NASA Glenn Analysis Middle
Historic Amenities
Overview
Within the late Forties the Nationwide Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) realized it wanted a bigger, extra highly effective facility to check the jet engines of the longer term in simulated altitude circumstances. Design of the Propulsion Methods Laboratory (PSL) started in 1947, and development adopted in September 1949. The primary take a look at was run in October 1952.
Researchers used PSL throughout the Fifties to enhance new turbojet and ramjet engines. Analysis shifted to chemical rocket engines throughout the early Nineteen Sixties. By the late Nineteen Sixties the middle returned to plane propulsion and added two new take a look at chambers to the power. All 4 chambers supported the middle’s aeropropulsion efforts throughout the Nineteen Seventies. Reductions in funding led to the closure of PSL No. 1 and a couple of in 1979. After sitting in mothballs for 25 years, NASA determined to demolish the unique PSL take a look at chambers within the 2000s.
Engine Testing on the AERL
Congress established the NACA in 1915 to coordinate aeronautical analysis in america. The NACA quickly constructed a laboratory at Langley Area to conduct its personal analysis. The NACA made many key aeronautical developments throughout its first twenty years of its existence, nevertheless it had largely ignored plane engines. Within the late Thirties, nonetheless, its leaders found the superior state of aviation in Germany. The NACA rapidly determined so as to add two new laboratories, together with one particularly designed to review engine methods. This new Plane Engine Analysis Laboratory (AERL) in Cleveland, Ohio grew to become operational in 1942.
The primary facility to come back on-line on the AERL was the Engine Propeller Analysis Constructing, or Prop Home. The Prop Home contained 4 24-foot-diameter take a look at cells that might run 4000-horsepower piston engines in ambient circumstances. The Altitude Wind Tunnel (AWT), which was accomplished in early 1944, was a way more advanced and helpful facility. It may function these engines in circumstances that simulated altitudes as much as 50,000 toes and at air speeds as much as 500 miles per hour. The AWT was so profitable that its schedule quickly grew to become backed up for months. The lab determined to rapidly construct two static engine take a look at stands within the Engine Analysis Constructing. This 4 Burner Space may additionally run full-size engines at simulated altitudes as much as 50,000 toes. Through the late Forties and early Fifties, nonetheless, the jet engine was quickly rising in energy and dimension. It grew to become clear {that a} extra highly effective take a look at facility was wanted on the lab (renamed the Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory in 1948).
Paperwork
Designing the PSL
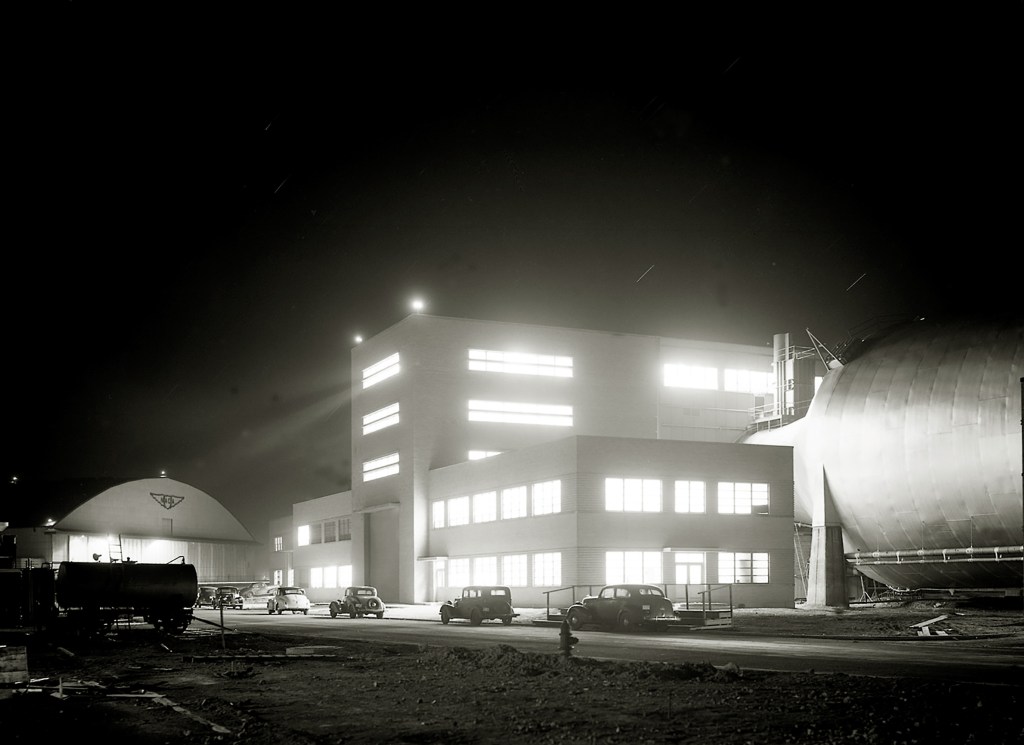
