZIF-8, and clean) (Fig. 3F). In contrast with pure horseradish peroxidase (HRP), CaCN displays a decrease Km worth and the next obvious Vmax/Km ratio, which confers a relative benefit at sub-millimolar substrate concentrations (Supplementary Fig. 3 A). Temperature-dependent experiments revealed that the response fee elevated with temperature, as evidenced by a extra pronounced absorbance peak at 652 nm below 37 °C in comparison with 20 °C (Supplementary Fig. 3B). Moreover, upon publicity to 1064 nm laser irradiation, the response was notably accelerated, attributed to laser-induced fast temperature elevation, highlighting the potential of CaCN for photothermal-enhanced catalysis. The free power profile (Fig. 3H) corroborated these observations, indicating that the Ca-N4 lively middle facilitates spontaneous response pathways with a big discount in power limitations. Collectively, these outcomes verify that the distinctive single-atom Ca-N4 construction performs a pivotal function within the superior catalytic efficiency of CaCN below numerous response circumstances.
Chemical State and Energetic Web site Evaluation. (A) The synthesis means of CaCN. Structural evaluation of CaCN by X-ray absorption superb construction (XAFS) spectroscopy. (B) Fourier rework (FT) of the Ca Ok-edge prolonged XAFS (EXAFS) spectra of CaCN and CaO at k-space. (C) Ca Ok-edge X-ray absorption close to edge construction spectra of CaCN and CaO. (D) Fourier rework (FT) of the Ca Ok-edge prolonged XAFS (EXAFS) spectra of CaCN and CaO at R-space. (E) Corresponding EXAFS becoming curve of CaCN in R. Insets are the schematic mannequin of Ca-N4. Mild gray, blue, and inexperienced balls signify C, N, and Ca atoms, respectively. (F) Peroxidase-like exercise of the Ca/CN-SAzyme at completely different Concentrations. (NC refers back to the management pattern ready with out Ca. Management refers back to the situation with none added nanomaterials.). (G) Peroxidase-like exercise of the Ca/CN-SAzyme at completely different Concentrations. (H) Proposed catalytic mechanism of Ca/CN-SAzyme
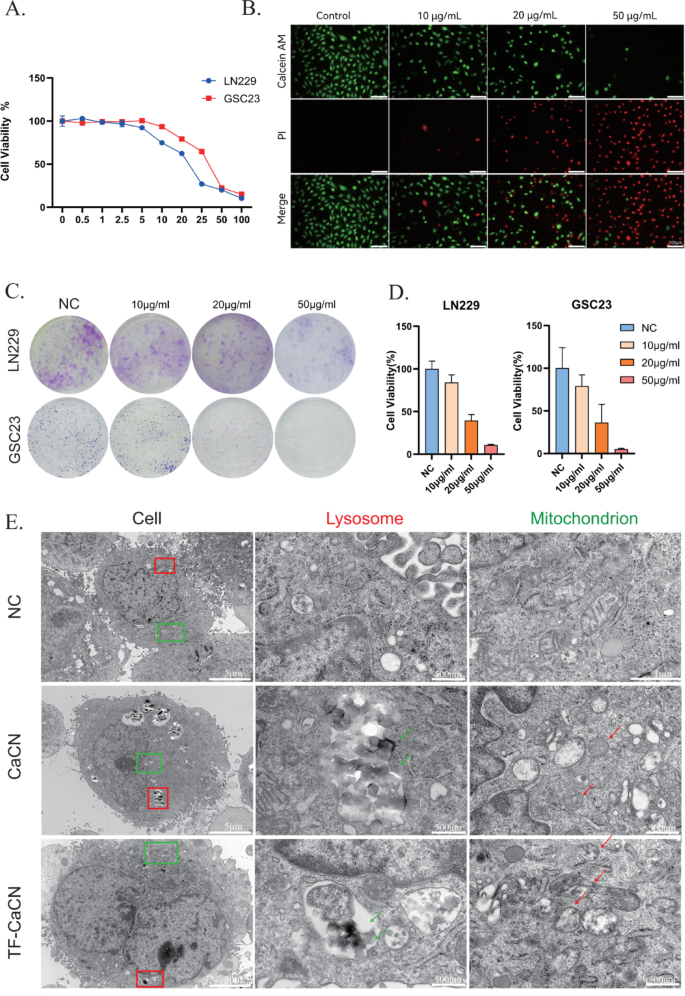
CaCN nanozymes induce glioma cell demise
The anti-tumorigenic properties of CaCN had been initially assessed on the mobile stage. To look at the results of various concentrations of CaCN on glioma cells, cell viability was decided utilizing Cell Counting Equipment-8 (CCK-8) assay on LN229 and GSC23 cells handled with gradient concentrations of CaCN, respectively. Subsequent, cell viability curves below every focus of nanozyme remedy had been plotted (Fig. 4A), and the IC50 of CaCN in LN229 and GSC23 cells was decided. In the meantime, we evaluated the cytotoxicity of each ZIF-8 and CaCN, and the outcomes confirmed that CaCN exhibited stronger cytotoxicity, which can be attributed to its increased catalytic exercise (Fig. 3F). Particularly, the IC50 was 20.13 µg/ml in LN229 cells and 