The concept of life attaining a sequence of plateaus, every of which is a protracted and threatening slog, has critical implications for SETI. It was Brandon Carter, now on the Laboratoire Univers et Théories in Meudon, France, who proposed the notion of such ‘arduous steps’ again within the early Nineteen Eighties. Comply with-up work by a lot of authors, particularly Frank Tipler and John Barrow (The Anthropic Cosmological Precept) has refined the idea and added to the steps Carter conceived. Since then, the concept life would possibly take a considerable quantity of the lifetime of a star to emerge has bedeviled those that wish to see a universe stuffed with technological civilizations. Every ‘arduous step’ is unlikely in itself, and our existence relies upon upon our planet’s having achieved all of them.
Carter was motivated by the timing of our emergence, which we are able to spherical off at 4.6 billion years after the formation of our planet. He reasoned that the higher restrict for habitability at Earth’s floor is on the order of 5.6 billion years after Earth’s formation, a suspicious reality – why would human origins require a time that approximates the extinction of the biosphere that helps us? He deduced from this that the common time for clever beings to emerge on a planet exceeds the lifespan of its biosphere. We’re, in different phrases, a fortunate species that squeezed in our improvement early.

Picture: Two extremely influential physicists. Brandon Carter (proper) sitting with Roy Kerr, who found the Einsteinian resolution for a rotating black gap. Carter’s personal early work on black holes is extremely regarded, though lately he appears primarily recognized for the ‘arduous steps’ speculation. Credit score: College of Canterbury (NZ).
Figuring a G-class star just like the Solar having a lifetime on the order of 10 billion years, most such stars would spawn planetary techniques that by no means noticed the evolution of intelligence, and maybe not any type of life. As a result of an apparent arduous step is abiogenesis, and though the universe appears filled with elements, we have now no proof but of life anyplace else. The truth that it did occur right here tells us nothing greater than that, and till we dig out proof of a ‘second genesis,’ maybe right here in our personal Photo voltaic System inside an icy moon, or on Mars, we are able to type no agency conclusions.
There’s a readable overview of the ‘arduous steps’ notion on The Dialog, and I’ll direct you each to that in addition to to the paper simply out from the authors of the overview, which runs in Science Advances (quotation under). In each, Penn State’s Jason Wright and Jennifer Macalady collaborate with Daniel Brady Mills (Ludwig Maximilian College of Munich) and the College of Rochester’s Adam Frank to explain such ‘steps’ as the event of eurkarytic cells – i.e., cells with nuclei. We people are eukaryotes, so this tough step needed to occur for us to be studying this.
We might maintain including to the record of arduous steps because the dialogue has spun out over the previous few a long time, but it surely appears agreed that photosynthesis is an enormous one. The so-called ‘Cambrian explosion’ is likely to be thought of a tough step, because it includes sudden complexity, refinements to physique elements of all types and specialised organs, and it occurs rapidly. And what of the emergence of consciousness itself? That’s an enormous one, particularly since we’re a great distance from explaining simply what consciousness really is, and the way and even the place it develops. Robin Hanson has used the arduous steps idea to debate ‘filters’ that separate fundamental lifeforms from complicated technological societies.
Whichever steps we select, the concept of a sequence of extremely inconceivable occasions leveraging one another on the highway to intelligence and know-how appears to make the possibilities of civilizations elsewhere distant. However let’s pause proper there. Wright and colleagues be aware of the work of evolutionary biologist Geerat Vermeij (UC-Davis), who argues that our view of innovation via evolution is inescapably affected by info loss. Right here’s a bit on this from the brand new paper:
Vermeij concluded that info loss over geologic time might clarify the obvious uniqueness of historic evolutionary improvements when (i) small clades [a clade comprises a founding ancestor and all of its descendants] that independently developed the innovation in query go extinct, leaving no residing descendants, and (ii) an historic innovation developed independently in two carefully associated lineages, or inside a brief time frame, and the genetic variations between these two lineages grow to be “saturated” to the purpose the place the lineages grow to be genetically indistinguishable.
