Right here in regards to the seaside I wander’d, nourishing a youth elegant
With the fairy tales of science, and the lengthy results of Time…
—Tennyson
Temporal coincidence performs havoc with our concepts about different civilizations within the cosmos. If we need to detect them, their society should not less than have developed to the purpose that it may possibly manipulate electromagnetic waves. However its know-how must be of adequate power to be observed. The type of alerts folks have been listening to 100 years in the past on crystal units wouldn’t remotely match the invoice, and neither would our primitive TV alerts of the Fifties. So we’re searching for sturdy alerts and cultures older than our personal.

Now take into account how quick a time we’re speaking about. Now we have been utilizing radio for a bit over a century, which is on the order of 1 half in 100,000,000 of the lifespan of our star. You could recall the work of Brian Lacki, which I wrote about 4 years in the past (see Alpha Centauri and the Seek for Technosignatures). Lacki, now at Oxford, factors out how unlikely it will be to search out any two stars remotely close to one another whose civilization ‘window’ corresponded to our personal. In different phrases, even when we final 1,000,000 years as a technological civilization, we’re simply the blink of an eye fixed in cosmic time.
Picture: Brian Lacki, whose work for Breakthrough Hear continues to discover each the scientific and philosophical implications of SETI. Credit score: College of Oxford.
Adam Frank on the College of Rochester has labored this identical panorama. He thinks we would properly discover ourselves in a galaxy that at one time or one other had flourishing civilizations which are lengthy gone. We’re separated not solely in house but additionally in time. Perhaps there are things like civilizations which are immortal, however it appears extra probably that every one cultures ultimately finish, even when by morphing into another type.
What would a billion 12 months previous civilization seem like? Clearly we do not know, however it’s conceivable that such a tradition, absolutely non-biological and maybe non-corporeal, would be capable of manipulate matter and spacetime in ways in which would possibly merely mimic nature itself. Not possible to search out that one. A extra probably SETI catch can be a civilization that has had house applied sciences simply lengthy sufficient to have the potential of interstellar flight on a big scale. In a brand new paper, Lacki appears to be like at what its technosignature would possibly seem like. In the event you’re considering Dyson spheres or swarms, you’re heading in the right direction, however because it seems, such vitality gathering constructions have time issues of their very own.
Lacki’s description of a megaswarm surrounding a star:
These swarms, virtually by definition, must have numerous components, whether or not their function is communication or exploitation. Furthermore, the swarm orbital belts must have a variety of inclinations. This ensures that the luminosity is being collected or modulated in all instructions. However this in flip implies a variety of velocities, similar to the round orbital velocity. One other downside is that the variety of belts that may “match” right into a swarm with out crossing is proscribed.

Picture: Artist’s impression of a Dyson swarm. Credit score: Archibald Tuttle / Wikimedia Commons. CC BY-SA 4.0.
Shards of Time
The temporal downside persists, for even 1,000,000 12 months ‘window’ is a sliver on the cosmic scale. The L issue within the Drake equation is a superb unknown, however it’s conceivable that the loss of life of a million-year previous tradition can be survived by its artifacts, performing to offer us clues to its previous simply as fossils inform us in regards to the early levels of life on Earth. So would possibly we hope to search out an historical, deserted Dyson swarm round a star shut sufficient to watch?
Lacki is thinking about failure modes, the issue of issues that break down. Helpfully, megastructures are by definition gigantic, and it’s not inconceivable that. Dyson constructions of 1 sort or one other might register in our astronomical information. Because the paper notes, all kinds masking completely different fractions of the host star will be imagined. We are able to scale a Dyson swarm down or up in measurement, with maybe the biggest ever proposed being from none aside from Nikolai Kardashev, who discusses in a 1985 paper a disk parsecs-wide constructed round a galactic nucleus (!).
