(CI Photographs/Shutterstock)
The DNA Storage Alliance, which is a part of the SNIA neighborhood, final month launched a technical whitepaper detailing the progress up to now in creating DNA storage, after we would possibly see industrial DNA storage choices, and the technical hurdles that stay.
Because of its unbelievable density, common applicability, and multi-century lifespan, DNA storage is considered by some as a potential storage medium for the longer term. The concept is gaining new backing as an archive of final resort, significantly because the AI revolution surges into excessive gear, main individuals discover larger worth in knowledge that they beforehand would have discarded.
The present knowledge dynamic is placing stress on conventional storage applied sciences, which aren’t maintaining with surging knowledge retention charges, the DNA Storage Alliance says in its new whitepaper, titled “DNA Knowledge Storage Know-how Overview.”
“The capital prices related to conventional storage media usually are not scaling with the speed of information era, and operational prices of refreshing knowledge, or creating copies, utilizing present storage applied sciences is changing into prohibitive,” the whitepaper authors write. “The speed of HDD and tape media storage density progress is slowing, and media lifetime just isn’t bettering considerably.”
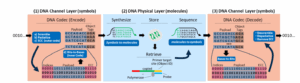
DNA storage gives one various storage methodology that would meet the info storage tsunami. Right here’s the way it works at a excessive degree: Binary knowledge is encoded into ACGT language of DNA–(A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T)–the place it’s translated into molecular strings saved in DNA. To retrieve the saved knowledge, the method is reversed.
Whereas the overall “bits to bases” and “bases to bits” concept holds true, there are specific limitations to bear in mind with this course of, the DNA Storage Alliance writes in its paper. For starters, there’s a have to right for numerous bodily errors which will happen within the DNA “bodily layer.” Sure sequences must also be prevented because of the likelihood of inflicting synthesis or sequencing errors.
There are additionally numerous ways in which practitioners can encode the DNA knowledge. Probably the most fundamental path is a straight binary illustration, the place A, C, G, and T are encoded as 00, 01, 10, and 11. There may be additionally the ternary illustration, which makes use of a base-3 encoding, which avoids producing strings of repeated bases, or homopolymers. Practitioners can even use combinatorial meeting that makes use of quick DNA sequences as constructing blocks to create larger DNA molecules, which may present a full alphabet of information encoders.
One other approach is known as topological modification, the place the info is transformed right into a positional construction, which the authors describe as a “DNA punch card” (however please don’t inform the mainframers). DNA nanostructures may also be used to encode knowledge, and there may be additionally the potential to create composite DNA letters, which additional will increase the scale of the obtainable alphabet.
Like all types of storage, DNA storage requires error correction. DNA synthesis has a few 1% pure error price, however there are numerous approaches to right them, together with use of parity codes, low density parity checks, CRC checksums, erasure codes, fountain codes, and Viterbi codes. Relying on the scenario, a practitioner would possibly mix a number of of those error correction codes collectively right into a single course of, in accordance with the whitepaper authors.
Some DNA patterns can enhance the percentages of an error, which is why DNA storage should incorporate constraints to keep away from them. The whitepaper authors talk about numerous methods for constructing these constraints, together with native and international constraints, in addition to biosafety and biosecurity issues.
Different facets to think about for DNA storage are the varied knowledge storage protocols that have to be constructed and applied. For example, since a single GB might not match right into a DNA molecule, the supply knowledge object have to be damaged up into smaller items, or packetized. DNA is common, which is considered one of its huge promoting factors, however sure care have to be taken to make sure that the info will be explored in a DNA archive, the authors write. Lastly, tags shall be utilized in DNA storage to hurry up random file entry.
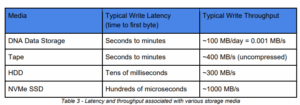
Like different storage mediums, DNA storage will perform at a sure throughput and with sure latencies. On the latency entrance, present DNA storage writes to media at about the identical price because it does to tape, in seconds to minutes. On the throughput entrance, DNA storage will be capable to deal with about 100 MB per day, which is orders of magnitude slower than tape (about 400 MB per second), not to mention NVMe disk.
Velocity clearly received’t be DNA storage’s sturdy go well with, a minimum of because it’s presently envisioned. Nonetheless, when refrained from daylight, water, and air, DNA storage has the potential to retailer knowledge for a really very long time. The whitepaper authors remind us that DNA has been recovered from fossilized mammals that had been 2 million years outdated. Most organizations would in all probability be proud of a few a long time.
To protect DNA, one should create a DNA Containment System (DCS), which makes use of vessels geared up with seals, components, and inert gases, the authors inform us. At the moment, the price of implementing error correction is limiting DNA storage to single strands that retailer tens of bytes. Storing larger knowledge units would require encoding into DNA sub-strands and utilizing encoding indices, the authors write.
Inside three to 5 years, DNA storage shall be viable for archival use circumstances, the DNA Storage Alliance authors write.
“You will need to see DNA knowledge storage not as a substitute for any present storage know-how, however as a complementary functionality that allows the info storage hierarchy to develop, resolving the ‘save/discard’ dilemma with a viable TCO for zettabyte scale and knowledge preservation,” they write. “Whereas DNA knowledge storage remains to be fairly nascent and there stay vital challenges to commercialization, the foundations of writing, storing, retrieving, and studying knowledge utilizing DNA have been proven to work on scalable know-how platforms.”
The DNA Storage Alliance, which is a element of the Storage Networking Trade Affiliation (SNIA), has dozens of members, together with Western Digital, Twist Bioscience, Catalog, Imagene, Biomemory, Los Alamos Nationwide Laboratory, Kioxia, Dell Applied sciences, Seagate, IBM, and others.
You may obtain the whitepaper right here.
Associated Gadgets:
Harvard’s New Knowledge Storage Is to Dye For, Avoids DNA Storage Pitfalls
Storage Strategy Mimics DNA in Fossils
DNA to Carry New Knowledge Burden