30.77 µg/ml in GSC23 cells. For subsequent experiments, we chosen concentrations barely above these values to make sure steady organic results, specifically 30 µg/ml for LN229 cells and 40 µg/ml for GSC23 cells. Subsequently, for subsequent research on TF-CaCN, we chosen the identical experimental focus. We additionally in contrast the toxicity of TF-CaCN between regular astrocyte cells (NHA) and glioblastoma cells (LN229) utilizing CCK8. The outcomes confirmed that the IC50 worth within the NHA cell line was a lot increased than that within the LN229 cell line (Supplementary Fig. 4B), indicating that the distinctive intracellular microenvironment of tumor cells is extra favorable for catalysis by single-atom nanozymes. As a result of tumor cells generate extra H2O2 than regular cells, we sought to research whether or not H2O2 impacts the catalytic efficiency of CaCN inside cells. WB experiments confirmed that below remedy with solely 25 µM H2O2 for 3 h, apoptosis markers weren’t altered. Nevertheless, when cells had been co-treated with CaCN and H2O2, the apoptosis markers had been even increased than these noticed with CaCN alone (Supplementary Fig. 4 C). This means that H2O2 enhances the catalytic impact of CaCN inside cells. The inhibitory impact of CaCN on glioma cells was subsequently examined through live-dead fluorescence staining (Fig. 4B). The inhibitory impact of CaCN on the proliferative talents of glioma cells was investigated utilizing colony formation assay (Fig. 4C), demonstrating that completely different concentrations of CaCN exerted vital inhibitory results on glioma cells (Fig. 4D). After remedy of glioma cells with CaCN on the IC50 focus, visualization below TEM depicted that CaCN was intracellularly engulfed by glioma cells and predominantly localized in lysosomes and cytoplasm, while the realm and perimeter of mitochondria in CaCN-treated cells was lowered. Moreover, mitochondrial cristae nearly disappeared in comparison with the mitochondria within the untreated cells (Fig. 4E). These outcomes collectively advised that CaCN remedy activated related demise mechanisms and disrupted the traditional morphology of mitochondria, finally resulting in glioma cell demise.
CaCN nanozymes induce glioma cell demise. A) Viability curves of LN229 and GSC23 cells handled with completely different concentrations of CaCN. B) Reside and useless cell staining of LN229 cells with completely different concentrations of CaCN. C) Colony formation experiments of LN229 and GSC23 handled with completely different concentrations of CaCN. D) Proportion of cell viability for colony formation experiments obtained by imageJ counting. E) Transmission electron microscopy imaging of CaCN and TF-CaCN handled GSC23 cells earlier than and after 12 h. (The purple arrow signifies the lysosome engulfing the nanozyme, whereas the inexperienced arrow factors to the deformed mitochondrion.)