I’m speaking about Dyson swarms as a substitute of spheres as a result of from what we all know of fabric science, stable constructions would endure from excessive instabilities. However swarms will be actively managed. Now we have a historical past of curiosity in swarms courting again to 1958, when Venture Needles at MIT contemplated putting a hoop of 480,000,000 copper dipole antennas in orbit to boost navy communications (the concept was also referred to as Venture West Ford). Though two launches have been carried out experimentally, the undertaking was ultimately shelved due to advances in communications satellites.
So we people already ponder enclosing the planet in a technique or one other, and planetary swarms, as Lacki notes, are already with us, contemplating the constellations of satellites in Earth orbit, the very early levels of a mini Dyson swarm. Simply yesterday, the announcement by SpinLaunch that it’s going to launch tons of of microsatellites into orbit utilizing a centrifugal cannon gave us one other occasion. Enclosing a star in a step by step thickening swarm looks as if one approach to harvest vitality, but when such constructions have been constructed, they must be constantly maintained. The civilization behind a Dyson swarm must survive if the swarm itself is to stay viable.
For the gist of Lacki’s paper is that on the timescales we’re speaking about, an deserted Dyson swarm can be in bother inside a surprisingly quick time period. Certainly, collisions can start as soon as the steerage programs in place start to fail. What Lacki calls the ‘collisional time’ is roughly an orbital interval divided by the masking fraction of the swarm. How lengthy it takes to develop right into a ‘collisional cascade’ relies upon upon the configuration of the swarm. Let me quote the paper, which identifies:
…a serious risk to megastructure lifespans: if deserted, the person components ultimately begin crashing into one another at excessive speeds (as famous in Lacki 2016; Sallmen et al. 2019; Lacki 2020). Not solely do the collisions destroy the crashed swarm members, however they spray out many items of wreckage. Every of those items is itself transferring at excessive speeds, in order that even items a lot smaller than the unique components can destroy them. Thus, every collision can produce tons of of missiles, leading to a fast development of the possibly harmful inhabitants and accelerating the speed of collisions. The result’s a collisional cascade, the place the swarm components are smashed into fragments, which are in flip smashed into smaller items, and so forth, till your entire construction has been lowered to mud. Collisional cascades are thought to have formed the evolution of minor Photo voltaic System physique objects like asteroid households and the irregular satellites of the large planets (Kessler 1981; Nesvorn.
You would possibly suppose that swarm components might be organized in order that their orbits cut back or eradicate collisions or render them gradual sufficient to be innocent. However gravitational perturbations stay a key downside as a result of the swarm isn’t an remoted system, and within the absence of energetic upkeep, its degradation is comparatively swift.
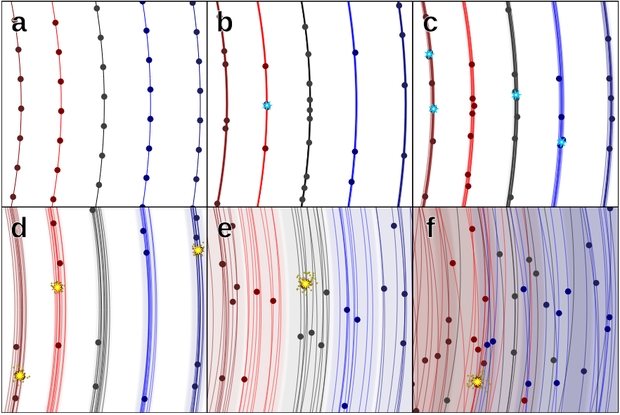
Picture: That is Determine 2 from the paper. Caption: A sketch of a sequence of coplanar belts heating up with randomized velocities. In panel (a), the belt is a single orbit on which components are positioned in an orderly trend. Very small random velocities (meters per second or much less) trigger small deviations within the components’ orbits, although so small that the belt continues to be “sharp”, narrower than the weather themselves (b). The random velocities trigger the phases to desynchronize, resulting in collisions, though they’re too gradual to wreck the weather (cyan bursts). The collision time decreases quickly on this regime till the belt is as vast as the weather themselves and turns into “fuzzy” (c). The collision time is at its minimal, though impacts are nonetheless too small to trigger harm. In panel (d), the belts are nonetheless not vast sufficient to overlap, however relative speeds throughout the belts have grow to be quick sufficient to catastrophically harm components (yellow explosions), and are far more frequent than the naive collisional time implies due to the excessive density inside belts. Additional heating causes the density to fall and collisions to grow to be rarer till the belts begin to overlap (e). Lastly, the belts develop so vast that every belt overlaps a number of others, with collisions occuring between objects in several belts too (f), at which level the swarm is basically randomized. Credit score: Brian Lacki.
