Astronomers have confirmed a uncommon and extraordinary discovery: the third recognized interstellar object to enter our photo voltaic system.
Named 3I/ATLAS, the place 3I stands for “third interstellar”, and designated C/2025 N1 (ATLAS), the article was first noticed on July 1, 2025, by the Deep Random Survey distant telescope in Chile, a part of the ATLAS (Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Final Alert System) venture.
It is a vital discover. However what precisely is it?
Initially referred to by the momentary designation A11pl3Z, 3I/ATLAS drew instant consideration from astronomers due to its peculiar movement. Speedy follow-up observations and reanalysis of earlier information led to the preliminary conclusion that the article was not certain by the solar’s gravity. That makes it an interstellar object — solely the third ever seen after 1I’Oumuamua in 2017 and 2I/Borisov in 2019. “If confirmed, will probably be the third recognized interstellar object from outdoors our photo voltaic system that we have now found, offering extra proof that such interstellar wanderers are comparatively widespread in our galaxy,” Mark Norris, Senior Lecturer in Astronomy on the College of Central Lancashire, informed House.com on the time of 3I/ATLAS’s discovery.
Much more thrilling? 3I/ATLAS is the most important and brightest interstellar object but, which implies it may assist scientists unlock clues in regards to the formation of different star methods.
How do we all know it is interstellar? May it strike Earth? Can we ship a spacecraft to intercept it? Listed below are your entire questions answered and every part else you might want to learn about this uncommon discovery, together with why it could be the primary of many extra interstellar objects to be detected.
