We’re lucky sufficient to be dwelling within the best period of discovery within the historical past of our species. Astronomical observations via ever extra delicate devices are deepening our view of the cosmos, and simply as satisfyingly, forcing questions on its previous and unsure future. I’d a lot quite reside in a universe with puzzling indicators of accelerated growth (nonetheless topic to sturdy debate) and proof of matter that doesn’t work together with the electromagnetic drive (darkish matter) than in a single I might fully clarify.
Thus the sheer enjoyment of thriller, a delight accented this morning as I ponder the detection of a so-called ‘darkish object’ of unusually low mass. Introduced in each Nature Astronomy and Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, the papers describe an object that might solely be detected via gravitational lensing, a well-recognized exoplanet detection software that reshapes mild passing close to it. With correct evaluation, the character of the distortion can produce a stable estimate of the quantity of matter concerned.
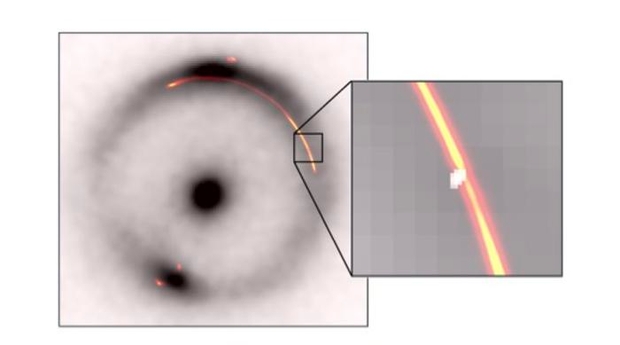
Picture: The black ring and central dot present an infrared picture of a distant galaxy distorted by a gravitation lens. Orange/crimson reveals radio waves from the identical object. The inset reveals a pinch attributable to one other, a lot smaller, darkish gravitational lens (white blob). Credit score: Devon Powell, Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics.
We wouldn’t have any notion of darkish matter had been it not for the truth that whereas we can’t see it by way of photons, it does work together with gravity, and was certainly first hypothesized due to the anomalous rotation of distant galaxies. Fritz Zwicky was making conjectures concerning the Coma Cluster of galaxies manner again within the Thirties, whereas Jan Oort contemplated mass and noticed movement of the Milky Manner’s stars in the identical interval. It will be Vera Rubin within the Seventies who reawakened the research of darkish matter, together with her observations of stellar rotation round galactic facilities, which proved to be too quick to be defined with out extra mass, that means mass that we at present couldn’t see.
The current work entails the Inexperienced Financial institution Telescope in West Virginia, the Very Lengthy Baseline Array in Hawaii and the European Very Lengthy Baseline Interferometric Community, which creates a digital telescope the scale of Earth. Heavy-hitter instrumentation for certain, and all of it needed to identify the infinitesimal alerts of the gravitational lensing created by this object.
Devon Powell (Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics, Germany is lead writer of the paper in Nature Astronomy:
“Given the sensitivity of our knowledge, we had been anticipating to seek out a minimum of one darkish object, so our discovery is in line with the so-called ‘chilly darkish matter principle’ on which a lot of our understanding of how galaxies kind is predicated. Having discovered one, the query now could be whether or not we will discover extra and whether or not the numbers will nonetheless agree with the fashions.”
An fascinating query certainly. It raises the query of whether or not darkish matter can exist in areas with none stars, and gives a minimum of a tentative reply. Or will we subsequently study that this object is one thing a bit extra prosaic, a compact and inactive dwarf galaxy from the very early universe? The authors level out that that is the bottom mass object ever discovered via gravitational lensing, which factors to the probability that future searches will uncover different examples. We’re clearly firstly of the research of darkish matter and stay blind to its make-up, so we will count on this work to proceed. New lens-modeling methods and datasets taken at excessive angular decision present the instruments wanted to make photos extra detailed than any earlier than taken of the high-redshift universe and gravitationally lensed objects.
From the Powell et al. paper:
Robust gravitational lensing gives a robust various pathway for learning low-mass objects with little to no EM luminosity. A spatially prolonged supply in a galaxy-scale robust lens system acts as a backlight for the gravitational panorama of its lens galaxy, revealing low-mass perturbers via their gravitational results alone. Moreover, lens galaxies usually lie within the redshift vary 0.2 ≲ z ≲ 1.5, which signifies that low-mass, low-luminosity objects will be detected and studied throughout cosmic time. To this point, observations of galaxy-scale lenses with resolved arcs have been used to detect three low-mass perturbers: found by Hubble, Keck and ALMA…[E]xpanding the mass vary that we will robustly probe necessitates that we use robust lens observations on the highest doable angular decision.
The primary paper is Powell et al., “One million-solar-mass object detected at a cosmological distance utilizing gravitational imaging,” Nature Astronomy 4 March 2025. Full textual content. The second paper is McKean et al., “An prolonged and intensely skinny gravitational arc from a lensed compact symmetric object at redshift of two.059.” Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society Vol. 544, Concern 1 (November, 2025), L24-30. Full textual content.