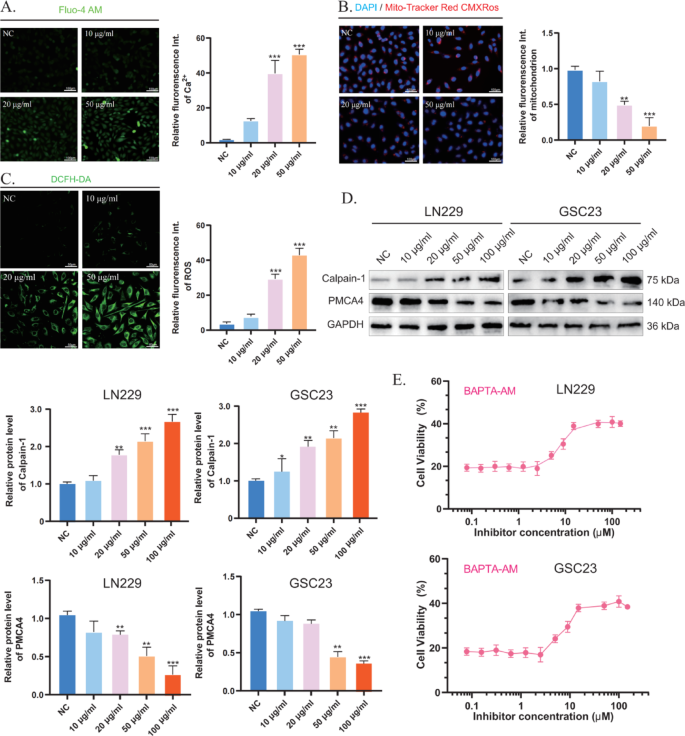
CaCN triggers intracellular calcium overload-induced apoptosis
As is effectively documented, Ca2+ performs a essential function in apoptosis [13]. The buildup of Ca2+ in mitochondria results in a sustained improve in intracellular Ca2+ ranges, resulting in mitochondrial dysfunction and finally to mitochondrial rupture and apoptosis. On the whole, when intracellular ROS ranges are excessively excessive, they work together with proteins and set off oxidative reactions that may alter protein construction and performance [14]. Thus, within the presence of excessive ranges of ROS, calcium channels, and pump proteins could endure irreversible desensitization and injury [15]. The extent of intracellular free Ca2+ following remedy with completely different concentrations of CaCN was detected utilizing a Fluo-4 AM fluorescent probe (Fig. 5A), which might bind to Ca2+ to provide intense inexperienced fluorescence. As anticipated, the fluorescence depth elevated with rising CaCN concentrations, indicating that CaCN elevated intracellular Ca2+ ranges. As well as, the MitoTracker Purple CMXRos probe was employed to find out the diploma of mitochondrial injury elicited by Ca2+ overload. Beneath physiological circumstances (excessive mitochondrial membrane potential), MitoTracker Purple CMXRos accumulates within the mitochondrial matrix and produces purple fluorescence. Following mitochondrial injury (low mitochondrial membrane potential), the fluorescence depth decreases (Fig. 5B) [16]. The outcomes uncovered that the fluorescence depth decreased with rising CaCN concentrations, indicating that CaCN-induced calcium overload strongly disrupted the mitochondrial membrane. The calcium pump PMCA4 ATPase is a calcium ion efflux pump current on the cell membrane and concerned within the excretion of calcium ions from tumor cells, and its exercise might be instantly inhibited by ROS [15]. CaCN, owing to its peroxidase-like properties, catalyzes the technology of enormous quantities of reactive oxygen species (ROS) within the tumor microenvironment of gliomas at low pH values. Thus, 2’,7’-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) was used to measure ROS ranges in tumor cells, unveiling that ROS ranges had been considerably elevated within the CaCN group, thereby validating the peroxidase-like properties of CaCN (Fig. 5C). Afterward, Western blot evaluation was performed to detect the expression of calcium-related proteins in glioma cells in an effort to analyze the molecular mechanism of calcium overload. Calpain-1 is a calcium-regulated non-lysosomal thiol protease that may be activated by excessive concentrations of Ca2+ [17]. WB outcomes confirmed that PMCA4 expression was down-regulated in glioma cells after CaCN remedy, whereas that of Calpain-1 was up-regulated. These outcomes counsel that CaCN generates a considerable amount of ROS throughout the cells, and as a result of ROS-mediated inhibition of calcium channels, the intracellular Ca2+ ranges repeatedly rise, finally resulting in calcium overload in glioma cells (Fig. 5D). Thereafter, the membrane-permeable Ca2+ chelator BAPTA-AM was used to find out the impact of Ca2+ overload on apoptosis. The survival fee of CaCN-treated glioma cells was considerably elevated with gradient concentrations of BAPTA-AM, suggesting that CaCN-induced apoptosis was extremely correlated with calcium overload (Fig. 5E).
CaCN, in distinction to standard calcium-based nanomaterials, induces a rise in calcium ions whereas producing ROS by its POD-like enzyme properties, thereby inhibiting calcium channels and triggering calcium overload.