In different phrases, as we study life on early Earth, we have now to reckon with incompleteness in our fossil report (big gaps attainable there), with species we all know nothing about going extinct regardless of having achieved a tough step. The authors level out that if that is so, then we are able to’t actually describe proposed arduous steps as ‘arduous.’ Different prospects exist, together with that improvements do occur solely as soon as, however they could be so highly effective that creatures with a brand new evolutionary trait rapidly change their atmosphere in order that different lineages of evolution don’t have time to develop.
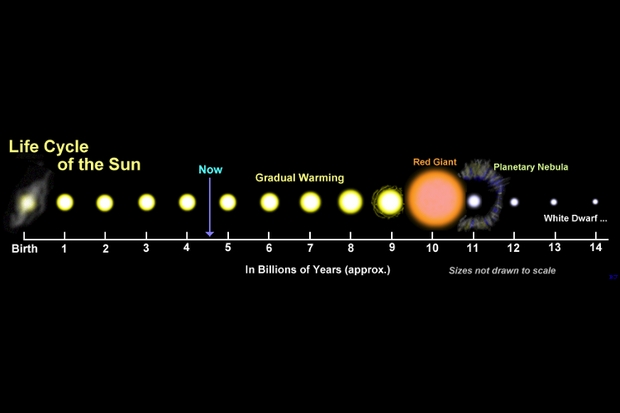
Picture: Earth’s habitability is compromised by a Solar that can, about 5.6 billion years after its formation, grow to be too scorching to permit life. Picture credit score: Wikimedia Commons.
We’re nonetheless left with the query of why it has taken a lot of the lifetime of the Solar to provide ourselves, a query that bothered Carter sufficiently in 1983 that it drove him to the arduous steps evaluation. Right here the authors supply one thing Carter didn’t, an evaluation of Earth’s habitability over time. It’s one that may change the end result. For every of the arduous steps units up its personal evolutionary necessities, and these may very well be met solely as Earth’s atmosphere modified. Think about, for instance, that fifty p.c of our planet’s historical past elapsed earlier than fashionable eukaryotic cells had sufficient oxygen to thrive.
So perhaps our planet needed to cross sure environmental thresholds:
…we increase the likelihood that there are not any arduous steps (regardless of the looks of main evolutionary singularities within the common tree of life) (51) and that the broad tempo of evolution on Earth is about by global-environmental processes working on geologic timescales (i.e., billions of years) (30). Put otherwise, people originated so “late” in Earth’s historical past as a result of the window of human habitability has solely opened comparatively lately in Earth historical past.
Suppose abiogenesis isn’t a tough step. Biosignatures, then, needs to be widespread in planetary atmospheres, at the very least on planets like Earth which might be geologically lively, within the liveable zone of their stars, and have atmospheres involving nitrogen, carbon dioxide and water. If oxygenic photosynthesis is a tough step, then we’ll discover atmospheres which might be low in oxygen, wealthy in methane and carbon dioxide and different elements of the ambiance of the early Earth. If no arduous steps exist in any respect, then we should always discover the total vary of atmospheric sorts from early Earth (Archean) to current day (Phanerozoic). Our research of atmospheres will assist us make the decision on the very existence of arduous steps.
Given an absence of arduous steps, if this mannequin is appropriate, then the evolution of a biosphere seems extra predictable as habitats emerge and evolve. That might supply us a unique manner of assessing Earth’s previous, but additionally suggest that the identical traits have emerged on different worlds like Earth. Our existence in that sense would suggest that clever beings in different stellar techniques are extra possible than Carter believed.
The paper is Mills et al., “Reassessment of the “hard-steps” mannequin for the evolution of clever life,” Science Advances. Vol. 11, Challenge 7 (14 February 2025). Full textual content. Brandon Carter’s well-known paper on the arduous steps is “The Anthropic Precept and its Implications for Organic Evolution.” Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London A 310 (1983), 347–363. Summary.


