There’s a disaster in technical training. The golden highway to a profession has all the time been via a school training. Nevertheless, this “golden highway” has developed deep cracks and is badly in want of upkeep. Postsecondary training is quickly changing into unaffordable, even at public faculties and universities. Tuition has risen at a charge 50% higher than inflation. However there’s a deeper subject. Past the out-of-control price, there’s proof that levels don’t map to the talents wanted in immediately’s job market, and there’s an growing disconnect—notably in laptop science—between the talents employers need and the talents faculties educate.
Employers are battling a associated downside: preserving the people who find themselves already on their workers up-to-date with the talents they want. It’s frequent for consultants who spend their waking hours working on the reducing fringe of the expertise trade to really feel like they’re falling behind. The development has solely elevated within the period of generative AI. A graduate diploma is an choice for workers who can afford it, however it doesn’t assist employers. After spending a yr getting a grasp’s diploma, an worker is unlikely to return to the identical employer, not to mention the identical job.
Why, and extra essential how, are faculties and universities failing? And what can firms that want to rent junior workers and upskill their present workers do about it?
The Downside with Faculty: Agility and Fragility in Disruptive Occasions
Schools and universities are hardly ever agile. They don’t reply to modifications shortly, and that leaves them notably weak when offering coaching for industries the place change is fast. The normal CS main could also be the place faculties and universities are at their weakest. The tempo of change may be very fast, notably when in comparison with the profession of tenured school, and the resistance to vary may be particularly sturdy when change is fast. CS departments have tailored properly to AI, partly as a result of AI originated in academia. However many roles require abilities that incessantly aren’t taught in conventional CS departments, resembling cloud improvement, Kubernetes, and microservices.
Why aren’t these establishments capable of adapt to modifications in expertise? Professors spend a lot of their time doing analysis—properly, in actuality, they spend most of their time serving on committees. There’s little time left over to seek out out what trade is doing, not to mention develop programs to show it. Staying present within the tech trade is a bit like being an expert athlete: It’s important to prepare each day to take care of your bodily conditioning. Totally new paradigms rise shortly: cloud computing, information engineering, machine studying engineering, cellular improvement, and huge language fashions. To additional complicate issues, subjects like cloud computing, software program operations, and even AI don’t match properly inside a college IT division. They require going exterior to business cloud distributors, which requires expense accounts and funds commitments that aren’t lined by analysis grants. No college has the computing assets similar to Google, and even to a well-funded startup. Nor have they got expertise constructing and working extremely distributed techniques.
Subjects like microservices and cloud native computing current an extra downside: wage commitments. Can an administrator justify the wage of a senior school member who makes a speciality of a subject that could be forgotten 5 or ten years sooner or later, even when that’s what trade desires proper now? Can the administration decide to paying a tenured school wage for 30 or so years if that professor’s specialty could also be irrelevant lengthy earlier than they retire? It’s much less dangerous to rent adjunct professors with trade expertise to fill educating roles which have a vocational focus: cellular improvement, information engineering, and cloud computing.
Utilizing adjuncts to show the talents that trade desires creates its personal downside: an underclass throughout the college educating workers. It’s no surprise that I’ve heard professors say “Cloud computing is a fad and never value educating.” It’s no surprise that many school members see these subjects as “vocational training” whereas they’re making an attempt to show long-term verities: these “vocational” subjects fulfill the wants of trade slightly than the analysis group and are taught by school with short-term contracts who come and go annually. It’s comprehensible that professors are reluctant to show a topic that’s primarily based virtually solely on proprietary expertise that may change with minimal discover. Nevertheless, if that’s the sort of experience firms need, college students who want that coaching will discover it elsewhere—and if universities can’t present the coaching college students want, they are going to lurch towards irrelevance.