CaCN triggers intracellular calcium overload-induced apoptosis. A) Inverted fluorescence microscopy photographs of intracellular calcium ions in glioma cells after remedy with completely different concentrations of CaCN and corresponding semiquantitative evaluation of intracellular calcium ion modifications. (n = 3, imply ± SD, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). B) Mito-Tracker Purple CMXRos staining of glioma cells after completely different remedies and corresponding Mito-Tracker Purple CMXRos had been analyzed semi-quantitatively for relative fluorescence depth. (n = 3, imply ± SD, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). C) Detection of ROS in tumor cells handled with completely different concentrations of CaCN utilizing 2’,7’-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA). D) Western blot evaluation of calcium overload-related proteins (Calpain-1, PMCA4) in glioma cells after completely different remedies. E) Cell viabilities of glioma cells co-treated with CaCN and BAPTA-AM
CaCN triggers intracellular ferroptosis
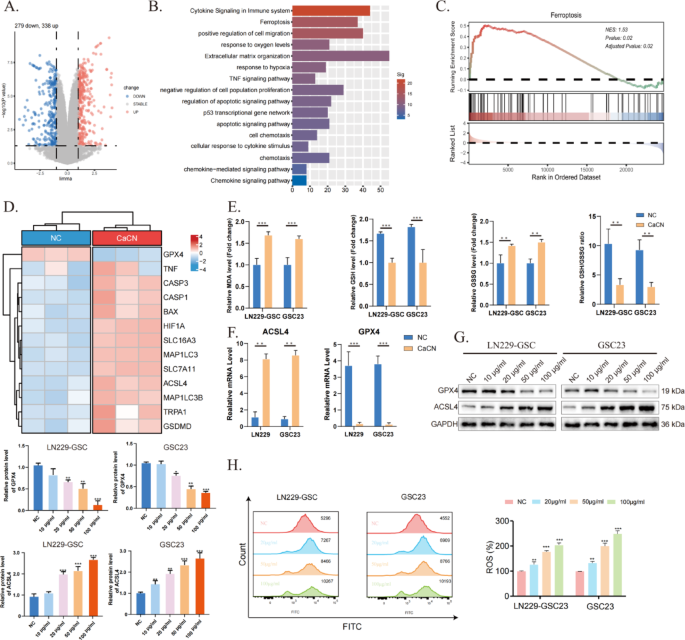
To establish genes concerned in glioma cell demise after CaCN remedy, RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) was carried out on three teams of regular GSC23 cells and three teams of CaCN-treated GSC23 cells. Volcano plots illustrate variations in gene expression in CaCN-treated glioma cells in comparison with the traditional group (Fig. 6A). Moreover, pathway enrichment evaluation of up-regulated differential genes decided that demise of CaCN-treated glioma cells was related to pathways such because the immune pathway, apoptotic pathway, ferroptosis pathway, and sensitivity to hypoxia (Fig. 6B). Subsequently, the doable mechanisms of cell demise had been explored, and single-sample gene enrichment evaluation (ssGSEA) highlighted that CaCN can induce ferroptosis (Fig. 6C). The heatmap illustrates variations in consultant genes within the ferroptosis pathway (Fig. 6D).
In contrast to different programmed cell demise processes corresponding to apoptosis, necrosis, and autophagy, ferroptosis displays typical mitochondrial phenotypic modifications, together with mitochondrial shrinkage, membrane wrinkling, elevated membrane density, and decreased mitochondrial cristae [18]. That is in line with our observations below the transmission electron microscope. Ferroptosis is a novel sort of iron-dependent programmed cell demise characterised by lipid peroxidation and glutathione depletion [19]. On this research, the degrees of GSH and MDA had been decided in CaCN-treated glioma cells, observing that the degrees of GSH/GSSG had been decreased and the degrees of MDA had been elevated, suggesting that CaCN induced the ferroptosis of glioma cells (Fig. 6E). Depletion of GSH inactivates GPX4 and induces lipid peroxidation, which in flip promotes ferroptosis. Subsequently, the lowered expression of GPX4 is a key biomarker of ferroptosis [20]. Along with GPX4, acyl-coenzyme A synthase long-chain member 4 (ACSL4) is one other indicator of ferroptosis [21]. Consequently, the expression ranges of GPX4 and ACSL4 had been detected utilizing PCR and WB. Lowered GPX4 expression and elevated ACSL4 expression ranges had been noticed within the CaCN-treated group in contrast with the management group, implying that CaCN induced ferroptosis (Fig. 6F, G). Movement cytometry outcomes additional demonstrated elevated ROS manufacturing in GBM cells after CaCN remedy (Fig. 6H).
