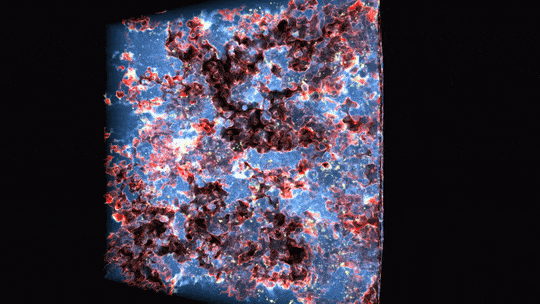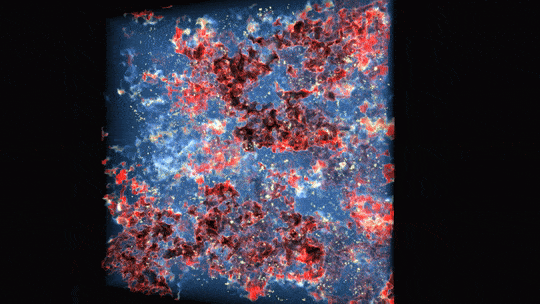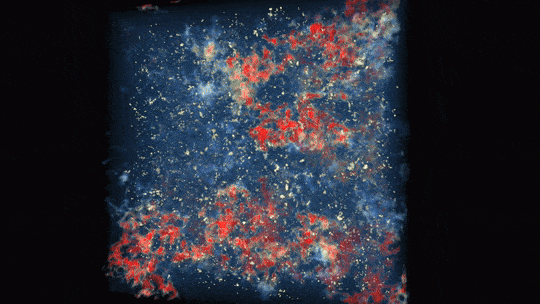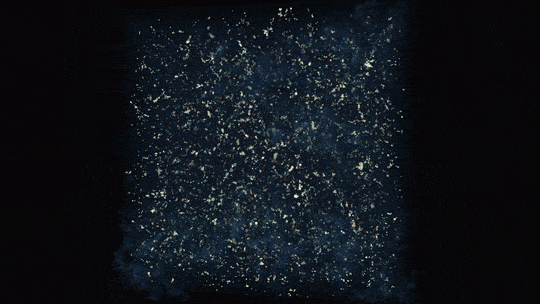
Observations from each NASA’s James Webb and Hubble area telescopes created this colourful picture of galaxy cluster MACS0416. The colours of various galaxies point out distances, with bluer galaxies being nearer and redder galaxies being extra distant or dusty. Some galaxies seem as streaks on account of gravitational lensing — a warping impact brought on by giant lots gravitationally bending the area that mild travels by way of.
Whereas Taylor’s Eras Tour explores many years of music, our universe’s eras set the stage for all times to exist at this time. By unraveling cosmic historical past, scientists can examine the way it occurred, from the universe’s origin and evolution to its attainable destiny.
This infographic outlines the historical past of the universe.
0 SECONDS | To start with, the universe debuted extraordinarily small, scorching, and dense
Scientists aren’t certain what precisely existed on the very starting of the universe, however they assume there wasn’t any regular matter or physics. Issues most likely didn’t behave like we anticipate them to at this time.
Artist’s interpretation of the start of the universe, with representations of the early cosmos and its growth.
10^-32 SECONDS | The universe quickly, fearless-ly inflated
When the universe debuted, it nearly instantly grew to become unstable. Area expanded sooner than the pace of sunshine throughout a really transient interval often called inflation. Scientists are nonetheless exploring what drove this exponential growth.