In a latest Wall Road Journal article, “Why Individuals Have Misplaced Religion within the Worth of Faculty,” Douglas Belkin highlights one other subject: essential pondering. As Belkin explains,
The misalignment between universities and the labor market is compounded by the failure of many faculties to show college students to assume critically. Professors compete for tenure on the idea of the standard of their analysis and publishing monitor file. Educating is usually an afterthought. Professors who earn tenure negotiate lighter educating hundreds. To fill the hole, colleges rent cheaper adjuncts with little job safety. These precariously employed adjuncts rely upon sturdy scholar efficiency critiques for job safety, a system that incentivizes them to make few calls for in change for top rankings.
Any metric may be gamed (usually referred to as Goodhart’s regulation)—and grades aren’t any exception, gamed each by school who want good rankings from college students and by college students who need good grades from school. Grades are a part of the essential pondering downside, as is a dismissal of writing, studying, and non-STEM abilities. It’s not as if essential pondering isn’t taught in universities. The humanities are nothing with out essential pondering, whether or not or not they’re taught by overwhelmed and underpaid adjuncts—however humanities departments are those most threatened by funds cuts and, at some colleges, outright elimination.
Vocational abilities are a necessity, whether or not or not CS departments wish to educate them. Evaluation is a necessity, and it’s one thing companies take very significantly, at the least for in-house coaching applications. However making vocational abilities and evaluation priorities dangers letting grades turn out to be a motivating issue, and that’s counterproductive. Is something extra conformist than aspiring to do what your instructor says to get an A? Or to construct your educational profession round getting a job at a prestigious, high-profile firm? College students have to learn to make errors. They should learn to push their concepts so far as they’ll after which slightly farther. In my courses I encourage college students to fail early and infrequently. A failure is a desired end result: It means they tried one thing arduous and distinctive or that they realized a giant lesson.
Educating college students to think about issues from many views, together with these which might be uncomfortable, is a necessity. Too many college students graduate pondering that science is a set of info slightly than understanding that it’s a means of skeptical inquiry pushed by experiment. Too many college students assume that engineering is about getting the reply at the back of the ebook, not about making the trade-offs which might be crucial in the actual world. And too many firms fail as a result of they’ll’t query their very own assumptions. That is all essential pondering—and something much less shortchanges each college students and the businesses that ultimately rent them.
Corporations want well-trained expertise
So—faculties and universities are failing trade. They aren’t offering graduates who’re skilled within the abilities firms want; they aren’t nurturing essential thinkers; and they’re pricing themselves out of the vary of all however the ultrawealthy. What can firms do to amass and retain the expertise they want?
Understanding trade wants isn’t a static challenge. In 2020, the World Financial Discussion board estimated that automation will displace 85 million jobs by 2025 however will even create 97 million new jobs. One other publication estimated that there have been 13 million unfilled expertise jobs. Within the twenty first century, churn is ever current. No matter your job is now, it will likely be completely different in 5 to 10 years: Your abilities might be out of date, and also you’ll have to study new ones. That’s an issue for each new graduates and skilled workers, to say nothing of the businesses that make use of them. And as we’ve seen, it’s an excellent larger downside for faculties and universities.
To begin, we’ll take a look at what firms really want, utilizing information from O’Reilly’s studying platform. There are two elements: course enrollments, which present what college students are finding out, and course completion, which can reveal abilities in excessive demand.
Course completion
The median course completion share on the O’Reilly platform is analogous for B2B customers and B2C customers, and roughly matches trade requirements. The next completion charge may point out that the course teaches an rising talent that’s required in trade. Examples of those abilities are synthetic intelligence (immediate engineering, GPT, and PyTorch), cloud (Amazon EC2, AWS Lambda, and Microsoft’s Azure AZ-900 certification), Rust, and MLOps. It’s essential to notice that CISSP (the Licensed Data Techniques Safety Skilled) certification is on the checklist; though safety abilities are hardly a brand new requirement, company attitudes towards safety have modified drastically prior to now few years. Executives don’t like seeing their firms within the information for a safety breach. Another subjects with excessive completion charges are ggplot (for data-driven graphics in R), GitHub, and Selenium (a software program testing framework). SolidWorks is an outlier; SolidWorks programs have comparatively few customers, however virtually all of the customers full them.