How do we all know 3I/ATLAS is from one other star system?
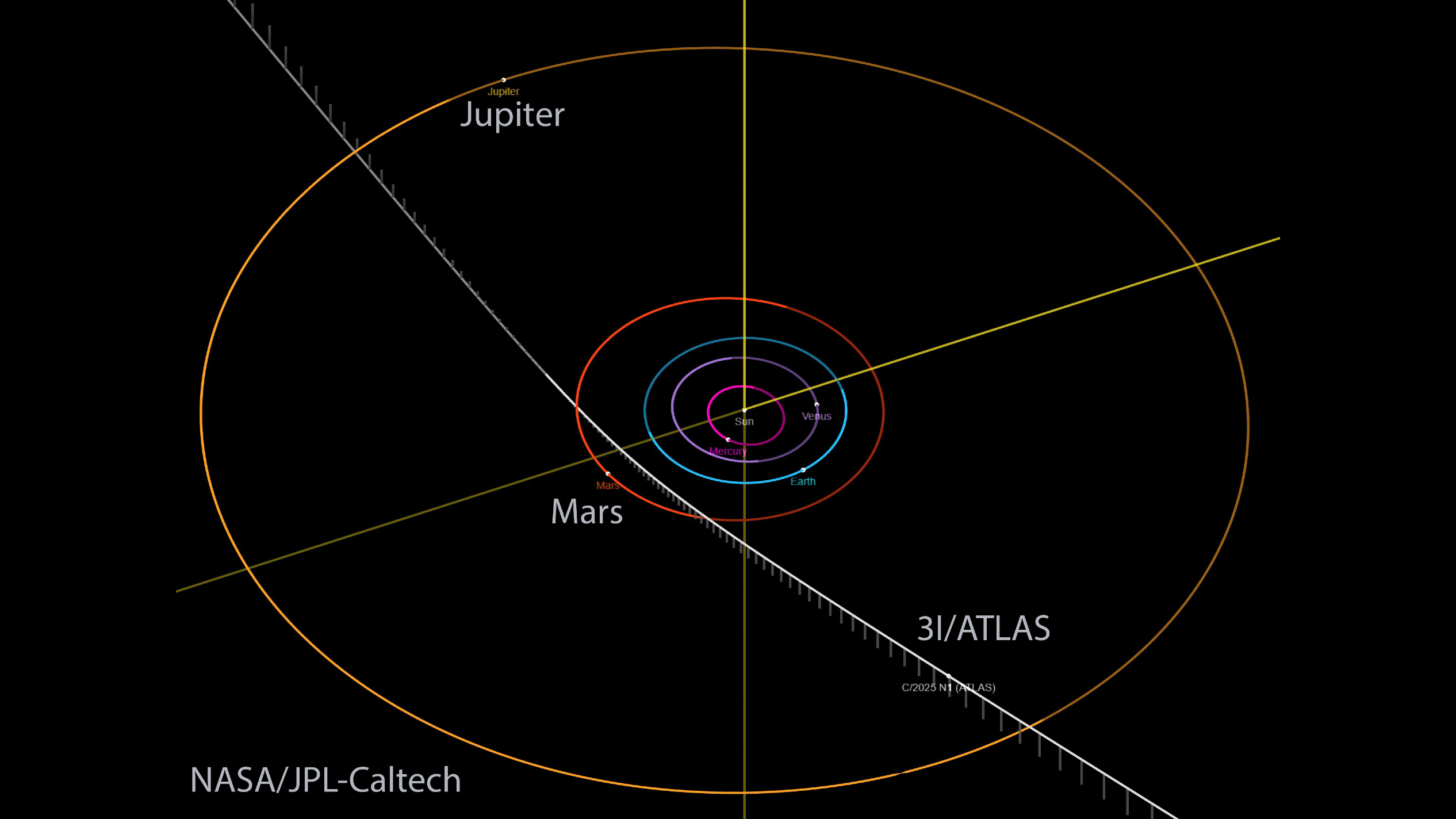
What makes astronomers sure in regards to the interstellar nature of 3I/ATLAS is its trajectory. The item follows a extremely hyperbolic orbit, which implies it is not gravitationally certain to the solar. Its orbital path additionally has an eccentricity of 6.2. For context, any object with an eccentricity above 1 is on a path that doesn’t loop again across the solar, implying it comes from — and can return to — interstellar house. As compared, the primary recognized interstellar customer, 1I/’Oumuamua, had an eccentricity of about 1.2, and 2I/Borisov got here in at 3.6. 3I/ATLAS massively outpaces each.
“Some long-period comets may have a brush with Jupiter that modifies its orbit to 1.05, i.e., hyperbolic on the best way out, however simply barely,” Olivier Hainaut, an astronomer on the European Southern Observatory, informed House.com. “This one is firmly hyperbolic on the best way in, so interstellar.”
How is 3I/ATLAS completely different from 1I/’Oumuamua and 2I/Borisov?

Other than being considerably extra hyperbolic, essentially the most putting distinction is dimension.
“3I/ATLAS is far bigger than the opposite two — it is about 15 kilometers (km) [9 miles] in diameter, with enormous uncertainty, in comparison with 100m for 1I/’Oumuamua and fewer than 1km for 2I/Borisov,” mentioned Hainaut. 3I/ATLAS could even be as broad as 12 miles (20 km). Nonetheless, that conclusion may change with extra observations.
What’s 3I/ATLAS?