1 MICROSECOND | Inflation’s finish began the story of us: we wouldn’t be right here if inflation continued
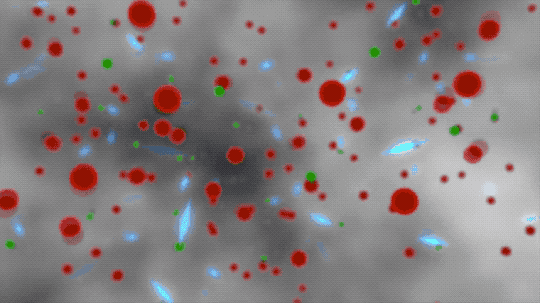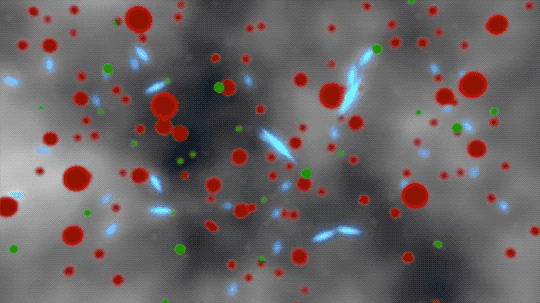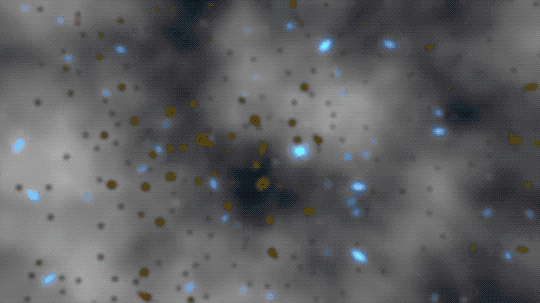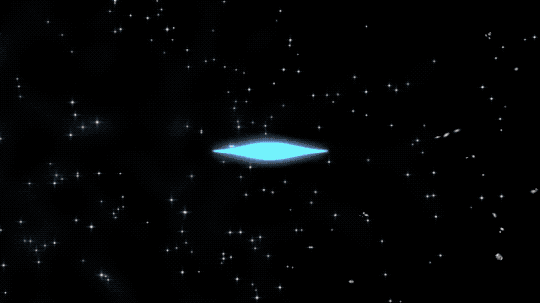
When inflation ended, the universe continued to broaden, however a lot slower. All of the vitality that beforehand drove the speedy growth went into mild and matter — regular stuff! Small subatomic particles — protons, neutrons, and electrons — now floated round, although the universe was too scorching for them to mix and kind atoms.
The particles gravitated collectively, particularly in clumpy spots. The push and pull between gravity and the particles’ lack of ability to stay collectively created oscillations, or sound waves.
Artist’s interpretation of protons and neutrons colliding to kind ionized deuterium — a hydrogen isotope with one proton and one neutron — and ionized helium — two protons and two neutrons.
THREE MINUTES | Protons and neutrons mixed all too nicely
After about three minutes, the universe had expanded and cooled sufficient for protons and neutrons to stick collectively. This created the very first parts: hydrogen, helium, and really small quantities of lithium and beryllium.
But it surely was nonetheless too scorching for electrons to mix with the protons and neutrons. These free electrons floated round in a scorching foggy soup that scattered mild and made the universe seem darkish.
This animated artist’s idea begins by displaying ionized atoms (purple blobs), free electrons (inexperienced blobs), and photons of sunshine (blue flashes). The ionized atoms scattered mild till impartial atoms (proven as brown blobs) fashioned, clearing the best way for mild to journey farther by way of area.
380 THOUSAND YEARS | Impartial atoms fashioned and left a clean area for mild
Because the universe expanded and cooled additional, electrons joined atoms and made them impartial. With the electron plasma out of the best way, some mild might journey a lot farther.
A picture of the cosmic microwave background (CMB) throughout the complete sky, taken by ESA’s (European Area Company) Planck area telescope. The CMB is the oldest mild we will observe within the universe. Frozen sound waves are seen as miniscule fluctuations in temperature, proven by way of blue (colder) and purple (hotter) coloring.
As impartial atoms fashioned, the sound waves created by the push and pull between subatomic particles stopped. The waves froze, leaving ripples that have been barely denser than their environment. The surplus matter attracted much more matter, each regular and “darkish.” Darkish matter has gravitational affect on its environment however is invisible and doesn’t work together with mild.
This animation illustrates the absorption of photons — mild particles — by impartial hydrogen atoms.
