- Mars in all probability had liquid water on its floor billions of years in the past. However Mars’ water disappeared over time, leaving the planet chilly and dry. The place did Mars’ water go?
- Might water now lie under Mars’ floor? New analysis from from Scripps Establishment of Oceanography – primarily based on information from NASA’s InSight lander – suggests this chance.
- Mars’ underground water is perhaps sufficient to type a worldwide ocean, these scientists say, if it had been on the floor.
Oceans of water on Mars, underground?
There’s ample proof in the present day for liquid water on Mars a couple of billion years in the past. However in the present day’s Mars is a frozen desert. The place did its water go? A brand new examine, led by Vashan Wright, a geophysicist at UC San Diego’s Scripps Establishment of Oceanography, offers potential proof of water – plenty of it – deep under the floor within the crust. The findings are primarily based on information from NASA’s now-defunct InSight mission. The researchers mentioned on August 12, 2024, that Mars’ mid-crust could also be saturated with water, sufficient to type a worldwide ocean if that water had been on the floor.
The researchers revealed their peer-reviewed examine within the Proceedings of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences on August 12, 2024.
Wright posted the information on X on August 12:
? Liquid Floor Water Discovered on Mars ?
by: Myself, Michael Manga, and Mattias Morzfeldhttps://t.co/FIVXp1IZ0T
— Island Prof ??? (@DrVasshe) August 12, 2024
Water on Mars might lay in historical aquifers
Mars had rivers, lakes and probably even oceans. However, billions of years in the past, the planet misplaced all its floor water. Mars’ floor turned dry, chilly and inhospitable. Scientists have give you hypotheses about the place all of the water went. There’s proof that a few of it escaped into house. However a lot of it may also have merely seeped underground. The brand new findings – if confirmed – would appear to validate that chance. Because the paper acknowledged:
Giant volumes of liquid water transiently existed on the floor of Mars greater than three billion years in the past. A lot of this water is hypothesized to have been sequestered within the subsurface or misplaced to house.
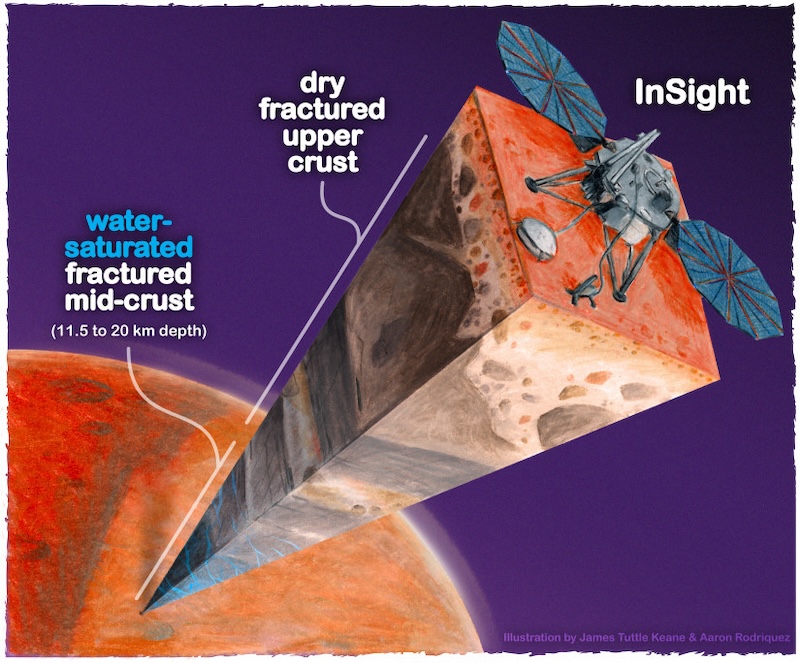
The brand new examine says that the majority of Mars’ water remains to be underground in the present day, and is liquid, not simply ice. We already know of in depth ice deposits each on the floor on the poles and under the floor as properly. This examine, nonetheless, focuses on the mid-crust, deeper down than the place the ice deposits are. The depth is between 7 to 13 miles (11 to twenty km). The information got here from NASA’s InSight lander, which studied the Martian inside: the crust, mantle and core. These information, together with information from Mars rovers, assist scientists perceive how Mars advanced, how a lot water it as soon as had and the way a lot water should still exist. Wright mentioned:
Understanding the Martian water cycle is vital for understanding the evolution of the local weather, floor and inside. A helpful place to begin is to determine the place water is and the way a lot is there.
The examine estimated there’s sufficient water to fill a planet-wide ocean about 1 mile (1.6 km) deep.
Utilizing @NASAInSight information, a brand new evaluation led by Scripps Oceanography geophysicist Vashan Wright (@DrVasshe) offers the most effective proof to this point that Mars comprises liquid water deep in its crust. Be taught extra concerning the examine revealed in @PNASNews. ?? https://t.co/8O6rntesZ8 pic.twitter.com/SQQJaqhTvY
— Scripps Establishment of Oceanography (@Scripps_Ocean) August 12, 2024

Liquid water most certainly clarification
InSight ended its mission in December 2022, after an excessive amount of mud lastly disadvantaged the solar-powered lander of sufficient energy. However in the course of the 4 years it operated, it collected monumental quantities of knowledge concerning the within Mars. This included detecting 1000’s of marsquakes, the equal of earthquakes on our planet. By measuring the speeds at which the seismic waves transfer under the floor, scientists can decide what sorts of rocks, ice or different materials are current. The analysis crew used a mannequin knowledgeable by a mathematical principle of rock physics. The outcome? the researchers decided that the presence of liquid water within the crust most certainly defined the information from InSight. The paper mentioned:
A mid-crust composed of fractured igneous rocks saturated with liquid water greatest explains the prevailing information. Our outcomes have implications for understanding Mars’ water cycle, figuring out the fates of previous floor water, trying to find previous or extant life, and assessing in situ useful resource utilization for future missions. Whereas accessible information are greatest defined by a water-saturated mid-crust, our outcomes spotlight the worth of geophysical measurements and higher constraints on the mineralogy and composition of Mars’ crust.
Hotter temperatures deep within the crust
Whereas ice deposits are widespread within the near-surface of Mars, the potential liquid water is deeper down, within the mid-crust, the place temperatures are hotter. The paper acknowledged:
Liquid water within the pores of the mid-crust additionally requires excessive sufficient permeability and heat sufficient temperatures within the shallow crust to allow alternate between the floor and better depths.
The researchers even postulate that there must be extra water within the mid-crust zone than the quantities proposed to have stuffed the hypothesized historical Martian oceans. That’s quite a lot of water!
A window to previous Mars and doable house for all times
If there actually is an ocean’s value of water inside Mars, then that gives fascinating clues concerning the planet’s previous. Co-author Michael Manga of UC Berkeley mentioned:
Establishing that there’s a huge reservoir of liquid water offers some window into what the local weather was like or might be like. And water is important for all times as we all know it. I don’t see why [the underground reservoir] is just not a liveable surroundings. It’s definitely true on Earth; deep, deep mines host life, the underside of the ocean hosts life. We haven’t discovered any proof for all times on Mars, however no less than we’ve recognized a spot that ought to, in precept, be capable of maintain life.

Backside line: The place did Mars’ water go? A brand new examine utilizing information from NASA’s InSight mission offers proof for oceans of water on Mars, deep under the floor within the crust.
Supply: Liquid water within the Martian mid-crust
Through Scripps Establishment of Oceanography
Learn extra: To search out water on Mars, take heed to marsquakes
Learn extra: InSight Lander reveals 1st marsquakes on Mars