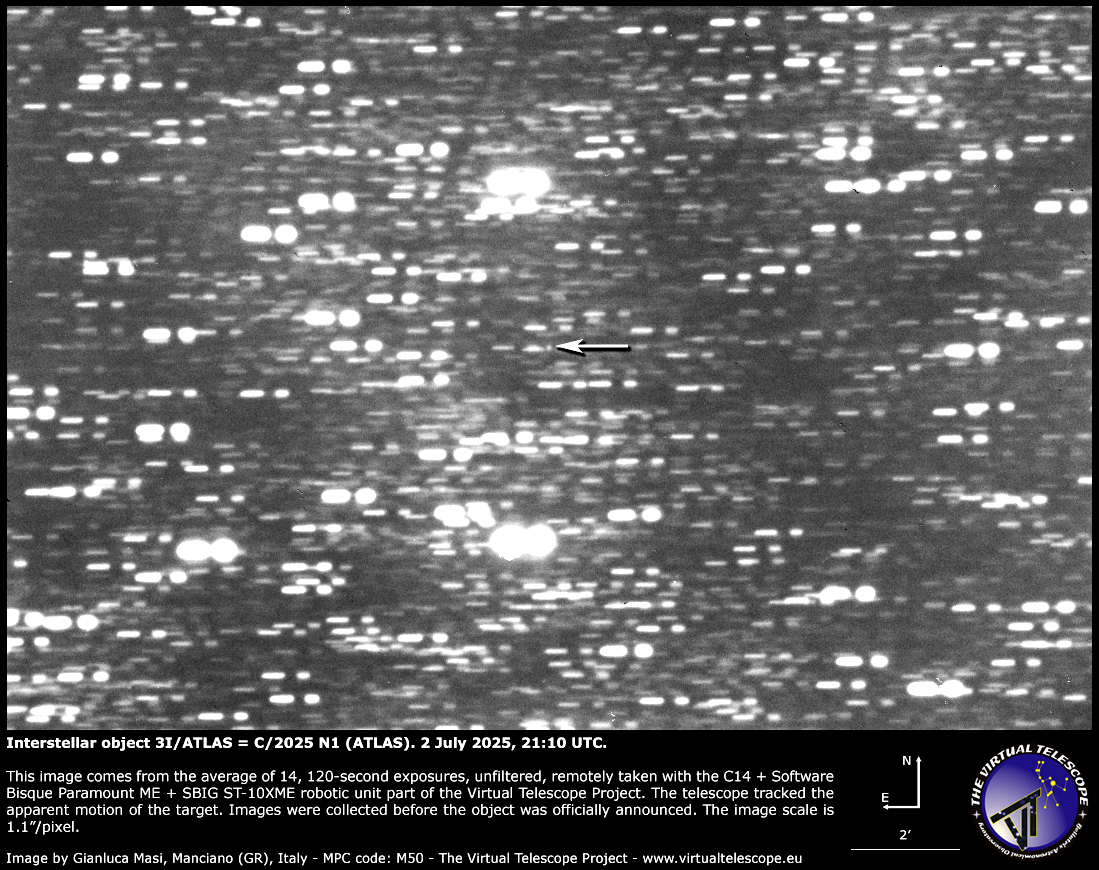
What 3I/ATLAS and 2I/Borisov have in widespread is that they’re each comets. Shortly after its discovery, indicators of a comet-like coma and tail grew to become evident, giving it an extra designation of C/2025 N1 (ATLAS), the naming conference for comets.
Since 1I/ʻOumuamua was noticed solely because it was leaving the photo voltaic system, it was tough for astronomers to get sufficient information on it to verify its precise nature — therefore the loopy theories about it being an alien spaceship — although it is virtually actually an asteroid or a comet.
May 3I/ATLAS strike Earth?
Proper now, 3I/ATLAS is inside Jupiter’s orbit, about 323 million miles (520 million km) from Earth and 420 million miles (670 million km) from the solar.
3I/ATLAS will attain roughly 167 million miles (270 million km) from Earth on Dec. 19, and at no level will it pose a menace. It is going to get to inside 18 million miles (30 million km) of Mars on Oct.2 and to inside 130 million miles (210 million km) of the solar — its closest level (perihelion) — on Oct. 29. At perihelion, will probably be touring at round 42 miles (68 km) per second/second or about 152,000 miles (245,000 km) per hour.
Is 3I/ATLAS seen within the night time sky?
