As knowledge facilities develop to run bigger synthetic intelligence (AI) fashions to feed a breakneck adoption charge, the electrical energy wanted to energy huge numbers of GPU-filled servers is skyrocketing.
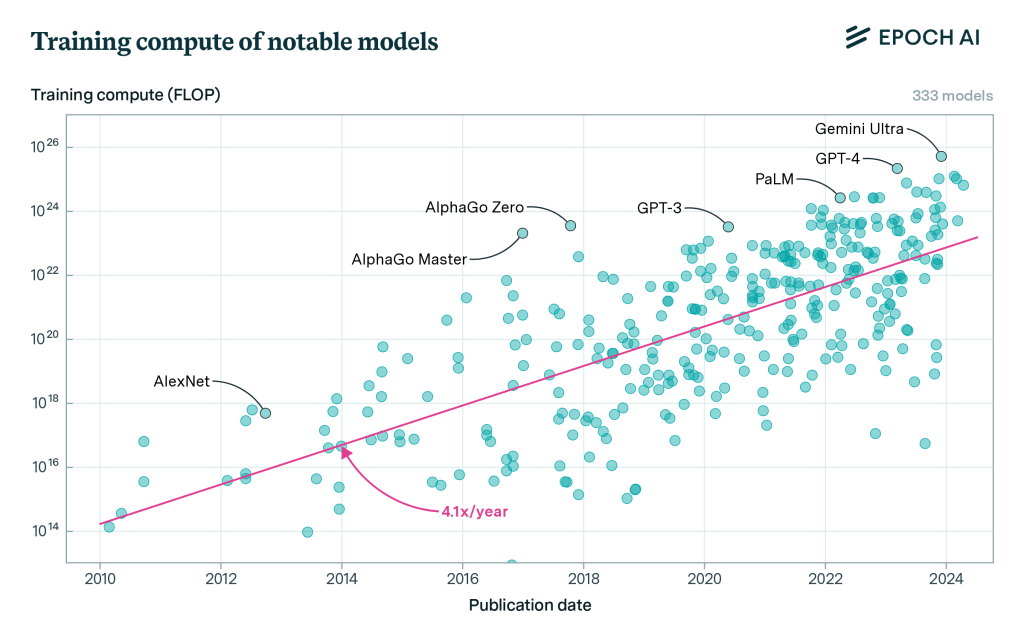
The compute capability wanted to energy AI massive language fashions (LLMs) has grown 4 to 5 instances per 12 months since 2010, and that features the largest fashions launched by OpenAI, Meta, and Google DeepMind, in line with a research by Epoch AI, a analysis institute investigating key AI traits.
Epoch AI
AI service suppliers reminiscent of Amazon Net Providers, Microsoft, and Google have been on the hunt for energy suppliers to satisfy the rising electrical energy calls for of their knowledge facilities, and that has landed them squarely in entrance of nuclear energy vegetation. The White Home just lately introduced plans to assist the event of recent nuclear energy vegetation as a part of its initiative to extend carbon-free electrical energy or inexperienced energy sources.
AI as vitality devourer
The computational energy required for sustaining AI’s rise is doubling roughly each 100 days, in line with the World Financial Discussion board (WEF). At that charge, the group stated, it’s pressing for the development of AI to be balanced “with the imperatives of sustainability.”
“The environmental footprint of those developments usually stays missed,” the Geneva-based, nongovernmental group suppose tank acknowledged. For instance, to realize a tenfold enchancment in AI mannequin effectivity, the computational energy demand might surge by as much as 10,000 instances. The vitality required to run AI duties is already accelerating with an annual progress charge between 26% and 36%.
“This implies by 2028, AI may very well be utilizing extra energy than your complete nation of Iceland utilized in 2021,” the WEF stated.
Put merely, “AI isn’t very inexperienced,” stated Jack Gold, principal analyst with tech {industry} analysis agency J. Gold Associates.