CaCN triggers intracellular ferroptosis. (A) Differential gene volcano map of CaCN-treated GSC23 cells.(Log2Fold Change (FC) ≥ 1, Padj ≤ 0.05). (B) Pathway enrichment of up-regulated differential genes. (C) Associated Pathways Enriched by ssGSEA. (D) Warmth map of consultant differential genes of associated pathways.(Log2Fold Change (FC) ≥ 1, Padj ≤ 0.05). (E) Relative ranges of MDA, GSH, GSSG, and the relative ratio of GSH/GSSG in CaCN-treated LN229 cells and GSC23 cells.(n = 3, imply ± SD, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). (F) Relative mRNA ranges of GPX4 and ACSL4 in CaCN-treated LN229 cells and GSC23 cells as decided by qt-PCR.(n = 3, imply ± SD, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). (G) Western blot outcomes of GPX4, ACSL4 and GAPDH in LN229 and GSC23 cells handled with completely different concentrations of CaCN. (H) Movement cytometry was carried out to look at the modifications in ROS in LN229 and GSC23 cells handled with completely different concentrations of CaCN
CaCN can transform the tumor immune microenvironment
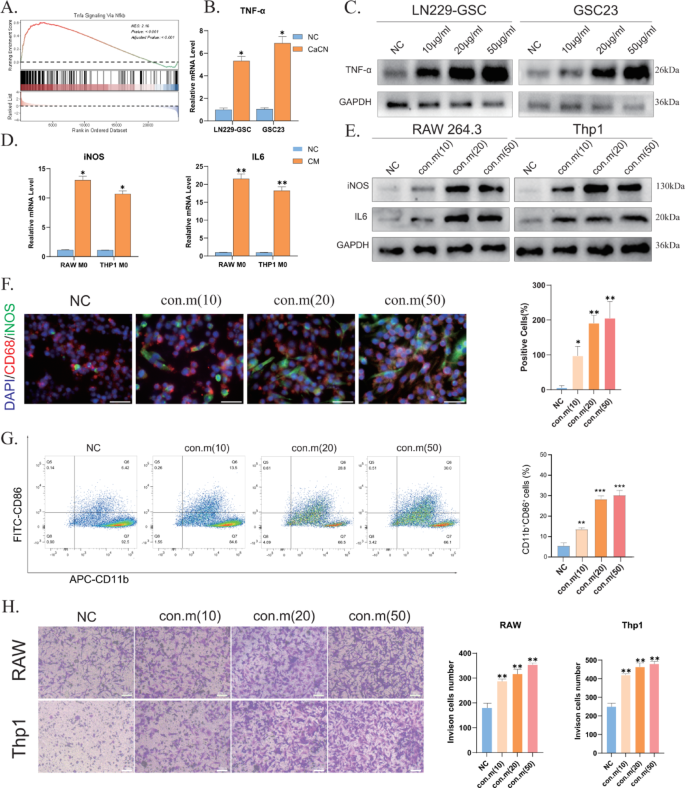
In response to a earlier research, inflammatory elements activate the Nfkb signaling pathway, stimulating tumor cells to synthesize TNF-α [22]. Pathway enrichment evaluation revealed enrichment of immune-related pathways, together with the TNF pathway (Fig. 5B). Performing ssGSEA on the differential genes recognized through sequencing demonstrated enrichment of the TNF-α signaling pathway (Fig. 7A). On the similar time, PCR and WB outcomes indicated that CaCN drives TNF-α manufacturing in glioma cells (Fig. 7B, C), and the flexibility of glioma cells to synthesize TNF-α elevated with rising concentrations of CaCN. This impact could also be ascribed to the discharge of related inflammatory elements after lysosomal phagocytosis of CaCN.
TNF-α has been evinced to stimulate the polarization of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) from the M0 phenotype to the M1 phenotype [23], thereby reversing tumor immunosuppression. Consequently, an rising variety of researchers are specializing in methods to advertise TAM polarization towards the M1 phenotype [24]. To find out the impact of CaCN on the immune microenvironment, the conditioned medium from GL261 and LN229 cells handled with CaCN was cultured with RAW264.7 and Thp1 cells (PMA-treated polarized to M0 macrophages). PCR and WB outcomes revealed elevated expression ranges of iNOS and IL-6 indicators in macrophages cultured within the conditioned media (Fig. 7D, E), suggesting macrophage polarization from the M0 to the M1 phenotype. To keep away from the potential affect of CaCN itself on macrophages, we instantly handled RAW and THP-1 cells with CaCN. PCR outcomes confirmed that CaCN didn’t trigger a big improve in IL-6 and iNOS expression in macrophages, indicating that the direct impact of CaCN on stimulating macrophage polarization is restricted (Supplementary Fig. 6 A). Moreover, the immunofluorescence (IF) assay advised that because the focus of CaCN elevated, there was a extra pronounced diploma of polarization of macrophages cultured within the conditioned medium on the corresponding focus (Fig. 7F), in step with the outcomes of WB evaluation. THP-1 macrophages induced to an M0 state with PMA had been individually co-cultured with CaCN-treated glioma cell strains untreated with nanoscale enzymes for 36 h. Subsequent move cytometry evaluation revealed that macrophages demonstrated vital polarization in the direction of an M1 phenotype following CaCN remedy (Fig. 7G). Following this, sequencing knowledge and the cibersort algorithm had been employed to investigate the immune infiltration of CaCN-treated glioma cells, which confirmed that CaCN-treated cells activated varied immune cells, with elevated ranges of M1 macrophages in comparison with controls (Supplementary Fig. 5), corroborating our earlier findings.
