It was simply two years in the past {that a} tiny robotic manta ray grew to become the world’s fastest-swimming soft-bodied robotic. Properly, certainly one of its descendants has now smashed that report – and it makes use of much less vitality than its predecessor, besides.
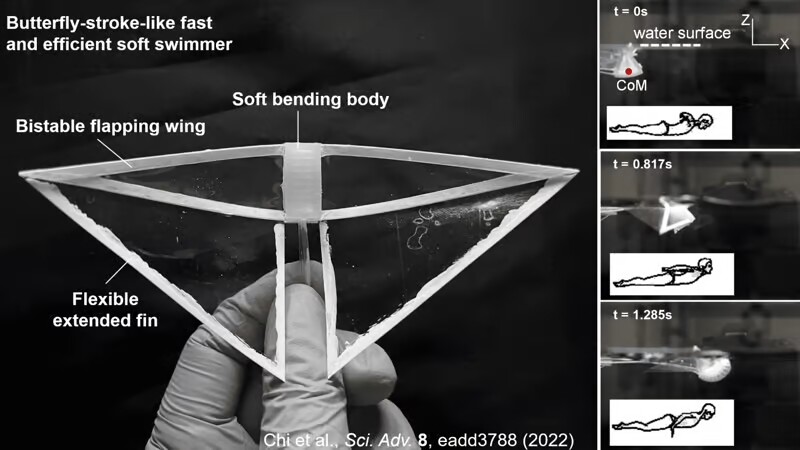
The 22.8-mm-long authentic robotic was designed by Assoc. Prof. Jie Yin and colleagues at North Carolina State College.
It featured two versatile polyester manta-ray-like wings, which have been truly the left- and right-hand ends of a single curved bistable construction. Bistability refers to a tensioned construction’s potential to stay in both of two positions with out requiring any vitality to take action – a hair clip is an efficient instance of a bistable construction.
North Carolina State College
The center of the robotic’s bistable wing construction was sandwiched between high and backside smooth silicone pneumatic actuators.
When air was pumped into the highest actuator, it buckled upward and pulled up on the center of the wing construction, inflicting it to “snap” right into a place that drew the 2 wings downward. When the highest actuator was deflated and the backside one was inflated, the construction snapped in the wrong way, bringing the wings again up once more. The mechanism is demonstrated within the following video.
A butterfly-stroke-like smooth robotic swimmer that’s quick and environment friendly
By activating the 2 actuators backwards and forwards on this method (by way of an exterior air pump), it was attainable to flap the wings quick sufficient for a median swimming velocity of three.74 physique lengths per second. In accordance with the scientists, this was about 4 instances quicker than what had beforehand been attainable for soft-bodied swimming robots.
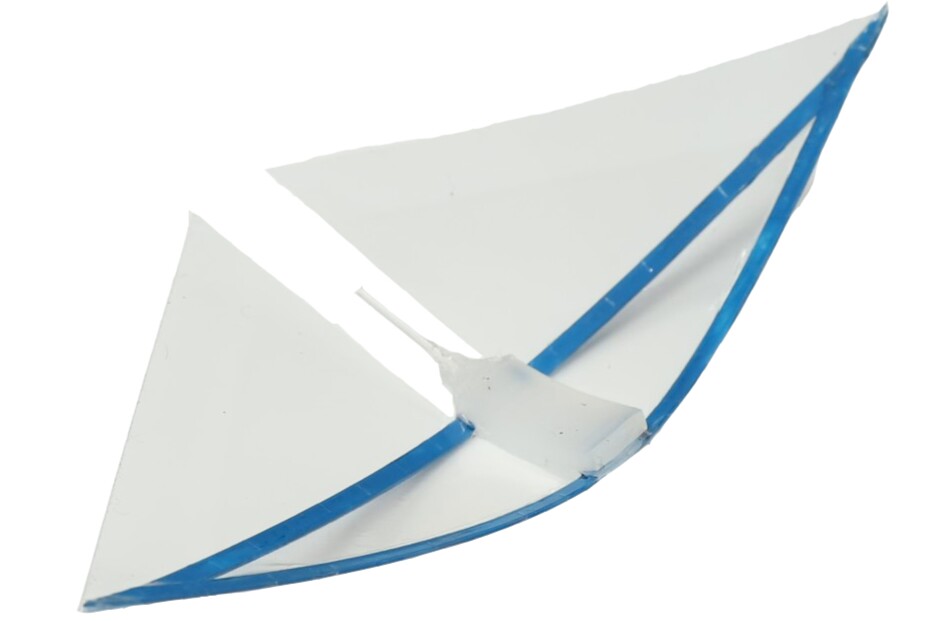
Within the 68-mm-long new robo-manta, Yin and his group did away with the bistable design together with the underside actuator. The versatile wing construction is now monostable, that means it’s going to at all times revert to only one place – curved down within the center with the wings up – when no vitality is utilized.
