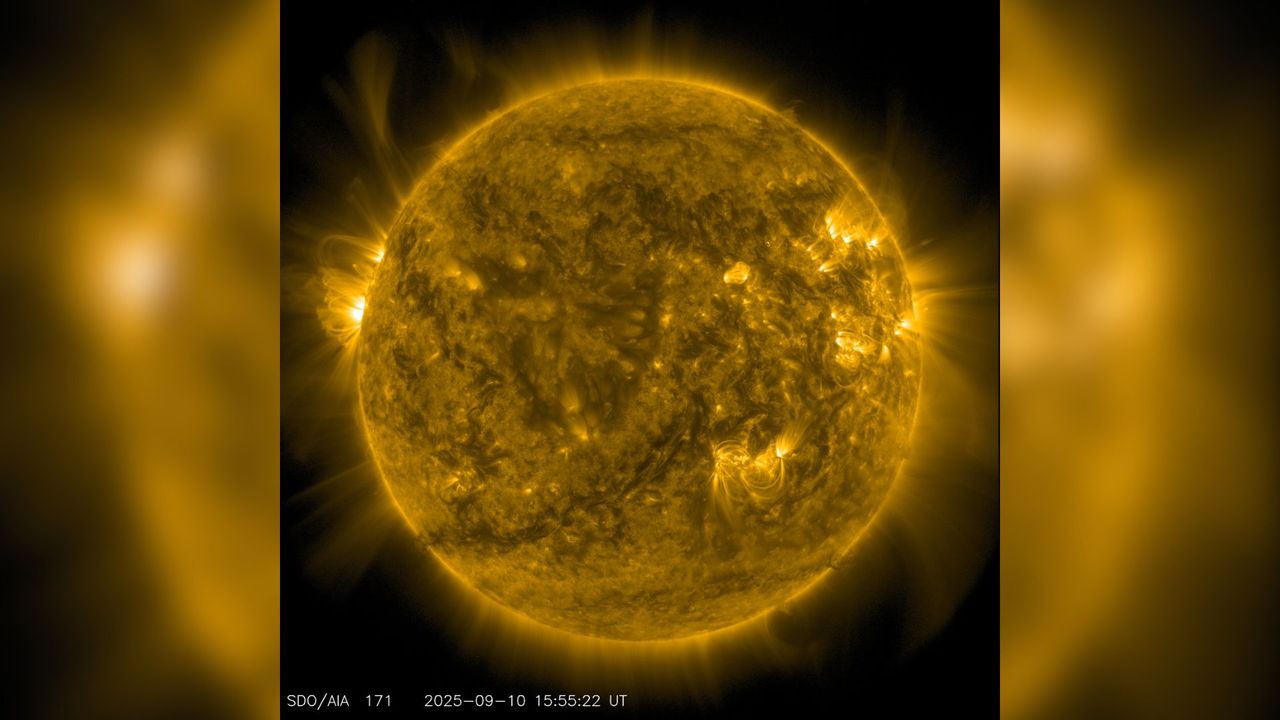
The solar has grown more and more energetic over the previous 17 years, bucking a downward pattern that had photo voltaic physicists questioning whether or not our star was heading in direction of a brand new “grand minimal” of the sort final seen in 1830.
Starting within the Nineteen Eighties, photo voltaic exercise began lowering general, with every subsequent 11-year sunspot cycle seeing fewer sunspots, fewer flares and fewer coronal mass ejections. Photo voltaic exercise reached a nadir in 2008, which was the lull at first of photo voltaic cycle 24. That 12 months had the weakest photo voltaic exercise on document.
“All indicators have been pointing to the solar going into a protracted part of low exercise,” stated Jamies Jasinski of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in a assertion. “So it was a shock to see that pattern reversed. The Solar is slowly waking up.”
Jasinski led analysis that compiled information from a wide range of missions learning each the solar and the photo voltaic wind, which is a stream of charged particles radiating from the solar.
The research confirmed that since 2008, all indicators have been rising. Amongst them, solar-wind velocity is up 6%, photo voltaic wind density has elevated 26%, the solar-wind temperature has seen an increase of 29% and there was a soar within the energy of the interplanetary magnetic discipline carried by the photo voltaic wind equal to about 31%. That is all reflective of elevated magnetic exercise on the solar.
Certainly, with elevated photo voltaic exercise comes extra geomagnetic storms that generate auroral lights in Earth‘s sky; elevated coronal mass ejections and radiation flares pose better hazard to satellites, house stations and astronauts.
Why the solar has reversed course stays a big unknown — although it has occurred earlier than.
Between 1645 and 1715, there was a interval that has come to be referred to as the Maunder Minimal, named after the late nineteenth century and early twentieth century astronomer Edward Maunder, who first observed the 11-year photo voltaic cycle by watching how the variety of sunspots waxes and wanes. historic data, Maunder realized that between 1645 and 1715, there had been not more than 50 sunspots on the solar in complete. That is an awfully low quantity, and is indicative of there being little or no magnetic exercise of the sort that produces flares and coronal mass ejections. For comparability, in the course of the time of most exercise in an peculiar photo voltaic cycle, there could be greater than 100 sunspots. One other low exercise interval additionally occurred between 1790 and 1830.
Intriguingly, the Maunder Minimal coincided with a interval anecdotally known as the “Little Ice Age,” which noticed a sequence of exceptionally chilly winters throughout the Northern Hemisphere, prompting the River Thames in London to utterly freeze over on a number of events. Whereas there have been makes an attempt to attach the Little Ice Age with the Maunder Minimal, the Little Ice Age started earlier than the onset of the Maunder Minimal, and a few researchers even recommend that it ran from 1300 to 1850.
The reason for the Little Ice Age is unclear, however volcanic exercise belching volcanic ash excessive into the environment and blocking daylight is among the most probably explanations. Alternatively, variations in photo voltaic exercise such because the Maunder Minimal, the interval between 1790 and 1830 and the lower between the Nineteen Eighties and 2008 don’t appear to have a lot of an impact on Earth’s local weather, and any cooling they seem to trigger is being overridden by the a lot better warming results ensuing from human-induced local weather change.
Nonetheless, durations such because the Maunder Minimal and the years main as much as 2008 are tough for scientists to clarify. Whereas the solar’s 11-year cycle of magnetic exercise is pretty nicely understood, “The longer-term traits are rather a lot much less predictable and are one thing we do not utterly perceive but,” stated Jasinski.
The findings have been revealed on Sept. 8 in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.