Holding the Swarm Alive
Lacki’s mathematical therapy of swarm breakdown is exhaustive and properly above my payscale, so I ship you to the paper if you wish to observe the calculations that drive his simulations. However let’s speak in regards to the implications of his work. Removed from being static technosignatures, megaswarms surrounding stars are proven to be extremely weak. Even the minimal occulter swarm he envisions seems to have a collision time of lower than 1,000,000 years. A megaswarm wants energetic upkeep – in our personal system, Jupiter’s gravitational impact on a megaswarm would destroy it inside a number of hundred thousand years. These are wafer-thin time home windows if scaled in opposition to stellar lifetimes.
The answer is to actively preserve the megaswarm and take away perturbing objects by ejecting them from the system. An fascinating science fiction situation certainly, during which extraterrestrials would possibly sacrifice programs planet by planet to take care of a swarm. Lacki works the simulations by gravitational perturbations from passing stars and in-system planets and factors to the Lidov-Kozai impact, which turns round orbits at excessive inclination into eccentric orbits at low inclination. Additionally thought of is radiation stress from the host star and radiative forces ensuing from the Yarkovsky impact.
How else to maintain a swarm going? From the paper:
For all we all know, the builders are essentially long-lived and may preserve an energetic watch over the weather and actively stop collisions, or not less than counter perturbations. Conceivably, they might additionally launch tender robots to do the job for them, or the swarm components have automated steerage. Admittedly, their programs must be stored up for thousands and thousands of years, vastly outlasting something now we have constructed, however this is perhaps extra believable if we think about that they’re self-replicating. On this view, at any time when a component is destroyed, the fragments are consumed and cast into a brand new ingredient; management programs are continuously regenerated as new generations of tenders are born. Even then, self-replication, restore, and waste assortment are most likely not completely environment friendly.
The outer reaches of a stellar system can be a greater place for a Dyson swarm than the internal system, which might be hostile to small swarm components, although the benefit of such a place can be extra environment friendly vitality assortment. The liveable zone round a star is probably the least probably place to search for such a swarm given the perturbing results of different planets. And if we take the actually huge image, we are able to speak about the place within the galaxy swarms is perhaps probably: Low density environments the place interactions with different stars are unlikely, as within the outskirts of enormous galaxies and of their haloes. “This implies,” Lacki provides, “that megaswarms usually tend to be present in areas which are generally thought of disfavorable for habitability.”
Finally, an deserted Dyson swarm is floor into microscopie particles by way of the collision cascades Lacki describes, evolving into nothing greater than dispersed ionized fuel. If we hope to search out an deserted megastructure like this in our apply of galactic archaeology, what are the percentages that we’ll discover it throughout the window of time inside which it may possibly survive with out energetic upkeep? We’d higher hope that the swarm creators have extraordinarily long-lived civilizations if we’re to exist in the identical temporal window because the swarm we need to observe. A dearth of Dyson constructions up to now noticed might merely be an absence of temporal coincidence, as we seek for programs which are inevitably carrying down with out the restoring hand of their creators.
The paper is Lacki, “Floor to Mud: Collisional Cascades and the Destiny of Kardashev II Megaswarms,” accepted at The Astrophysical Journal (preprint). The Kardashev paper referenced above is “On the Inevitability and the Doable Construction of Tremendous Civilizations,” in The Seek for Extraterrestrial Life: Current Developments, ed. M. D. Papagiannis, Vol. 112, 497–504.