ALSO 380 THOUSAND YEARS | The universe grew to become darkish — name it what you need, however scientists name this time interval the Darkish Ages
Apart from the cosmic microwave background, there wasn’t a lot mild throughout this period since stars hadn’t fashioned but. And what mild there was normally didn’t make it very far since impartial hydrogen atoms are actually good at absorbing mild. This kicked off an period often called the cosmic darkish ages.
This animation illustrates the start of star formation as gasoline begins to clump on account of gravity. These protostars warmth up as materials compresses inside them and throw off materials at excessive speeds, creating shockwaves proven right here as increasing rings of sunshine.
200 MILLION YEARS | Stars created daylight (that was nonetheless blocked by hydrogen atoms)
Over time, denser areas pulled in increasingly more matter, in some locations turning into so heavy it triggered a collapse. When the matter fell inward, it grew to become scorching sufficient for nuclear fusion to start out, marking the beginning of the primary stars!
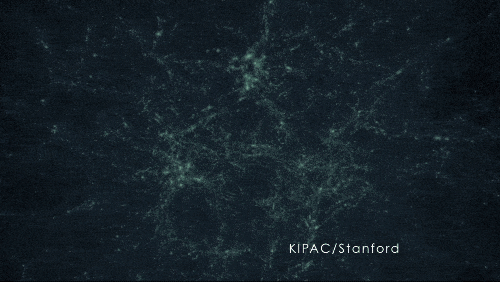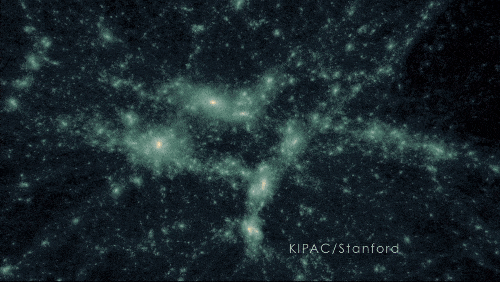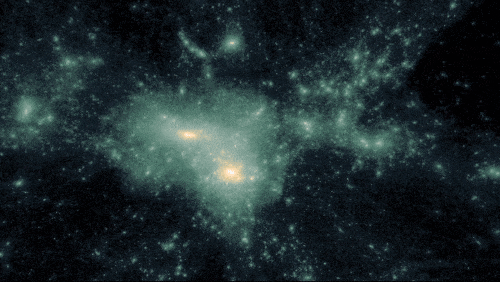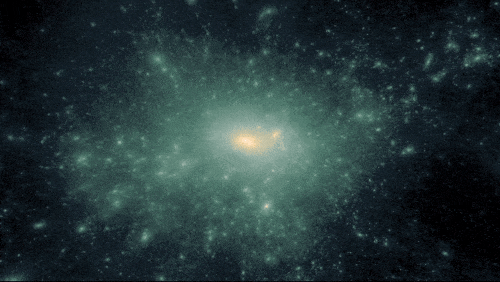
A simulation of darkish matter forming construction on account of gravity.
400 MILLION YEARS | Darkish matter acted like an invisible string tying galaxies collectively
Because the universe expanded, the frozen sound waves created earlier — which now included stars, gasoline, mud, and extra parts produced by stars — stretched and continued attracting extra mass. Pulling materials collectively ultimately fashioned the primary galaxies, galaxy clusters, and wide-scale, web-like construction.
On this animation, ultraviolet mild from stars ionizes hydrogen atoms by breaking off their electrons. Areas already ionized are blue and translucent, areas present process ionization are purple and white, and areas of impartial gasoline are darkish and opaque.
1 BILLION YEARS | Ultraviolet mild from stars made the universe clear for evermore
The primary stars have been huge and scorching, which means they burned their gasoline provides rapidly and lived quick lives. Nonetheless, they gave off energetic ultraviolet mild that helped break aside the impartial hydrogen across the stars and allowed mild to journey farther.
Animation displaying a graph of the universe’s growth over time. Whereas cosmic growth slowed following the top of inflation, it started selecting up the tempo round 5 billion years in the past. Scientists nonetheless aren’t certain why.