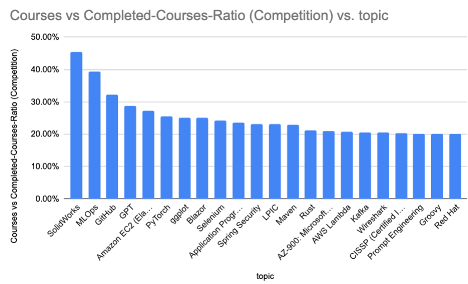
What are folks finding out? The earlier graph contains all customers of the O’Reilly studying platform. What can we see if we take a look at B2B and B2C customers individually? There’s a excessive correlation between completion charges for each kinds of customers on the platform. The Pearson correlation is 0.8, which means B2B and B2C customers transfer collectively 80% of the time, however there are some essential variations:
- B2C customers full technical programs on subjects like Java, net improvement, and safety at a better charge than B2B customers.
- B2B customers full programs in administration and “delicate abilities” at a a lot increased charge than B2C customers. These programs embrace subjects like design pondering, communication, entrepreneurship, and challenge administration, along with programs on Microsoft Phrase and Excel.
Particular person customers (B2C) are studying about applied sciences—maybe to assist in getting a brand new job or to amass abilities they want of their present job, maybe to assist with their private tasks. Customers who’re coming from company accounts (B2B) behave in a different way. They’re studying abilities which might be essential in a enterprise setting: communications, teamwork, challenge administration. Additionally, take note there could also be outliers right here like SolidWorks, which could possibly be a course an employer requires an worker to finish.
Mapping abilities to jobs
Linkedin’s analysis on mapping abilities to jobs led the corporate to develop a abilities genome. Right here’s the way it’s described:
For any entity (occupation or job, nation, sector, and many others.), the talents genome is an ordered checklist (a vector) of the 50 “most attribute abilities” of that entity. These most attribute abilities are recognized utilizing the TF-IDF algorithm to establish probably the most consultant abilities of the goal entity whereas down-ranking ubiquitous abilities that add little details about that particular entity (e.g., Microsoft Phrase).
Primarily, this method exhibits which you could rank abilities by how usually they present up in job postings. Skipping the maths, right here’s an intuitive description of TF-IDF:
Time period Frequency (TF): Measures how incessantly a phrase (or talent, on this case) seems inside a doc or job posting. The next frequency would possibly point out relevance.
Inverse Doc Frequency (IDF): Measures how frequent or uncommon a phrase is throughout a bigger assortment of paperwork (or job postings). Frequent phrases like “the” or “and” obtain a decrease IDF rating, de-emphasizing their significance.
We will accomplish one thing comparable by doing subject modeling on O’Reilly’s information. First, we discover the highest phrases related to every subject. Then we use zero-shot classification to map the subjects to jobs. That course of yields outcomes like these:
Cybersecurity skilled:
– Matched Subject 1: [‘kubernetes’, ‘ckad’, ‘developer’, ‘application’, ‘certified’] | Rating: 0.976
– Matched Subject 2: [‘security’, ‘professional’, ‘certified’, ‘systems’, ‘information’] | Rating: 0.918
Expertise advisor:
– Matched Subject 1: [‘kubernetes’, ‘ckad’, ‘developer’, ‘application’, ‘certified’] | Rating: 0.579
– Matched Subject 2: [‘azure’, ‘microsoft’, ‘az’, ‘fundamentals’, ‘900’] | Rating: 0.868
– Matched Subject 3: [‘linux’, ‘gpt’, ‘artificial’, ‘intelligence’, ‘go’] | Rating: 0.623
– Matched Subject 4: [‘learning’, ‘machine’, ‘deep’, ‘design’, ‘driven’] | Rating: 0.527
The job “cybersecurity skilled” requires abilities in Kubernetes (together with CKAD certification), together with safety abilities. A job as a expertise advisor requires a broader group of abilities: cloud improvement, linux, AI, and extra. “Expertise advisor” doesn’t match to subjects as sharply as does “cybersecurity skilled,” however it nonetheless offers us a superb place to begin.