As well as, chemokine-related pathways had been additionally enriched (Fig. 6B). This implies that within the presence of CaCN, glioma cells generate chemokines that probably improve macrophage chemotaxis and infiltration. Consequently, the Transwell co-culture system was used to evaluate macrophage chemotaxis and infiltration following M1 polarization. To simulate TEM, macrophages had been cultured within the higher chamber, and a conditioned medium from glioma cells handled with completely different concentrations of CaCN was positioned within the decrease chamber. The Transwell co-culture system was employed to evaluate macrophage chemotaxis and infiltration following M1 polarization. Briefly, macrophages had been cultured within the higher chamber, whereas a conditioned medium from glioma cells handled with completely different concentrations of CaCN was positioned within the decrease chamber. After 10 h of incubation, a progressive improve within the stage of macrophage infiltration was famous with rising concentrations of conditioned medium (Fig. 7H).
These outcomes conjointly counsel that CaCN successfully induced TAM polarization towards the M1 phenotype, enhanced TAM infiltration, and exerted a multifaceted inhibitory killing impact on glioma cells.
CaCN can transform the tumor immune microenvironment. A) Tnfa Signaling By way of Nfkb Signaling Pathway Enriched by ssGSEA. B) Relative mRNA ranges of TNF-αin CaCN-treated LN229 cells and GSC23 cells as decided by qt-PCR.(n = 3, imply ± SD, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). C) Western blot outcomes of TNF-α and GAPDH in LN229 and GSC23 cells handled with completely different concentrations of CaCN. D) Relative mRNA ranges of iNOS and IL6 in situation media-treated RAW264.7 cells and Thp1 cells as decided by qt-PCR.(n = 3, imply ± SD, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). E) Western blot outcomes of iNOS and IL6 in RAW264.7 cells and Thp1 cells handled with completely different conditioned media. F) Detection of iNOS expression in RAW264.7 cells utilizing immunofluorescence staining after 6 h of tradition in conditioned medium of GL-261 cells handled with completely different concentrations of CaCN. (saclebars,100 μm)Proportion of iNOS-expressing optimistic cells in RAW264.7 cells handled with completely different conditioned media counted utilizing picture J counting.(n = 3, imply ± SD, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). G) Movement cytometry was carried out to look at the proportion of M0-type THP1 cells polarised to M1-type macrophages after remedy with completely different concentrations of conditioned medium. H) The infiltration of RAW264.7 cells and Thp1 cells which were induced to M1 morphology within the transwell system had been handled with completely different concentrations of conditioned medium, respectively. The variety of invaded cells after transwell of RAW264.7 and Thp1 cells handled with completely different concentrations of conditioned medium was obtained utilizing picture J counting.(n = 3, imply ± SD, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001).
TF-CaCN successfully enhanced the permeability of the blood-brain barrier
Though single-atom nanozymes can penetrate the blood-brain barrier to some extent, their penetration effectivity is comparatively low. Subsequently, we launched transferrin (TF) to boost the concentrating on and penetration effectivity of CaCN throughout the blood-brain barrier, thereby bettering its potential for scientific utility.
First, characterization evaluation confirmed the typical hydrodynamic diameter of TF-CaCN (Supplementary Fig. 6B), confirming the profitable modification with TF and indicating that the dimensions distribution was throughout the anticipated vary. Within the TEM photographs (Fig. 4E), TF-CaCN displayed lipid-like coating surrounding the dense CaCN core, indicative of PEG encapsulation. These vesicular options had been noticed earlier than full lysosomal digestion, in line with partial lipid protection. Then we verified in vitro whether or not the addition of the TF ligand in TF-CaCN would alter the unique catalytic effectivity. CCK8 outcomes confirmed that the IC50 values of TF-CaCN and CaCN had been very comparable (Supplementary Fig. 6 C). Then again, WB outcomes indicated that TF-CaCN, like CaCN, can modulate the exercise of calcium ion channel proteins (Supplementary Fig. 6D). The outcomes point out that the TF ligand doesn’t alter the inherent properties of CaCN.