SOMETIME AFTER 10 BILLION YEARS | Darkish vitality grew to become dominant, accelerating cosmic growth and creating an enormous query…?
By finding out the universe’s growth fee over time, scientists made the surprising discovery that it’s dashing up. They’d thought ultimately gravity ought to trigger the matter to draw itself and decelerate growth. Some mysterious stress, dubbed darkish vitality, appears to be accelerating cosmic growth. About 10 billion years into the universe’s story, darkish vitality – no matter it could be – grew to become dominant over matter.
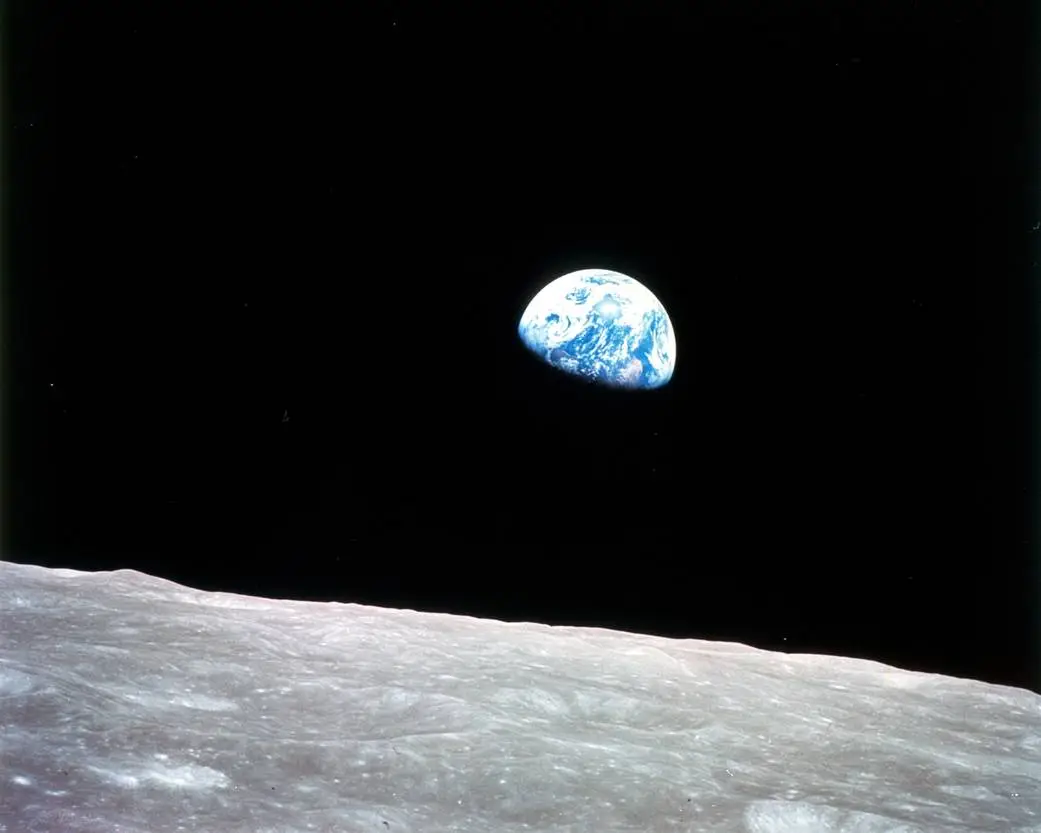
A picture of Earth rising within the Moon’s sky. Nicknamed “Earthrise,” Apollo 8 astronauts noticed this sight throughout the first crewed mission to the Moon.
13.8 BILLION YEARS | The universe as we all know it at this time: 359,785,714,285.7 fortnights from the start
We owe our universe at this time to every of its distinctive phases. Nonetheless, scientists nonetheless have many questions on these eras.
Our upcoming Nancy Grace Roman Area Telescope will look again in time to discover cosmic mysteries like darkish vitality and darkish matter – two poorly understood facets of the universe that govern its evolution and supreme destiny.
Make sure that to comply with us on Tumblr to your common dose of area!