Haitao Qing, NC State College
Upon being inflated, the one high pneumatic actuator curls downward and pulls down on the center of the wing construction, inflicting the wings to snap downward. As quickly because the actuator is allowed to deflate, nevertheless, the elastic restoring power of the construction causes it to snap again to its default place, drawing the wings upward within the course of.
So, whereas the unique robotic needed to take the time and vitality to alternately inflate/deflate two actuators per up-and-down wing-flapping cycle, the brand new bot solely has to activate one. This enchancment offers the robotic a median swimming velocity of a whopping 6.8 physique lengths per second, whereas consuming 1.6 instances much less vitality than the unique.

Haitao Qing, NC State College
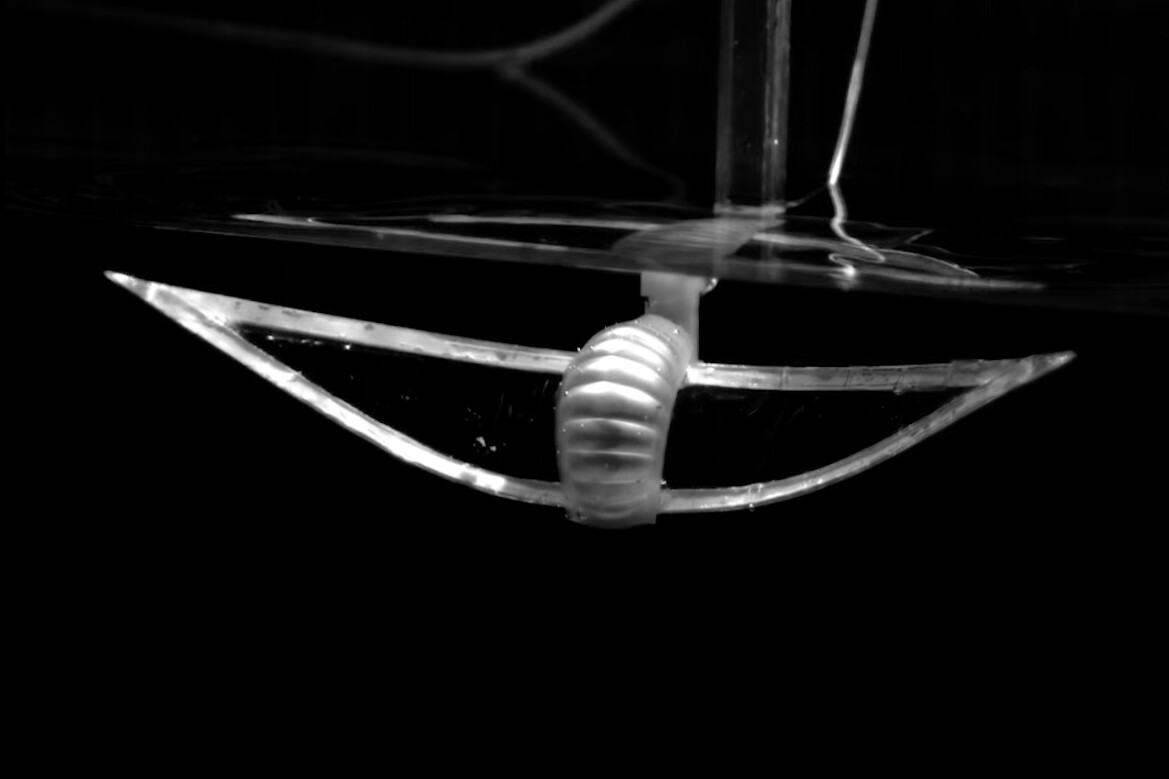
Moreover, the brand new design permits the bot to maneuver vertically inside the water column just by various its swimming velocity.
“When the robotic’s fins are at relaxation, the air chamber is empty, decreasing the robotic’s buoyancy. And when the robotic is flapping its fins slowly, the fins are at relaxation extra typically,” says PhD scholar Haitao Qing, first writer of the research. “In different phrases, the quicker the robotic flaps its fins, the extra time the air chamber is full, making it extra buoyant.”
The scientists are actually engaged on a technique of laterally steering the robotic, with a watch towards future purposes akin to ocean exploration and aquatic wildlife statement. You may see in it motion, within the video under.
A paper on the research was not too long ago printed within the journal Science Advances.
Manta ray-inspired quick and maneuverable smooth swimming robots
Supply: North Carolina State College