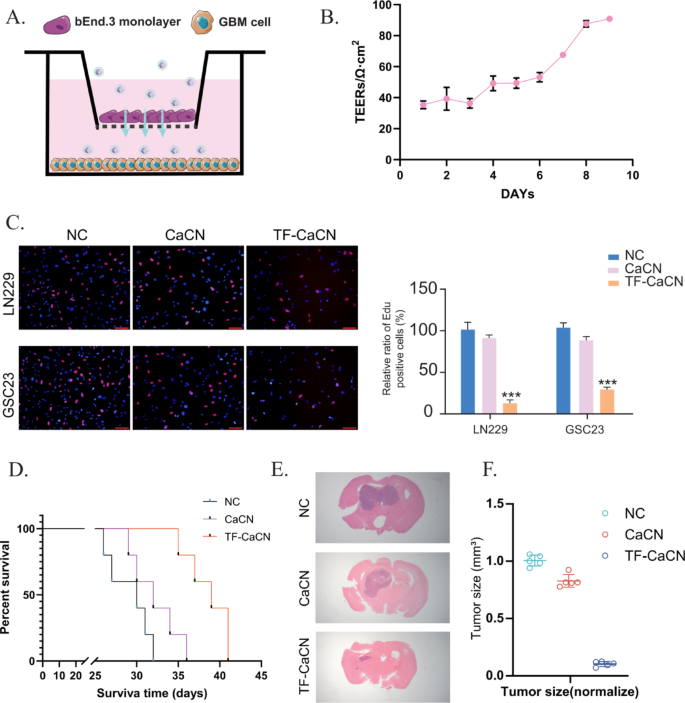
To guage BBB penetration in vitro, we established a Transwell BBB mannequin utilizing bEnd.3 endothelial cells (Fig. 8A). Briefly, 1 × 10^6 bEnd.3 cells had been seeded onto 2% gelatin–precoated inserts and cultured with medium modifications each 3–4 days till barrier formation, as indicated by transendothelial electrical resistance (TEER). When TEER reached roughly 100 Ω·cm², the BBB was thought of efficiently established (Fig. 8B). GBM cells had been cultured within the decrease chamber, whereas CaCN or TF-CaCN was added to the higher (endothelial) aspect of the insert to imitate luminal publicity.
The EdU assay revealed clear variations in nanoparticle penetration. In contrast with CaCN, TF-CaCN remedy resulted in markedly lowered EdU incorporation in GBM cells within the decrease chamber (Fig. 8C). This means that TF-CaCN crossed the endothelial monolayer extra effectively, delivering increased quantities of lively nanozymes to the glioma cells beneath the barrier. Thus, the in vitro outcomes present direct proof that transferrin modification drastically enhances BBB permeability and subsequent antitumor results.
We additional validated these findings in vivo utilizing an intracranial orthotopic glioblastoma mannequin. After tumor implantation, mice had been handled by tail vein injection with both CaCN or TF-CaCN. Survival evaluation demonstrated that mice receiving TF-CaCN survived considerably longer in contrast with these handled with CaCN (Fig. 8D). As well as, H&E staining of mind sections revealed smaller tumor volumes and lowered tumor cell density within the TF-CaCN group (Fig. 8E–F). These in vivo outcomes verify that transferrin conjugation improves the systemic supply of CaCN throughout the BBB and enhances accumulation at tumor websites.
Taken collectively, each the in vitro BBB mannequin and the in vivo glioma mannequin persistently display that transferrin modification considerably improves the BBB penetration capability of CaCN. This gives robust help for the usage of TF-CaCN as a clinically translatable nanosystem able to attaining efficient and focused supply to glioblastoma tissue.
TF-CaCN successfully enhanced the permeability of the blood-brain barrier. A) Schematic diagram of the in vitro BBB mannequin. B) After establishing the in vitro BBB mannequin, TEER values had been measured day by day. C) EDU assay outcomes indicated that TF-CaCN successfully penetrated the BBB mannequin and inhibited GBM cell proliferation, whereas CaCN exhibited considerably decrease penetration effectivity. D) Survival curves of every group of mice following remedy with CaCN and TF-CaCN, respectively. E) H&E staining of intracranial tumors from every group of mice after remedy with CaCN and TF-CaCN, respectively. F) Tumor quantity statistics of intracranial gliomas in every group of mice after remedy with CaCN and TF-CaCN, respectively
CaCN enhances the efficacy of temozolomide and inhibits tumor proliferation in vivo
Temozolomide (TMZ) is a generally used chemotherapeutic agent for the remedy of glioma and is taken into account the simplest therapeutic agent for glioma owing to its oral administration, capability to penetrate the blood-brain barrier, stability in acidic environments, and low toxicity profile [25]. Regardless of its mixture with different medication considerably bettering the survival outcomes of sufferers after surgical intervention, the efficacy of TMZ stays sub-optimal in scientific observe [26]. Of word, glioma resistance to TMZ is the first reason behind chemotherapy failure [27]. Contemplating that a number of research have highlighted the essential function of ferroptosis in conferring drug resistance [28], we posit that the mix of CaCN and TMZ could improve the killing of tumor cells.