Giant language fashions (LLMs), the algorithmic basis for AI, prepare themselves on huge quantities of knowledge scoured from the web and different sources. It’s the course of of coaching AI fashions (i.e., LLMs) and never the act of chatbots and different AI instruments providing customers solutions based mostly on that knowledge — referred to as “inference” — that requires the overwhelming majority of compute and electrical energy.
And, whereas LLMs received’t be coaching themselves 100% of the time, the information facilities during which they’re situated require that peak energy all the time be accessible. “In case you activate each gentle in your own home, you don’t need them to dim. That’s the actual difficulty right here,” Gold stated.
“The underside line is these items are taking a ton of energy. Each time you plug in an Nvidia H100 module or anybody’s GPU for that matter, it’s a kilowatt of energy getting used. Take into consideration 10,000 of these or 100,000 of these, like Elon Musk needs to deploy,” Gold stated.
The hunt for energy heats up
Versus including new inexperienced vitality to satisfy AI’s energy calls for, tech corporations are searching for energy from current electrical energy assets. That would elevate costs for different clients and maintain again emission-cutting objectives, in accordance The Wall Road Journal and different sources.
In line with sources cited by the WSJ, the homeowners of about one-third of US nuclear energy vegetation are in talks with tech corporations to offer electrical energy to new knowledge facilities wanted to satisfy the calls for of an artificial-intelligence increase.
For instance, Amazon Net Providers is anticipated to shut on a cope with Constellation Vitality to straight provide the cloud big with electrical energy from nuclear energy vegetation. An Amazon subsidiary additionally spend $650 million to buy a nuclear-powered knowledge middle from Talen Vitality in Pennsylvania, and it plans construct 15 new knowledge facilities on its campus that may feed off that energy, in line with Pennsylvania-based The Citizen’s Voice.
One obvious drawback with bringing new energy on-line is that nuclear energy vegetation can take a decade or extra to construct, Gold stated.
“The facility corporations are having an actual drawback assembly the calls for now,” Gold stated. “To construct new vegetation, you’ve received to undergo every kind of hoops. That’s why there’s an influence plant scarcity now within the nation. After we get a very scorching day on this nation, you see brownouts.”
The accessible vitality might go to the very best bidder. Satirically, although, the invoice for that energy can be borne by AI customers, not its creators and suppliers. “Yeah, [AWS] is paying a billion {dollars} a 12 months in electrical payments, however their clients are paying them $2 billion a 12 months. That’s how commerce works,” Gold stated.
“Apparently sufficient, Invoice Gates has an funding in a smallish nuclear energy firm that wishes to construct next-generation energy vegetation. They need to construct new vegetation, so it’s like a mini-Westinghouse,” Gold stated. “He could also be onto one thing, as a result of if we preserve constructing all these AI knowledge facilities, we’re going to wish that energy.”
“What we actually have to do is locate inexperienced AI, and that’s going to be powerful,” Gold added.
Amazon stated it has firmly set its sights on renewable vitality for its future and set a purpose to succeed in net-zero carbon emissions by 2040, ten years forward of the Paris Settlement. The corporate, which is the world’s largest purchaser of renewable vitality, hopes to match the entire electrical energy consumed by its operations with 100% renewable vitality by 2025. It’s already reached 90%, in line with a spokesperson.
“We’re additionally exploring new improvements and applied sciences and investing in different sources of unpolluted, carbon-free vitality. Our settlement with Talen Vitality for carbon-free vitality is one venture in that effort,” the Amazon spokesperson stated in an electronic mail response to Computerworld. “We all know that new know-how like generative AI would require a number of compute energy and vitality capability each for us and our clients — so whereas we’ll proceed to spend money on renewable vitality, we’ll additionally discover and spend money on different carbon-free vitality sources to steadiness, together with nuclear.
