Barely audible to human ears, wholesome soils produce a cacophony of sounds in lots of kinds—a bit like an underground rave live performance of bubble pops and clicks.
Particular recordings made by Flinders College ecologists in Australia present that this chaotic combination of soundscapes could be a measure of the range of tiny residing animals within the soil, which create sounds as they transfer and work together with their atmosphere.
With 75% of the world’s soils degraded, the way forward for the teeming group of residing species that reside underground faces a dire future with out restoration, says microbial ecologist Dr. Jake Robinson, from the Frontiers of Restoration Ecology Lab within the School of Science and Engineering at Flinders College.
This new area of analysis goals to analyze the huge, teeming hidden ecosystems the place virtually 60% of the Earth’s species reside, he says.
“Restoring and monitoring soil biodiversity has by no means been extra vital. Though nonetheless in its early levels, ‘eco-acoustics’ is rising as a promising device to detect and monitor soil biodiversity and has now been utilized in Australian bushland and different ecosystems within the UK. The acoustic complexity and variety are considerably larger in revegetated and remnant plots than in cleared plots, each in-situ and in sound attenuation chambers.
“The acoustic complexity and variety are additionally considerably related to soil invertebrate abundance and richness.”

The most recent examine, together with Flinders College professional Affiliate Professor Martin Breed and Professor Xin Solar from the Chinese language Academy of Sciences, has in contrast outcomes from acoustic monitoring of remnant vegetation to degraded plots and land that was revegetated 15 years in the past. The work seems within the Journal of Utilized Ecology.
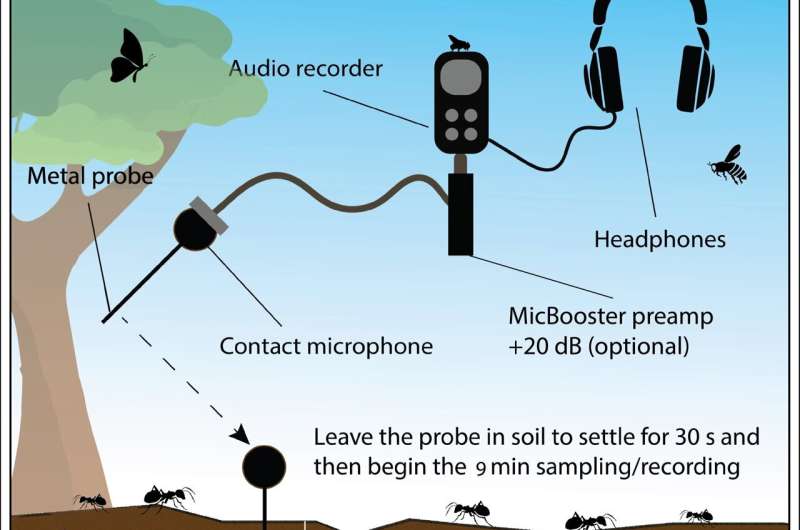
The passive acoustic monitoring used numerous instruments and indices to measure soil biodiversity over 5 days within the Mount Daring area within the Adelaide Hills in South Australia. A below-ground sampling system and sound attenuation chamber had been used to report soil invertebrate communities, which had been additionally manually counted.
“It is clear [that] acoustic complexity and variety of our samples are related to soil invertebrate abundance—from earthworms, beetles to ants and spiders—and it appears to be a transparent reflection of soil well being,” says Dr. Robinson. “All residing organisms produce sounds, and our preliminary outcomes recommend completely different soil organisms make completely different sound profiles relying on their exercise, form, appendages and dimension.
“This expertise holds promise in addressing the worldwide want for more practical soil biodiversity monitoring strategies to guard our planet’s most various ecosystems.”
Extra data:
Sounds of the underground replicate soil biodiversity dynamics throughout a grassy woodland restoration chronosequence, Journal of Utilized Ecology (2024). DOI: 10.1111/1365-2664.14738
Supplied by
Flinders College
Quotation:
Soundscape examine reveals how underground acoustics can amplify soil well being (2024, August 16)
retrieved 16 August 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-08-soundscape-underground-acoustics-amplify-soil.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.