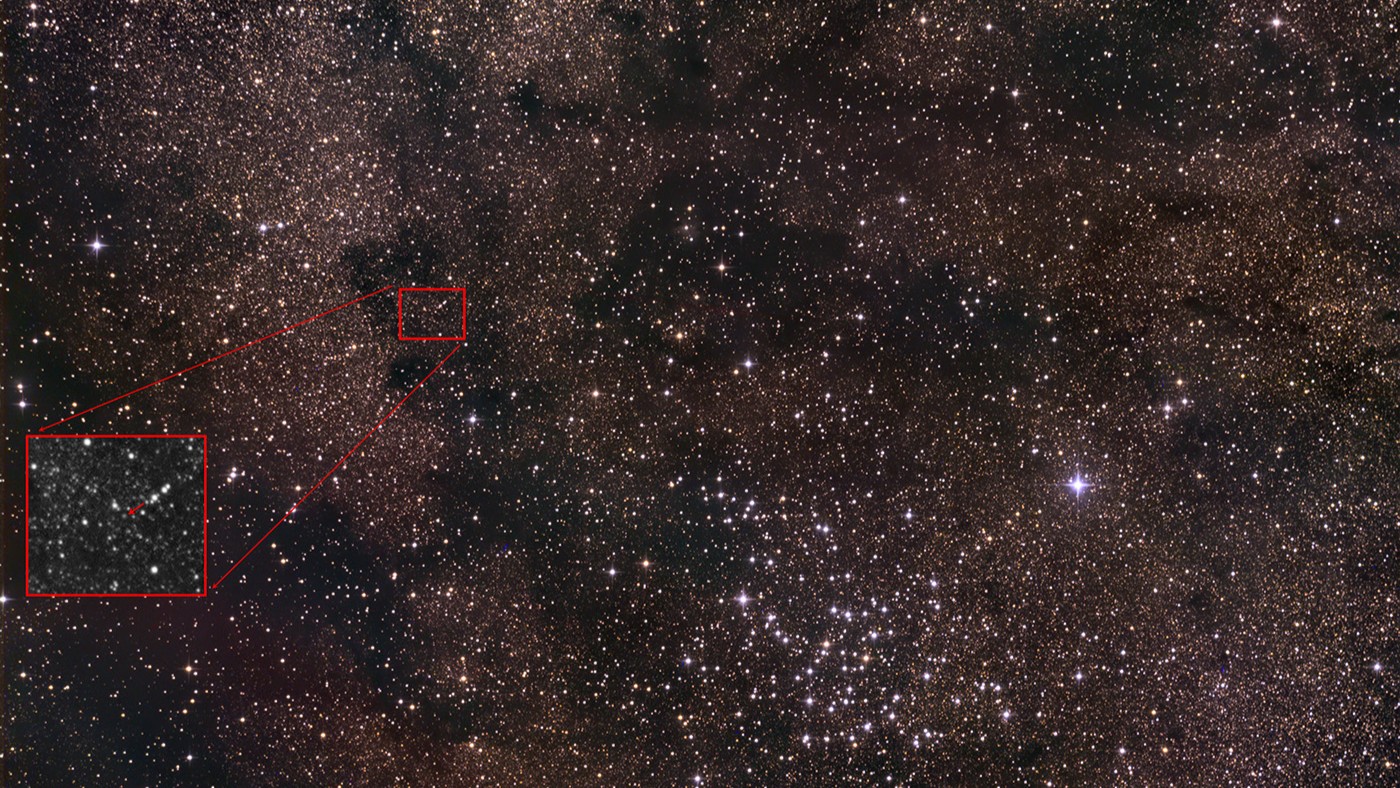

Solely with the correct tools — and endurance.
Proper now, 3I/ATLAS is within the constellation Sagittarius within the arc of the Milky Means, low on the southern horizon as seen from mid-northern latitudes in July. Touring south, it is round magnitude 18.5, making it about 2.5 million instances fainter than Polaris, based on Gianluca Masi on the Digital Telescope Mission, who imaged 3I/ATLAS on July 3. A 150-200mm/6-8-inch aperture telescope with a CCD digicam is required to picture 3I/ATLAS, whereas an optical telescope would wish an aperture of round 400 mm/16-inch.
