Scientists at ETH Zurich and the Swiss Federal Institute of Expertise Lausanne have developed a tool that directs sound waves in a single route with out losing vitality. This breakthrough sound wave director consists of a disk-shaped cavity with three equidistant ports for sending or receiving sound.
When activated, sound from one port is simply heard at a particular second port, not the third. That is achieved by introducing swirling air into the cavity at a exact velocity and depth, making a synchronized, repeating sample of sound waves.
The researchers consider that the sound wave director may assist them higher perceive and design future communications applied sciences. The method used to direct the sound waves not solely guides the waves in a single route however the researchers say it additionally amplifies them.
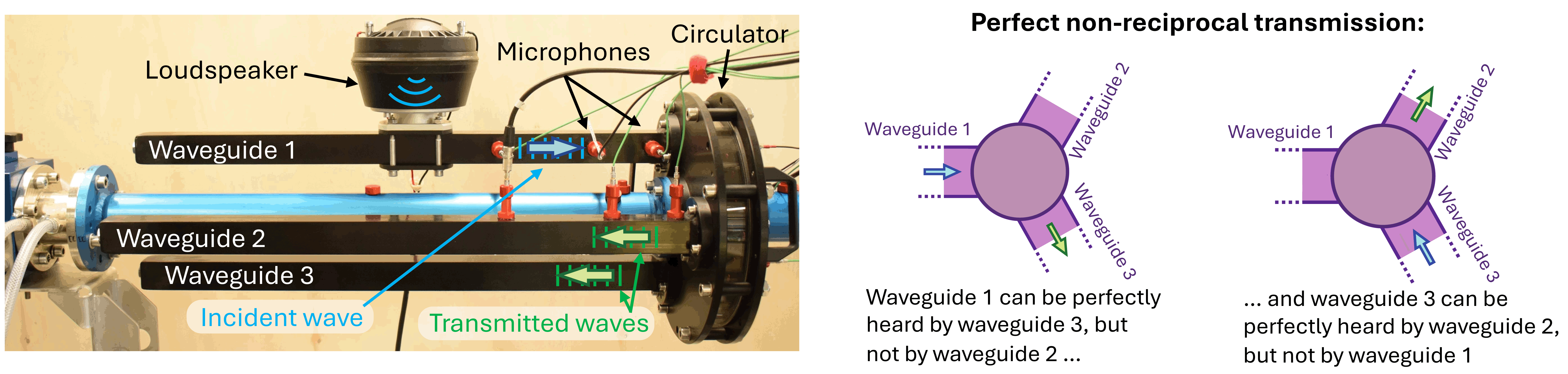
The researchers made this new discovery by enhancing upon a 2014 design from the College of Texas at Austin. That individual system suffered immensely from sound dissipation. Nonetheless, the brand new system makes use of self-sustaining oscillations to keep up and even improve the sound waves’ vitality so that they don’t die out earlier than reaching their vacation spot.
The know-how driving the sound wave director may have a number of functions in new varieties of noise suppression, communications, and even radar programs. The researchers consider it may even result in the event of latest metamaterials that enable us to govern electromagnetic waves.
The researchers consider this idea of “loss-compensated non-reciprocal wave propagation” may be utilized to different programs past acoustics, too, like gentle. The group has printed their findings on the brand new discovery within the journal Nature Communications.
In that paper, they focus on how they improved upon the unique design to create a sound wave director that doesn’t trigger the waves to lose vitality as they journey. In addition they hope that this new design will assist others research sound wave propagation and manipulation—like utilizing sound waves to make particles levitate.