“There isn’t a one-size-fits-all resolution in the case of transitioning to carbon-free vitality, and we consider that each one viable and scalable choices needs to be thought of,” the spokesperson stated.
AI as infrastructure planner
The US Division of Vitality (DOE) is researching potential issues which will consequence from rising knowledge middle vitality calls for and the way they might pose dangers to the safety and resilience of the electrical grid. The company can be using AI to investigate and assist preserve energy grid stability.
The DOE’s just lately launched AI for Vitality Report acknowledged that “AI itself might result in important load progress that provides burden to the grid.” On the identical time, a DOE spokesperson stated, “AI has the potential to scale back the price to design, license, deploy, function, and preserve vitality infrastructure by a whole bunch of billions of {dollars}.”
AI-powered instruments can considerably scale back the time required to consolidate and arrange the DOE’s disparate info sources and optimize their knowledge construction to be used with AI fashions.
The DOE’s Argonne Lab has initiated a three-year pilot venture with a number of work streams to evaluate utilizing basis fashions and different AI to enhance siting, allowing, and environmental assessment processes, and assist enhance the consistency of opinions throughout companies.
“We’re utilizing AI to assist assist environment friendly technology and grid planning, and we’re utilizing AI to assist perceive allowing bottlenecks for vitality infrastructure,” the spokesperson stated.
The way forward for AI is smaller, not larger
Whilst LLMs run in huge and increasing knowledge facilities run by the likes of Amazon, IBM, Google, and others are requiring extra energy, there’s a shift going down that may probably play a key position in decreasing future energy wants.
Smaller, extra industry- or business-focused algorithmic fashions can usually present higher outcomes tailor-made to enterprise wants.
Organizations plan to speculate 10% to fifteen% extra on AI initiatives over the subsequent 12 months and a half in comparison with calendar 12 months 2022, in line with an IDC survey of greater than 2,000 IT and line-of-business resolution makers. Sixty-six p.c of enterprises worldwide stated they might be investing in genAI over the subsequent 18 months, in line with IDC analysis. Amongst organizations indicating that genAI will see elevated IT spending in 2024, inside infrastructure will account for 46% of the overall spend. The issue: a key piece of {hardware} wanted to construct out that AI infrastructure — the processors — is in brief provide.
LLMs with a whole bunch of billions or even a trillion parameters are devouring compute cycles sooner than the chips they require will be manufactured or upscaled; that may pressure server capability and result in an unrealistically lengthy time to coach fashions for a selected enterprise use.
Nvidia, the main GPU maker, has been supplying the lion’s share of the processors for the AI {industry}. Nvidia rivals reminiscent of Intel and AMD have introduced plans produce new processors to satisfy AI calls for.
“Eventually, scaling of GPU chips will fail to maintain up with will increase in mannequin measurement,” stated Avivah Litan, a vice chairman distinguished analyst with Gartner Analysis. “So, persevering with to make fashions larger and larger isn’t a viable possibility.”
Moreover, the extra amorphous knowledge LLMs ingest, the larger the potential of unhealthy and inaccurate outputs. GenAI instruments are mainly next-word predictors, which means flawed info fed into them can yield flawed outcomes. (LLMs have already made some high-profile errors and might produce “hallucinations” the place the next-word technology engines go off the rails and produce weird responses.)
The answer is probably going that LLMs will shrink down and use proprietary info from organizations that need to make the most of AI’s capacity to automate duties and analyze massive knowledge units to provide helpful insights.
David Crane, undersecretary for infrastructure on the US Division of Vitality’s Workplace of Clear Vitality, stated he’s “very bullish” on rising designs for so-called small modular reactors, in line with Bloomberg.
“Sooner or later, much more AI goes to run on edge gadgets in any case, as a result of they’re all going to be inference based mostly, and so inside two to a few years that’ll be 80% to 85% of the workloads,” Gold stated. “So, that turns into a extra manageable drawback.”
This text was up to date with a response from Amazon.