After a bit of knowledge cleaning, we will invert this mapping to seek out out what jobs are related to any given subject. For instance, take the titles of programs, then map them to subjects, then take the subjects and map them to job titles. For instance in Subject 1, the talents “AWS” and “cloud” map to the job titles cloud engineer, AWS options architect, and expertise advisor. This result’s precisely what we should always anticipate, exhibiting that this method to discovering the labels of abilities mapping to jobs has benefit.Subject 1 (AWS, cloud):
Subject 1 (AWS, cloud):
- Cloud Engineer
- AWS Options Architect
- Expertise Advisor
Subject 2 (Python, AI design):
- Machine Studying Engineer
- AI Software program Engineer
Subject 3 (Software program structure):
- Software program Engineer
- Software program Architect
Subject 4 (Kubernetes, builders):
- Platform Engineer
- DevOps Engineer
Subject 5 (Java improvement):
- Again-end Developer
- Full-stack Developer
Subject 6 (Microservices):
- Again-end Developer
- Platform Engineer
Subject 7 (Safety techniques):
- Cybersecurity Analyst
- Data Safety Engineer
Subject 8 (Microsoft Azure):
- Cloud Options Architect
- Azure Developer
Subject 9 (Linux, AI):
- Machine Studying Engineer
- AI Engineer
Subject 10 (Deep studying):
- Machine Studying Engineer
- Information Scientist
Subject modeling can play an essential position in figuring out job abilities primarily based on the subjects learners eat. This might actually be utilized by academic establishments to present them a aggressive benefit. It actually is utilized by firms like O’Reilly, which offer coaching providers to particular person and company prospects. However extra importantly, it gives helpful data to HR departments in regards to the abilities they should rent for.
For establishments that may make use of this information, it serves as a aggressive benefit. It tells them what roles the subjects they educate are making ready the scholars for, and might help them plan curricula which might be extra related to the wants of trade. A college may use this evaluation to take a look at exterior traits together with inner course recognition. College students could have distinctive intuitions about what abilities they want primarily based on job interviews and internships. Analyzing alumni information may present what job titles their alumni have had, which could possibly be in contrast with the programs these alumni took whereas enrolled.
The position of trade
What does trade want? The course completion information exhibits that college students from our company purchasers are in search of delicate abilities like administration, communications, and product administration along with technical abilities. Whereas this would possibly replicate college students’ needs to “get forward” slightly than company wants, firms are conscious that good communications and administration abilities are important and never taught in diploma applications. And, let’s face it, everybody desires product managers.
Subject modeling exhibits that companies are in search of cloud abilities, software program structure (a extra senior talent to aspire to), AI abilities, Kubernetes, Java, Python, microservices, safety, and Linux. Aside from AI, Java, and Python, it’s troublesome or unimaginable to seek out programs on these subjects in school or college CS departments. We received’t identify names, however we problem you to do your individual analysis. Many of the colleges we checked out provided one or two programs on cloud computing (although nothing on particular cloud distributors); we had been unable to seek out any college that provided programs on microservices or Kubernetes, although little question some exist. Should you take up our problem, we advise that you simply take a look at the course choices in your state’s flagship college, considered one of its second-tier universities, a group school, and two personal establishments (one prestigious, one not). The much less prestigious colleges are extra possible to offer coaching in particular job-related abilities.
If faculties and universities don’t present coaching on abilities which might be essential to trade, who will? Accountability would appear to fall squarely on the shoulders of trade. Should you can’t rent folks with the talents you want, rent good folks and prepare them. However is coaching out there on the job? Too usually, the reply isn’t any. Why is that?