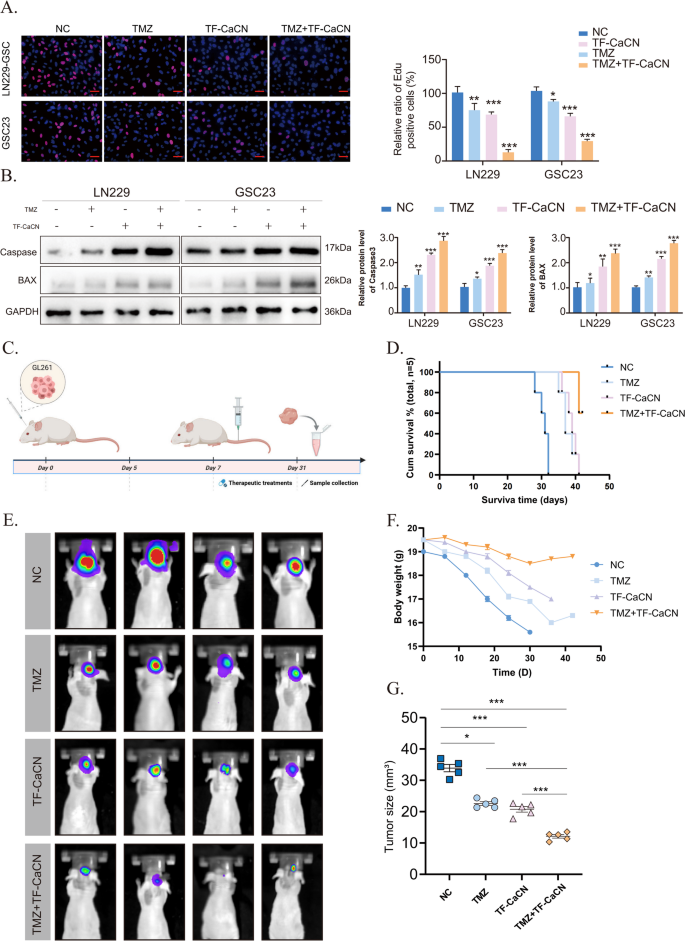
The EDU outcomes confirmed that the mix remedy of TMZ and TF-CaCN inhibited GBM cell proliferation extra successfully than both remedy alone (Fig. 9A). Certainly, WB outcomes confirmed that the apoptotic impact was considerably enhanced by the co-administration of TMZ and CaCN (Fig. 9B), suggesting that CaCN could synergistically improve the efficacy of TMZ.
Subsequently, we performed in vivo drug remedy experiments (Fig. 9C). Beginning on day 7 post-tumor implantation, when intracranial tumor development was established, mice acquired PBS, TMZ, TF-CaCN, or TMZ + TF-CaCN intravenously each different day at a dose of 1 mg/kg for two weeks. Mice in numerous teams acquired intravenous injections of TMZ, TF-CaCN, or a mix of each. Survival evaluation and physique weight measurements indicated that the mix remedy considerably improved the prognosis of glioblastoma-bearing mice in comparison with monotherapies (Fig. 9D, F). In vivo fluorescence imaging additional demonstrated that the mixed remedy successfully suppressed tumor development (Fig. 9E, G). These findings strongly help that TF-CaCN enhances the therapeutic efficacy of TMZ. Importantly, IHC outcomes demonstrated that CaCN activated peritumoral CD4 and CD8 indicators, indicating that the immune system was activated and altered the immune microenvironment in vivo (Supplementary Fig. 7). As well as, Hematoxylin Eosin (H&E) staining of main organs (coronary heart, liver, spleen, lungs, and kidneys) harvested from handled mice confirmed no vital histopathological injury within the TF-CaCN-treated group (Supplementary Fig. 8). General, these outcomes indicated that CaCN nanozymes possessed passable tumor development inhibitory exercise in vivo.
TF-CaCN enhances the efficacy of temozolomide and inhibits tumor development in vivo. (A) The EDU outcomes demonstrated that the mix of TMZ and TF-CaCN successfully inhibited the proliferation of GBM cells in in vitro experiments. (B) Western blot outcomes of caspase3, BAX, and GAPDH in IC50 concentrations of TF-CaCN, TMZ, and TMZ + TF-CaCN-treated LN229 and GSC23 cells. (C) Flowchart of drug administration after in situ modelling of intracranial gliomas in mice. (D) Survival of mannequin mice after remedy with TMZ, TF-CaCN and drug mixture, respectively. (E) Animal in vivo fluorescence imaging outcomes displaying intracranial tumour volumes in mannequin mice of various remedy teams. (F) Physique weight modifications in mannequin mice after remedy with TMZ, TF-CaCN and drug mixture, respectively. (G) Comparability of tumour dimension in numerous remedy teams