“It is not going to be seen to the bare eye, and I believe will probably be a problem for an novice, however some have spectacular tools lately,” Professor Martin Barstow on the College of Physics & Astronomy on the College of Leicester, informed House.com.
Nonetheless, that might change as a result of because it will get nearer, it is anticipated to brighten. “By the point it makes its closest strategy, will probably be a comparatively simple goal for novice astronomers to look at,” mentioned Norris. By then, it may attain magnitude 11. For many, 3I/ATLAS might be a captivating science story however not a skywatching alternative.
When will skilled telescopes observe 3I/ATLAS?

Most giant observatories are within the Southern Hemisphere, the place 3I/ATLAS might be finest positioned, so anticipate quite a few pictures to be shared over the approaching days and weeks.
Because it will get near its shiny perihelion, will probably be misplaced within the solar’s glare as seen from Earth, so skilled astronomers will research it — simply as quickly as the intense moon has departed the sky, possible within the weeks following the final quarter moon on July 18.
Extra observations are crucial as a result of what we learn about 3I/ATLAS relies purely on preliminary information. “It was found a number of days in the past and has been noticed solely with small telescopes,” mentioned Hainaut. “We’re scrambling to get the large guys on it as quickly as doable.”
Why is 3I/ATLAS so fascinating to astronomers?
Though a lot stays unknown, it’s already clear that this object is orders of magnitude bigger than ʻOumuamua and Borisov, making it a greater goal for research.
It could possibly be a beneficial alternative for planetary scientists, as interstellar objects supply a tangible connection to different star methods and carry chemical signatures that may present insights into how planetary methods kind, and even supply proof of life elsewhere within the galaxy.
“They undoubtedly carry chemical signatures from outdoors the photo voltaic system, so gaining observations tells us loads about the potential of materials touring between planetary methods,” Barstow mentioned. “If we may get a pattern from one, in the future, it will be an unbelievable breakthrough.”
Can we ship a spacecraft to intercept or fly by 3I/ATLAS?

Most likely not, it is simply too quick.
“We would wish a spacecraft prepared to do that in house, totally checked out and with a rendezvous functionality,” Barstow mentioned.
The necessity to have a spacecraft in orbit able to react to an incoming interstellar object, similar to 3I/ATLAS, has been thought-about earlier than. The European House Company is presently readying its Comet Interceptor venture for launch in 2029 to cope with intriguing comets that all of the sudden seem. “Nonetheless, even this mission won’t have the ability to address the excessive pace of an interstellar traveler,” Barstow mentioned.
Though a pattern of 3I/ATLAS is just not going to be doable, it will present an enormous shortcut for planetary scientists. “Even with our quickest rockets, it will take tens of 1000’s of years for us to succeed in close by stars,” mentioned Norris. “Thanks to those guests from outdoors our photo voltaic system, we could not should journey that far to pattern star methods past our personal [but] we’ll want the know-how to catch up and attain them earlier than they cross by means of our photo voltaic system.”
Why are astronomers all of the sudden discovering interstellar objects?
It is no coincidence.
“Clearly, our telescopes do not have an effect on the outer photo voltaic system, so the actual fact we get extra merely displays that we’re getting higher at discovering them,” Hainaut mentioned.
And we’re simply getting began. The brand new Vera C. Rubin Observatory, which simply launched its first pictures, may uncover many extra interstellar objects like 3I/ATLAS throughout its decade-long Massive Synoptic Survey Telescope (LSST) venture. There could possibly be lots to seek out; a 2020 paper estimated that round seven interstellar objects may cross inside one Earth-sun distance of the solar annually. We simply have not been capable of see them till now.
“It is going to be a dramatic enchancment,” Hainaut mentioned of the LSST. “Prepare for 4I, 5I … 42I!”
3I/ATLAS will be the brightest and largest interstellar customer but, nevertheless it virtually actually will not be the final.