An growing variety of firms are waking as much as the necessity for company coaching applications, however in doing so, they’re going towards the previous few many years of company pondering. For years, the incentives have been improper. Stockholders wish to see the worth of the inventory enhance and stress executives to make use of buybacks and layoffs to maximise their inventory’s near-term worth, usually on the expense of long-term pondering. In The Man Who Broke Capitalism, David Gelles notes,
Earlier than [Jack] Welch, company earnings had been largely reinvested within the firm or paid out to staff slightly than despatched again to inventory homeowners. In 1980, American firms spent lower than $50 billion on buybacks and dividends. By the point of Welch’s retirement, a a lot higher share of company earnings was going to traders and administration, with American firms spending $350 billion on buybacks and dividends in 2000.
Coaching is an funding within the firm—and it’s a sort of funding that has gone out of fashion.
Nevertheless, forward-thinking firms understand that an funding in upskilling their workers is a essential a part of long-term strategic pondering. Operating an organization as lean as attainable to maximise short-term revenue has dire results on coaching: If bills are reduce to the bone, firms can’t assist their workers sustain with modifications in expertise, nor can they put together latest school graduates to make the transition to the “actual world.” In flip, a workforce that lags behind present applied sciences results in poor long-term outcomes. A workers that falls behind the curve or by no means makes it to the curve to start with can have hassle creating profitable merchandise for the longer term. Shortchanging coaching solely results in an organization that underperforms in the long run.
Historic proof helps the worth of expert apprenticeship. Internships may be small “tiger groups” that enable college students to deal with particular issues with a mentor. Though we don’t hear a lot about apprenticeships within the twenty first century, internships (and even PhD applications) share many features of apprenticeship. Apprenticeships are a perfect method to deliver latest school graduates in control on abilities they want. They’re much less relevant for extra senior workers who have to sharpen their abilities or study new ones because the trade evolves. It’s essential to recollect what senior workers acquire from mentoring junior workers. When performed properly, mentoring exposes the seniors to new concepts from their college students. It requires them to assume via every part they already know; speaking and explaining solidifies their very own information.
Many firms present in-house coaching applications via merchandise such because the O’Reilly studying platform. Merchandise like these may be built-in with the corporate’s personal studying administration system (LMS) to create customized curricula relying on their workers’s wants and monitor progress via the educational program. This sort of answer works properly for each senior and junior workers: A senior developer could solely have to stand up to hurry on a couple of subjects of curiosity, like AI, whereas a brand new rent would possibly have to fill in primary information they didn’t get in class.
Vital pondering presents completely different points. Corporations through which everyone seems to be indoctrinated with the advertising and marketing literature and the annual report ultimately fail; they’re blindsided by new developments as a result of they’ll’t assume exterior of their containers. Vital pondering isn’t tied to any particular subject or talent, like microservices, however it may be realized in any context. Lately, our studying platform has begun to introduce choices for interactivity, together with interactive quizzes, coding sandboxes and labs the place you possibly can check out concepts, and problem workouts that take a look at new abilities. All of those studying instruments assist educate essential pondering. Vital pondering abilities may also be developed by studying books, writing about what you realized, and taking part in examine teams. One other key to essential pondering might be valuing educating as such—the sort of affected person educating or mentoring that doesn’t revolve round grades or scholar evaluations however that understands that every one educating is a means of exploration. To construct essential pondering abilities, firms have to transcend offering courseware. They should construct a tradition the place all concepts are revered, a tradition that encourages dialogue, exploration, and failure.
The necessity to prepare, upskill, and reskill job seekers isn’t being fulfilled. Universities alone aren’t sufficient to fulfill the calls for of a altering workforce. There aren’t any shortcuts. Studying requires doing; it may be messy, hectic, awkward, and troublesome. However with out the wrestle to study, there is no such thing as a future: not for particular person job seekers and never for the remainder of us who depend on their productiveness. For many college students, studying is a matter of filling the hole between educational examine and pragmatic abilities. Platforms like O’Reilly bridge the hole in bringing cutting-edge abilities, certifications, and information to college students.