In 1947, the lab’s Analysis Amenities Panel started planning for a brand new facility that mixed the static cell idea of the 4 Burner Space with the large infrastructure of the AWT. This was a part of a complete plan to enhance the altitude testing capabilities throughout the lab by linking the exhaust, refrigeration, and combustion air methods from all the most important take a look at services. On this manner, the methods at completely different services may complement the capabilities of each other. Congress allotted $10 million for the preliminary development of the brand new facility, initially known as the Propulsion Sciences Laboratory. Inside 5 months, veteran engineer Eugene Wasielewski transformed the panel’s suggestions into design specs. The Burns and Roe Firm labored intently with the NACA engineers to create the grasp drawings from these specs.
The general idea of PSL was comparatively easy, however the integration and efficiency of the large methods was very sophisticated. The ability consisted of two take a look at chambers, three exhaust fuel coolers, an gear constructing to deal with the exhausters and compressors, an entry constructing, cooling tower, pump home, and an workplace constructing. It additionally included a compressed air system that equipped combustion air, an altitude exhaust fuel system, analysis gear installations, a cooling water system, electrical energy system, in addition to primary utilities, an intercommunication system, management rooms, roads, and a fireplace safety system.
Paperwork
Authentic Development
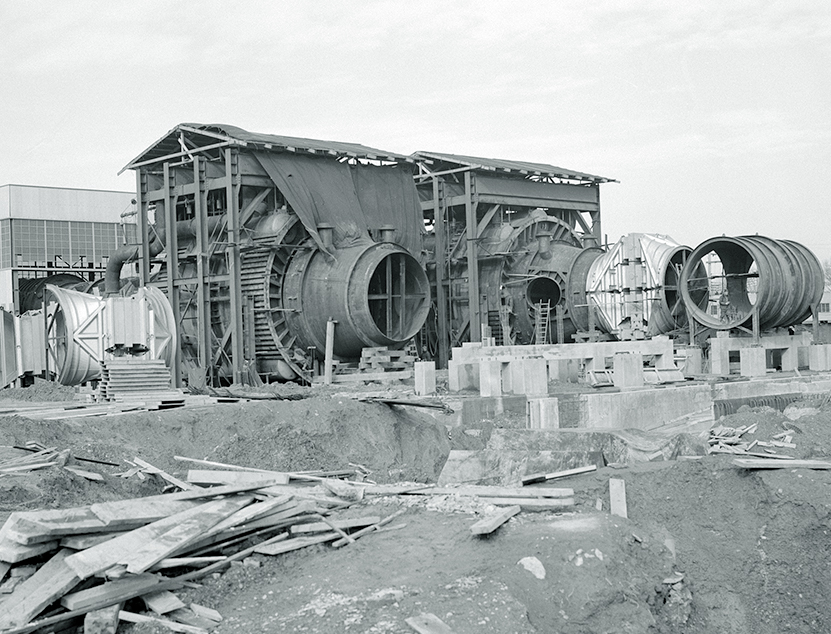
The NACA determined to assemble the PSL in two phases. The primary supplied the first development of the power. The second part, which started shortly after the power grew to become operational, considerably elevated the PSL’s capability. The Sam W. Emerson Firm, which had constructed lots of the lab’s buildings within the early Forties, carried out a lot of the fundamental development work. The Elliott Firm and the Ross Heater Firm designed the large compressors and coolers.
Development started in late summer time 1949 with the set up of an overhead exhaust pipe connecting PSL to the AWT and the Engine Analysis Constructing. Excavations for PSL started in September. Within the spring of 1950, the crew erected the power’s helps and put in the 2 giant exhaust fuel coolers. The big take a look at part items arrived in early 1951 and work on the Entry Constructing commenced. Development of the Gear Constructing started in early 1951, and the exhausters and compressors have been added within the spring of 1952. The PSL was accomplished in September 1952, three years after development started.
Paperwork
Further Data on PSL No. 1 and a couple of

Missiles and Turbojets
Within the Fifties, the PSL examined turbojet and ramjet engines for navy, earlier than transitioning to rocket engines for NASA’s early house program within the Nineteen Sixties.

Picture Gallery
View full-scale images associated to the PSL No.1 and a couple of facility featured on this web site.

Return to Major Web page
Return to the PSL No.1 and a couple of foremost web page to search out further info on the power and its historical past.